Today’s Current Affairs: 31st December 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Ol Chiki Script : Centenary celebrations

The President of India attended the Centenary celebrations of the Ol Chiki script of the Santhali Language in Jamshedpur, Jharkhand.
- Ol Chiki Script was invented in 1925 by Pandit Raghunath Murmu, a writer and teacher from Mayurbhanj state (now in Odisha) in India.
- Ol Chiki is also known as Ol Cemet’, Ol Ciki, Ol or the Santali alphabet.
- The Ol Chiki script itself is uniquely structured to suit the Santali language.
- It consists of 30 letters and is fully phonetic, with each letter corresponding to a distinct sound.
- The script was first publicized in 1939 at the Mayurbhanj State exhibition.
- Pandit Raghunath Murmu published various books in Santali in the Ol Chiki script, including novels, poetry, drama, grammars, dictionaries and other information about the language and script.
- It was created as a way to promote Santali culture.
- Santali Language is a member of the Munda branch of the Austroasiatic language family, which is an ancient family of languages spoken across parts of South and Southeast Asia.
- It is spoken mainly in Jharkhand and West Bengal states in northern India, and also in northwestern Bangladesh, eastern Nepal and Bhutan.
- It was included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution in 2003, with Ol Chiki recognised as its official script, giving the language constitutional status.
Narsapuram Lace Craft:

The Prime Minister of India praised the Narsapuram Lace Craft products made by self-help groups in Narsapur of Andhra Pradesh during his “Man-Ki-Baat” broadcast.
- Narsapur is situated on the bank of Godavari River in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- It is believed that the women of the farming community of this region started creating highly attractive artefacts from colourful lace, about 150 years ago.
- The craft has survived the Indian famine (1899) and the Great Depression (1929).
- Raw Materials: Primarily uses fine cotton threads in various thicknesses and colors.
- Artisans also incorporate silk, rayon, or synthetic threads for decorative pieces, with beads and sequins added to enhance export-quality designs.
- The main tool is the crochet hook, available in different sizes to create diverse patterns and textures.
- This craft showcases intricate floral, geometric, and paisley patterns inspired by nature and traditional motifs.
- Narsapur’s famed hand-made crochet industry produces doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bed spreads, table-runners, and table cloths etc.
- It was recognized with Geographical Indication tag.
Frequency Comb:
Frequency combs are an important modern tool which are used to calibrate atomic clocks and has various other applications.
- It is a special kind of laser light whose spectrum, or set of frequencies, resembles the teeth of a comb.
- Frequency combs are simple and compact tools that phase coherently connect the radio frequency domain (say below 100GHz) with the optical domain (say above 200THz).
- Instead of containing just one colour (one frequency), it emits a large number of evenly spaced frequencies. The spacing is extremely regular.
- Frequency combs are widely-used, high-precision tools for measuring and detecting different frequencies colors — of light.
- It has high stability and precision.
- It helps scientists compare an unknown light frequency to a stable reference with extraordinary precision.
- It is an important modern tool to calibrate atomic clocks and measure shifts in light caused by gravity.
- It is used to detect explanets.
- It is also used in high-speed spectroscopy.
The World Weather Attribution Annual Report 2025:

The World Weather Attribution (WWA) Annual Report 2025 warns that climate change-driven extremes in 2025 pushed millions of people close to the limits of adaptation, despite La Niña conditions.
- World Weather Attribution (WWA) is an international scientific collaboration that analyses how human-induced climate change influences extreme weather events such as heatwaves, floods, storms, droughts and wildfires.
Key findings (2025):
- Heatwaves intensified sharply: Heatwaves since 2015 have become significantly more intense, with some events nearly 10 times more likely, showing that even small increases in global temperature have outsized impacts.
- Crossing the 1.5°C threshold: The three-year global average temperature is projected to cross the 1.5°C limit for the first time, despite 2025 being a La Niña year, underlining the strength of long-term warming trends.
- Limits of adaptation reached: Several extreme events revealed that adaptation measures are no longer sufficient for vulnerable populations, especially in the Global South.
- Inequality in climate impacts: Marginalised communities were systematically the worst affected, while data gaps and weak climate models limited analysis of many Global South events.
Extreme event profile (2025):
- 157 humanitarian-impact events identified
- Heatwaves and floods (49 each) most frequent
- Storms (38), wildfires (11), droughts (7)
- Heatwaves emerged as the deadliest hazard, with tens of thousands of deaths in single events.
Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2024-25 Report:

