Today Current Affairs: 8th October 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Good Samaritan Scheme:

The Union government has launched a scheme for ‘Good Samaritan’. The scheme will be implemented from October 15.
- Under the Scheme Anyone who saves the life of a road accident victim by rushing them to a hospital within the “golden hour” will get a cash reward of ₹5,000.
- Each Good Samaritan would also receive a certificate of appreciation.
- An individual could be awarded a maximum of five times in a year.
- The ministry also said there will be 10 national-level awards each year for the worthiest Good Samaritans, who would be selected from all those who have been awarded during the whole year and they would be given an award of ₹1 lakh each.
- If more than one Good Samaritan saves the life of more than one victim, the amount of award would be ₹5,000 per victim saved, subject to maximum ₹5,000 per Good Samaritan.
Guru Ghasidas National Park And Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary As A Tiger Reserve:

National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has approved the Chhattisgarh government’s proposal to declare the combined areas of the Guru Ghasidas National Park and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary as a Tiger Reserve.
- The new Reserve is located in the northern part of the state, bordering Madhya Pradesh and Jharkhand.
- This will be the fourth Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh, after the Udanti-Sitanadi, Achanakmar, and Indravati Reserves.
- Guru Ghasidas National Park was the last known habitat of the Asiatic cheetah in the country.
- Tiger reserve created by The approval is granted by NTCA under Section 38V(1) of The Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- The State Government shall, on the recommendation of the Tiger Conservation Authority, notify an area as a tiger reserve.
UN Peacekeepers:

A total of 836 troops from the Indian Army serving with the UN peacekeeping mission in South Sudan have been awarded the United Nations medal for their services to ensure durable peace in the world’s youngest country.
- The civilian, police and military personnel from 73 countries serving with the United Nations Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS) are responsible for protecting civilians, creating conditions conducive to the delivery of humanitarian aid, supporting the implementation of a revitalised peace agreement, and monitoring and investigating human rights.
- United Nations Peacekeeping is a joint effort between the Department of Peace Operations and the Department of Operational Support.
- Every peacekeeping mission is authorized by the Security Council.
- The financial resources of UN Peacekeeping operations are the collective responsibility of UN Member States.
- According to the UN Charter, every Member State is legally obligated to pay their respective share for peacekeeping.
- UN peacekeepers (often referred to as Blue Berets or Blue Helmets because of their light blue berets or helmets) can include soldiers, police officers, and civilian personnel.
- Peacekeeping forces are contributed by member states on a voluntary basis.
- Civilian staff of peace operations are international civil servants, recruited and deployed by the UN Secretariat.
- UN peacekeeping is a unique global partnership.
- It brings together the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Secretariat, troop and police contributors and the host governments in a combined effort to maintain international peace and security.
- Its strength lies in the legitimacy of the UN Charter and in the wide range of contributing countries that participate and provide precious resources.
What Is Interpol?

The Interpol has launched an online campaign to apprise people of major cyberthreats to help them protect their computer systems, networks and personal information from cybercriminals.
- The three-week campaign, from October 4 to 22, would be run primarily through social media.
- Objective of the campaign:
- With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, in addition to increased levels of remote work and dependence on digital devices, the campaign will focus on ransomware, online scams and phishing, and business email compromise.
Interpol:
- The International Criminal Police Organisation, or Interpol, is a 194-member intergovernmental organisation.
headquartered in Lyon, France. - Formed in 1923 as the International Criminal Police Commission, and started calling itself Interpol in 1956.
- India joined the organisation in 1949, and is one of its oldest members.
- Interpol’s declared global policing goals include:
- Countering terrorism, promoting border integrity worldwide, protection of vulnerable communities, providing a secure cyberspace for people and businesses, curbing illicit markets, supporting environment security, and promoting global integrity.
New Biodegradable Polymer:
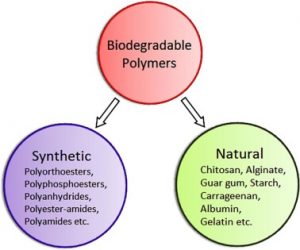
Scientists have developed a New biodegradable polymer, using Guar Gum, and Chitosan, which has high potential for packaging material.
- It is a guar gum-chitosan composite film which is a cross-linked polysaccharide developed with the help of solution casting method (a simple technique to make polymer films). It overcomes the challenges of polysaccharides.
- Polysaccharides is one of the biopolymers with high potential for use in synthesis of packaging material.
- However, due to some drawbacks of polysaccharides, such as low mechanical properties, high water-solubility, and low barrier properties, they are not preferred.
- Guar Gum, and Chitosan are polysaccharides extracted from guar beans and shells of crab and shrimps.
- Properties of the Film:
- High water stability, high mechanical strength as well as excellent resistance towards harsh environmental conditions.
- The fabricated cross-linked film is not easily soluble in water. As per scientists, it did not dissolve even after 240 hours.
- It is highly water repellent or hydrophobic because of its high contact angle of 92.8º.
- Water vapor permeability is low as compared to the film made only from chitosan.
- Vapour permeability is a material’s ability to allow a vapour (such as water vapour or, indeed any gas) to pass through it.
Heli-Borne Survey For Water Management:

The Ministry of Jal Shakti has launched a Heli-Borne Survey Technology for water management in the arid areas of Rajasthan.
- Developed by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)-National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI), it will provide information about level, quantity, quality and information of ground water.
- The NGRI is a geoscientific research organization established in 1961 under the CSIR.
- The Heli-borne geophysical mapping technique of CSIR-NGRI provides a high-resolution 3D image of the subsurface up to a depth of 500 metres below the ground.
- The main advantages of the Heliborne geophysical survey is that it is fast, highly data dense, precise and economical.
- This survey will be carried out in two phases, of which the first phase comprises an area spanning 1 lakh sq km.
- This includes 65,000 sq km in Rajasthan, 32,000 sq km in Gujarat and 2,500 sq km in Haryana.
- It is to be implemented in collaboration with the Ministry of Jal Shakti as a part of National Aquifer Mapping Project.
- Larger areas can be covered to derive more accurate data to help utilize groundwater for drinking purposes.
- It will help in water conservation, identification of new places for ground water recharging and that too at lesser cost than the prevalent ones like digging tube wells using geophysics and remote sensing techniques.
- It will help in devising new schemes for improvement in water level in water scant areas.
Anti-Defection Law:

The Calcutta High Court has given West Bengal Assembly Speaker a deadline to pass an order in the defection case involving a Member of Legislative Assembly (MLA).
- Anti-defection proceedings are also going on in other states such as Jharkhand and Rajasthan.
- The anti-defection law punishes individual Members of Parliament (MPs)/MLAs for leaving one party for another.
- Parliament added it to the Constitution as the Tenth Schedule in 1985. Its purpose was to bring stability to governments by discouraging legislators from changing parties.
- The Tenth Schedule – popularly known as the Anti-Defection Act – was included in the Constitution via the 52nd Amendment Act, 1985 and sets the provisions for disqualification of elected members on the grounds of defection to another political party.
- It was a response to the toppling of multiple state governments by party-hopping MLAs after the general elections of 1967.
- However, it allows a group of MP/MLAs to join (i.e. merge with) another political party without inviting the penalty for defection. And it does not penalise political parties for encouraging or accepting defecting legislators.
- As per the 1985 Act, a ‘defection’ by one-third of the elected members of a political party was considered a ‘merger’.
- But the 91st Constitutional Amendment Act, 2003, changed this and now at least two-thirds of the members of a party have to be in favour of a “merger” for it to have validity in the eyes of the law.
- The members disqualified under the law can stand for elections from any political party for a seat in the same House.
- The decision on questions as to disqualification on ground of defection are referred to the Chairman or the Speaker of such House, which is subject to ‘Judicial review’.
- However, the law does not provide a time-frame within which the presiding officer has to decide a defection case.
Grounds of Disqualification:
- If an elected member voluntarily gives up his membership of a political party.
- If he votes or abstains from voting in such House contrary to any direction issued by his political party or anyone authorised to do so, without obtaining prior permission.
- As a pre-condition for his disqualification, his abstention from voting should not be condoned by his party or the authorised person within 15 days of such incident.
- If any independently elected member joins any political party.
- If any nominated member joins any political party after the expiry of six months.
Science Technology And Innovation (STI) Hubs:

Union Minister of Science & Technology Jitendra Singh today said that the Government will be setting up 75 Science Technology and Innovation (STI) Hubs in different parts of the country, exclusively for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs).
- This will not only promote scientific talent but also contribute to socio-economic development of these communities.
- Science Technology and Innovation (STI) Hubs being established by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) will develop, nurture and ensure the delivery of appropriate and relevant technologies for inclusive socio-economic development through creation of sustainable livelihoods for the SC and ST population in tune to their growing aspirations.
- The training and skill development programmes under the STI Hubs will build the Science Technology and Innovation (STI) Capacities and Capabilities among SC/ST population.
- The STI Hubs also improve the Indigenous Knowledge Systems (IKS) through inputs of S&T and converting them to appropriate technologies for creating better livelihood options, he added.
- In the last two years, 20 STI Hubs (13 for SCs and 7 for STs) have already been established by DST which will directly benefit 20,000 SC and ST population through various interventions spreading across farm, non-farm, other allied livelihood sectors and various livelihoods assets like energy, water, health, education, etc.
- STI hubs will have mainly three-fold objectives:
- To address the weakest linkages in the predominant livelihood systems through Science & Technology (S&T) interventions;
- Creation of social enterprises based on the strengths in livelihood systems; and
- To improve the Indigenous Knowledge Systems (IKS) through inputs of S&T for strengthening the livelihoods.
Central Asian Flyway:

The two day Online Meeting of 30 range countries of Central Asian Flyway began with a resolve to strengthen the conservation actions for migratory birds and their habitats in the Central Asian Flyway.
- Central Asian Flyway (CAF) covers a large area of Eurasia between the Arctic and Indian Oceans.
- This flyway comprises several important migration routes of birds.
- Including India, there are 30 countries under the Central Asian Flyway.
- At the 13th meeting of the Conference of Parties (CoP) to the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS), held at Gandhinagar in February, 2020, a resolution (UNEP/CMS/Resolution 12.11 (Rev.COP13) and Decision 13.46 were adopted initer-alia providing for establishing, by COP14, under the umbrella of CMS an institutional framework, under the leadership of India with the aim to agree on conservation action for migratory birds.
- With a view to fulfill its commitment, India is organizing two day online meeting on 6th -7th October 2021 with CAF Range Countries, anchored in Wildlife Institute of India.
- Approximately one in five of the world’s 11,000 bird species migrate, some covering enormous distances. Conserving migratory birds requires cooperation and coordination along the entire flyway between countries and across national boundaries.
PM MITRA Parks:

To position India strongly on the Global textiles map, the Government of India has approved the setting up of 7 PM MITRA parks as announced in Union Budget for 2021-22.
- PM MITRA is inspired by the 5F vision of Prime Minister Modi. The ‘5F’ Formula encompasses – Farm to fibre; fibre to factory; factory to fashion; fashion to foreign.
- The 7 Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel Parks (PM MITRA) will be setup at Greenfield / Brownfield sites located in different willing States.
- The PM MITRA parks will have Core Infrastructure: Incubation Centre & Plug & Play facility, Developed Factory Sites, Roads, Power, Water and Waste Water system, Common Processing House & CETP and other related facilities e.g. Design Centre, Testing Centres etc.
- Support Infrastructure: Workers’ hostels & housing, logistics park, warehousing, medical, training & skill development facilities.
Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP):

Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI), the implementing agency of Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) has completed the target of opening of 8,300 Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJKs) for the FY 2021-22 before end of September, 2021.
- All the districts of the country have been covered under Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP).
- Government has set a target to increase the number of Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras (PMBJKs) to 10,000 by March 2024. As on 5th October, 2021, the number of stores has increased to 8355.
- These kendras will ensure easy access of affordable medicine to the people in every nook and corner of the country.
- Product basket of PMBJP presently comprises 1,451 drugs and 240 surgical instruments. Further, new medicines and nutraceutical products like glucometer, protein powder, malt-based food supplements, protein bar, immunity bar, etc. have been launched.
- “Janaushadhi Sugam” a mobile application for Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) facilitates the public by providing a digital platform at the tip of their fingers.
- Under the Scheme, medicines are procured from World Health Organization – Good Manufacturing Practices (WHO-GMP) certified suppliers for ensuring the quality of the products.
- Apart from this, each batch of drug is tested at laboratories accredited by ‘National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories’ (NABL). Only after passing the quality tests, the medicines are dispatched to PMBJP Kendras.
- Medicines available under PMBJP are priced 50%-90% less than that of branded prices.
Nobel Prize In Chemistry 2021:

Two scientists have been awarded the 2021 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their work on building molecules that are mirror images of one another.
- German-born Benjamin List and Briton David MacMillan (Born in Bellshill, United Kingdom and Professor at Princeton University, USA) were announced as the winners at an event in Stockholm.
- Their chemical toolkit has been used for discovering new drugs and making molecules that can capture light in solar cells.
- The winners will share the prize money of 10 million Swedish kroner (1,135.54 million US Dollars).
- The technique, called asymmetric organocatalysis, has made it much easier to produce asymmetric molecules – chemicals that exist in two versions, where one is a mirror image of the other.
- Chemists often just want one of these mirror images – particularly when producing medicines – but it has been difficult to find efficient methods for doing this.
First Anti-Malarial Vaccine:
In a historic move, the World Health Organization (WHO) endorsed the first anti-malarial vaccine.
- The WHO said that it was recommending the use of the RTS,S/AS01 (RTS,S) malaria vaccine among children in sub-Saharan Africa and in other regions with moderate to high P. falciparum malaria transmission.
- The WHO’s recommendation was based on the results from an ongoing pilot programme in Ghana, Kenya and Malawi.
- The development comes at a time when the WHO and its partners have reported a stagnation in the progress against the disease that kills more than 2,60,000 African children under the age of five annually.
- Malaria remains a primary cause of childhood illness and death in sub-Saharan Africa.
- The vaccine does significantly reduce life-threatening severed malaria, but It’s not the only tool. Vaccination against #malaria does not replace or reduce the need for other measures, including bed nets against mosquitoes.
- Using this vaccine on top of existing tools to prevent malaria could save tens of thousands of young lives each year.