RBI’s latest “Trend and Progress of Banking in India” report flags a resilient banking system with multi-decadal low NPAs, strong balance-sheet expansion and policy push for safer, more inclusive finance.
- An annual RBI flagship assessment of banking & NBFC performance, risks, regulation/supervision priorities, payments, technology adoption, financial inclusion and consumer protection, culminating in an overall systemic soundness assessment.
- Scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) grew at a double-digit pace in deposits and credit (with some moderation).
- SCBs’ GNPA ratio fell to a multi-decadal low.
- Banks are well-capitalised with leverage and liquidity ratios above regulatory minimum.
- 514 districts became fully digitally-enabled (at least one digital payment mode for every eligible individual).
- RBI’s FI Index improved to 67.0 (from 43.4 earlier), indicating deeper inclusion.
- 64 lenders (41 banks, 23 NBFCs) onboarded; using 136+ data services across 12 loan journeys.
- Shift approved to risk-based deposit insurance premium, moving beyond the flat premium (ceiling noted as 12 paise/₹100 assessable deposits).
Industrial Hemp:

Himachal Pradesh Chief Minister has launched a policy push to legalise and regulate the cultivation of industrial hemp.
- Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is botanically related to marijuana, but with very different properties.
- While marijuana is rich with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive component that makes pot a drug of choice by many, hemp contains only the smallest traces of THC (<0.3%),
- It is an herbaceous, dioecious plant belonging to the Cannabis genus within the Cannabaceae family.
- It is high in fiber and low in active tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
- It is used for varieties used for recreational, therapeutic, and industrial purposes, commonly referred to as marijuana and hemp, respectively.
- Its stalk can be used to produce biofuel, auto parts, paper, upholstery, and fiber for cloth and other textile items.
- Its stem can also be processed into building materials, industrial products and different kinds of papers.
- Its seeds can be used to produce feed or food or the sources of oil that can be converted into a lotion or cosmetic products.
Parvati-Arga Bird Sanctuary : Eco Sensitive Zone

The Government has declared the Parvati-Arga Bird Sanctuary of Uttar Pradesh as an Eco sensitive zone.
- It is situated in Gonda district of Uttar Pradesh.
- It is a permanent freshwater environment consisting of two oxbow lakes namely Parvati and Arga.
- It is designated as Ramsar site.
- It is the critically endangered white-rumped vulture (Gyps bengalensis) and Indian vulture (Gyps indicus), and the endangered Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) have all been recorded.
- Invasive species such as the common water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) is also found here.
- The Vegetation of the Sanctuary is representative of that of the indo-gangetive ecosystem.
- Eco-Sensitive Zone is also known as Ecologically Fragile Areas (EFAs).
- These are areas notified and regulated by the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) around Protected Areas, National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries.
- Purpose of declaring ESZs:
- To create some kind of shock absorbers to the protected areas by regulating and managing the activities around such areas
- To act as a transition zone from areas of high protection to areas involving lesser protection.
PM-YUVA 3.0 Scheme:

The results of the Prime Minister’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors (PM-YUVA 3.0) have been declared, with 43 young authors selected through an All-India contest.
- The Prime Minister’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors (PM-YUVA 3.0) aims to nurture young writers under 30 years of age, providing them with mentorship and exposure to hone their creative writing skills.
- The scheme will help to develop a stream of writers who can write on various facets of India, encompassing the past, present, and future.
- PM-YUVA 3.0 intends to bring to the fore the perspectives of the young generation of writers on the following themes:
- Contribution of Indian Diaspora in Nation Building;
- Indian Knowledge System; and
- Makers of Modern India (1950-2025).
- Besides, the scheme will also provide a window for the aspiring youth to articulate themselves and present a comprehensive outlook of the contribution of Indians across fields in ancient and present times.
- The National Book Trust (NBT), India, under the Ministry of Education as the Implementing Agency, will ensure phase-wise execution of the scheme under well-defined stages of mentorship.
- The scheme invites applications from aspiring writers through MyGov India’s online portal.
- The shortlisted candidates undergo a multi-stage selection process before the final selection.
- Applicants who had qualified for the PM-YUVA Scheme 1.0 and PM-YUVA Scheme 2.0 are not eligible for the PM-YUVA 3.0 scheme.
Passenger Assistance Control Room:

To address air travellers’ grievances more promptly, the civil aviation ministry recently set up the Passenger Assistance Control Room (PACR) that functions round-the-clock to resolve the issues.
- It was launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India.
- It is aimed at significantly improving the promptness and effectiveness of addressing air traveller grievances.
- It functions as an integrated hub bringing together officials from the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), Airports Authority of India (AAI), airline operators, and other key stakeholders under one roof at Udaan Bhawan, in New Delhi.
- It operates 24×7, continuously monitoring aviation operations, attending to passenger calls, and coordinating real-time assistance and grievance resolution.
- The AirSewa system has also been fully integrated into the PACR, enabling seamless handling of passenger grievances received through it.
- An omni-channel technology backbone converts passenger inputs into actionable cases, supported by data-driven dashboards that provide live visibility on grievance types, timelines, and stakeholder actions.
- The physical presence of airline representatives within the control room allows immediate coordination and on-the-spot resolution of issues.
- Grievances related to flight delays, cancellations, refunds, and baggage issues are prioritised and addressed in accordance with the provisions of the Passenger Charter.
INS Vagsheer:

The current President of India became the second Indian President to undertake a submarine sortie, embarking on INS Vaghsheer, a Kalvari-class submarine, from Karwar naval base recently.
- It is the sixth submarine of the first batch of six Kalvari-class, or Scorpene-class, submarines ordered by the Indian Navy under Project-75.
- It is named after the sandfish, a deadly deep-sea predator of the Indian Ocean.
- It was officially commissioned into the Indian Navy in 2025.
- It now joins its sister vessels INS Kalvari, INS Khanderi, INS Karanj, INS Vela, and INS Vagir.
- These submarines have been completely built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) through French technology transfer.
- It boasts advanced stealth technologies, including reduced radiated noise levels and sophisticated hydrodynamic design, making it one of the quietest submarines in the world.
- Armed with torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and mine-laying capabilities, it excels in anti-surface and anti-submarine warfare, intelligence gathering, and surveillance.
- It consists of indigenously developed systems like the air-conditioning plant, internal communication network, and the Ku-Band SATCOM system.
Parasynnemellisia khasiana:
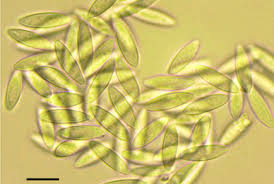
A previously unknown fungus named Parasynnemellisia khasiana has been discovered in the bamboo forests around Mawsynram, adding a new species — and even a new genus — to the scientific record from Meghalaya.
- It is a new species of fungus.
- It was discovered in the bamboo forests around Mawsynram, Meghalaya.
- It is named after the Khasi Hills.
- The fungus was found on dead stems of a thorny bamboo species (Chimonocalamus griffithianus) while surveying bamboo litter in the Mawsynram area.
- Laboratory analysis confirmed that the organism did not belong to any existing fungal genus.
- As a result, the researchers established a new genus, Parasynnemellisia, with khasiana as its first described species.
- It forms a distinct evolutionary lineage within the fungal family Phaeosphaeriaceae, separating it from superficially similar bamboo-associated fungi found elsewhere in Asia.
Viksit Bharat Shiksha Adhishthan Bill 2025:

The Viksit Bharat Shiksha Adhishthan (VBSA) Bill, 2025 was introduced in the Lok Sabha in the Winter Session of Parliament and referred to a joint parliamentary committee.
- The Bill aims to revamp India’s higher education regulation to implement the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- It is a proposed new law to create a unified regulatory architecture for higher education in India, framed under Entry 66 (determination of standards for higher education) of the Union List of the Constitution.
- Its core purpose is to empower Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs) to achieve excellence through effective coordination and the determination of standards.
- Need of the Bill: To overhaul the higher education regulatory framework in line with NEP 2020 by eliminating overlapping authorities, simplifying regulation, and reducing compliance burdens so institutions can focus on academic excellence.
- Proposed Major Changes:
- The Viksit Bharat Shiksha Adhishthan will be set up as the overarching authority. The Council of Architecture (CoA) will function as a Professional Standard Setting Body (PSSB), as envisaged in NEP 2020.
- Creates Three Specialized Councils:
- Viksit Bharat Shiksha Viniyaman Parishad: The Regulatory Council for coordination and maintenance of standards.
- Viksit Bharat Shiksha Gunvatta Parishad: The independent Accreditation Council.
- Viksit Bharat Shiksha Manak Parishad: The Standards Council for specifying minimum academic standards.
- The Bill provides for repealing the acts governing the University Grants Commission (UGC, 1956), the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE, 1987), and the National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE, 1993).
- All HEIs currently under these bodies will come under the Viksit Bharat Shiksha Adhishthan for standard-setting.
Srimanta Sankardeva:

The Union Home Minister inaugurated the redeveloped Batadrava Than, the birthplace of Vaishnavite saint Srimanta Sankardeva, in Assam’s Nagaon district.
- He was a 15th–16th century Bhakti saint who holds a high position in Assam’s history, society, culture, and religious beliefs. His diverse contributions led to a new phase of Assamese literature and culture, making him an important figure in the Indian Bhakti movement.
- Born in October 1449 to a family of Siromani Bhuyans (landed gentry), he undertook a transformative pilgrimage across North India in 1481 and composed his first Borgeet (devotional songs) at Badarikashrama (Badrinath).
- He faced opposition from kings and orthodox sections, shifted locations frequently, and passed away in 1568.
- Founder and propagator of the Neo-Vaishnava Bhakti movement in 15th-century Assam.
- He established eka-sarana-nama-dharma (also called Mahapurushiya dharma), whose cardinal principle was the worship of the single deity Vishnu (as Krishna), with its essence being the act of seeking refuge (sarana) in one God.
- Emphasized only two of the nine forms of Bhakti i.e., Sravana (hearing God’s name) and Kirtana (chanting God’s name).
- Preached universal brotherhood and sought to unite Assam’s heterogeneous society (multiple tribes, languages, communities) under the Neo-Vaishnava fold.
- He established Namghars (community prayer halls) and Satras (Vaishnava monasteries) which became centers for congregational worship, social equality, moral discipline, and the arts.
- Namghars, in particular, allowed the participation of all castes and communities, promoting social inclusivity.
- He translated eight of the twelve books of the Bhagavata Purana into Brajavali (common linguistic style in Assam) to make sacred Vaishnava texts accessible, with the Adi Dasama, covering Krishna’s childhood, being the most popular.
Scheme for Promotion of International Cooperation for AYUSH:

The Minister of State (IC) for Ayush informed about the Central Sector Scheme for Promotion of International Cooperation for AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy).
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
- It provides support to Indian Ayush drug Manufacturers/ Ayush Service providers to give boost to the export of Ayush products & services.
- Objectives:
- To promote and strengthen awareness and interest about AYUSH Systems of Medicine at international level.
- To facilitate International promotion, development and recognition of Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa-Rigpa and Homoeopathy.
- To foster interaction of stakeholders and market development of AYUSH at international level.
- To support international exchange of experts and information for promotion and propagation of AYUSH systems,
- To promote academics and research through establishment of AYUSH Academic Chairs in foreign countries.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of AYUSH
- Components of Scheme for Promotion of International Cooperation for AYUSH:
- International exchange of experts & officers,
- Incentive to drug manufacturers, entrepreneurs, AYUSH institutions, Hospitals etc. for international propagation of AYUSH by participating in international exhibitions, trade fairs, road shows etc.
- Support for international market development and AYUSH promotion-related activities,
- Establishment of AYUSH Information Cells and establishment and strengthening of Health Centre/ Institution in foreign countries.
- International Fellowship/ scholarship Programme for foreign nationals for undertaking AYUSH courses in premier institutions in India.
Australia to Eliminate Tariffs on 100% of Indian Exports:
Under the India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) Australia will provide duty-free access to 100% of Indian exports from 1 January 2026, marking a major milestone in bilateral trade relations.The ECTA, operational since December 2022, was an early-harvest deal, while negotiations for a broader India-Australia Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) are currently underway. Over three years, ECTA has delivered sustained export growth, wider market access, and stronger supply-chain resilience, benefiting exporters, MSMEs, farmers, and workers. India’s exports to Australia rose by 8% in 2024–25, improving the trade balance, with strong gains across manufacturing, chemicals, textiles, plastics, pharmaceuticals, petroleum products, and gems & jewellery.Agri-exports witnessed broad-based expansion with sharp rise in fruits & vegetables, marine products, spices, and exceptional growth in coffee exports.Full tariff removal is expected to unlock opportunities for MSMEs, farmers, and labour-intensive industries, enhancing employment and income generation. ECTA has strengthened supply-chain resilience, market diversification, and India’s Indo-Pacific economic integration.
Rashtra Prerna Sthal:
The Prime Minister (PM) inaugurated the Rashtra Prerna Sthal in Lucknow on the 101st birth anniversary of former PM Atal Bihari Vajpayee, dedicating it to the ideals of unity, self-respect, and service.The site honors Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay, and Dr. Syama Prasad Mookerjee with 65-feet bronze statues and a lotus-shaped museum.Atal Bihari Vajpaye He served as India’s PM 3 times—in 1996, 1998–1999, and 1999–2004—and was awarded the Padma Vibhushan (1994) and the Bharat Ratna (2015). His birth anniversary (25th December) is observed as Good Governance Day. Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay was an Indian politician and ideologue of RSS and Bharatiya Jana Sangh, focused on Antyodaya—uplifting the most disadvantaged. His philosophy of Integral Humanism emphasized social justice and self-reliance, and his birth anniversary (25th September) is observed as Antyodaya Diwas. Dr Syama Prasad Mookerjee: He was an Indian politician, the youngest Vice-Chancellor of Calcutta University (1934), and founder of the Bharatiya Jan Sangh (1951), which later evolved into the Bharatiya Janata Party. He famously opposed Article 370, arguing one nation cannot have two constitutions, two heads, or two flags, and was known for his sharp parliamentary debates, earning the title The Lion of Parliament.
Supreme Court stay on Aravallis Judgment:
The Supreme Court has stayed its November 20 judgment that accepted a 100-metre elevation criterion for defining the Aravalli hills, amid nationwide protests by environmental groups.The stay pauses the Court’s earlier acceptance of the Union government’s height-based definition of the Aravalli hills (landforms ≥100 m above local relief) for regulating mining. The interim order restores status quo ante, preventing immediate regulatory dilution while the Court re-examines ecological and constitutional implications.
Glacier Disappearance:
A new study published in Nature Climate Change projects that global glacier disappearance will peak around mid-century, with up to 4,000 glaciers vanishing annually under high-warming scenarios.Glacier disappearance refers to the complete extinction of individual glaciers when their area falls below 0.01 sq km or their remaining ice volume drops below 1% of original levels, due to sustained warming and mass loss. Global glacier extinction is projected to peak between 2041–2055, depending on warming levels.
Scale of loss:
~2,000 glaciers/year under +1.5°C warming
~4,000 glaciers/year under +4.0°C warming




