Today Current Affairs: 5th September 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
SPARK Program:

The Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS), has started the Studentship Program for Ayurveda Research Ken (SPARK) for Ayurveda (BAMS) students studying in recognised Ayurveda colleges.
- Aim is To help students develop an acumen for research and to further support and incentivise their research ideas.
- The selected students will be offered financial support of Rs.50,000 under the fellowship.
- Initially, there will be a total of 100 seats per session and further details may be accessed at the program portal.
Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS):
- It is an autonomous body of the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India.
- It is an apex body in India for the formulation, coordination, development and promotion of research on scientific lines in the Ayurveda and Sowa-Rigpa systems of medicine.
Jigyasa 2.0:

Ministry of S&T recently organized Jigyasa 2.0 for the renewable fuel program
- Jigyasa, a student-scientist connect programme by CSIR in collaboration with Kendriya Vidyalaya and is aimed at connecting school students and scientists so as to extend students’ classroom learning with that of a very well-planned research laboratory-based learning.
- It would inculcate the culture of inquisitiveness on one hand and scientific temper on the other, amongst the school students and their teachers.
- The program will also enable the students and teachers to visit CSIR laboratories and participate in mini-science projects.
Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT):
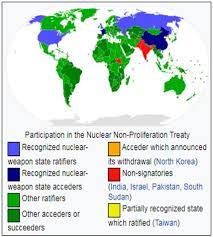
The Tenth Review Conference of the Parties to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) concluded last week in New York.
- The NPT is a multilateral treaty aimed at limiting the spread of nuclear weapons including three elements:
- Non-proliferation
- Disarmament
- Peaceful use of nuclear energy.
- The treaty was signed in 1968 and entered into force in 1970.
- The Treaty does not affect the right of state parties to develop, produce, and use nuclear energy for peaceful purposes.
- India is one of the only five countries that did not sign the NPT.
Grievance Redressal Index 2022:

Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has topped among all Ministries/Departments for resolving Public Grievances in the ranking report published by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- UIDAI has been a top performer in the resolution of cases received through the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS).
- UIDAI is a statutory authority established in 2009.
- Works under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- The UIDAI is mandated to assign a 12-digit unique identification (UID) number (Aadhaar) to all the residents of India.
Smart Solutions Challenge And Inclusive Cities Awards 2022:

Smart Solutions Challenge and Inclusive Cities Awards 2022 were awarded by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- In the category of early-stage innovations, the winner was a wearable technology product, Fifth Sense by Glovatrix Pvt. Ltd.
- This product translates sign language gestures to speech and text using sensors and Artificial Intelligence.
- In the second category of market-ready solutions, Mouseware by Dextroware Devices Pvt. Ltd. was the winner.
- Mouseware is a head-wearable device that enables hands-free control of computers and smart gadgets.
- Belagavi Smarty City’s system for those with disabilities to access education and healthcare was awarded the top prize in the category of implemented solutions.
- The Smart Solutions Challenge is an initiative of the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) and the United Nations (UN)) in India.
- NIUA and UN in India are looking for innovative ideas, solutions, technologies, products, and business solutions that can help break-down and resolve complex city-level inclusion and accessibility challenges faced by persons with disabilities, women and girls, and the elderly.
G-20 Education Ministers Meeting:

The Minister of Education addressed the G-20 Education Ministers’ Meeting in Bali, Indonesia.
- Theme: Recovery, Re-imagine and Rebuild Stronger.
- The G20 presidency is scheduled to move from Indonesia to India in December 2022.
Key Highlights:
- Emphasized on the importance of sharing mutual experiences & working together to create a new world in which education remains the nodal point for addressing common challenges.
- The National Education Policy 2020, based on the foundational principles of access, equity, quality, affordability and accountability is India’s guiding light for promoting lifelong learning opportunities and achieving the shared vision of G20.
- Highlighted India’s rapid strides towards building a more resilient and inclusive education and skilling ecosystem and realising the creative potential of each learner through the implementation of NEP 2020.
- India is giving special emphasis on formalizing early childhood care & education, supporting differently-abled children, boosting digital and multi-modal learning, flexible entry-exit pathways, integrating education with skills, which are keys to improve learning outcomes.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) Scheme:

The Ministry of Education informed Lok Sabha that, during 2021-22, more than 3 Lakh women were trained under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) scheme.
- Skill India Mission was launched by the government in 2015 under which the flagship scheme Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) is run.
- It aims to train over 40 crore people in India in different skills by 2022. It aims at vocational training and certification of Indian youth for a better livelihood and respect in the society.
- PMKVY is implemented by the National Skills Development Corporation (NSDC) under the guidance of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
PMKVY 1.0:
- India’s largest Skill Certification Scheme – Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) – was launched on 15th July, 2015 (World Youth Skills Day).
- Aim: To encourage and promote skill development in the country by providing free short duration skill training and incentivizing this by providing monetary rewards to youth for skill certification.
- Key Components: Short Term Training, Special Projects, Recognition of Prior Learning, Kaushal & Rozgar Mela, etc.
- In 2015-16, 19.85 lakh candidates were trained.
PMKVY 2.0:
- PMKVY 2016-20 (PMKVY 2.0) was launched by scaling up both in terms of Sector and Geography and by greater alignment with other missions of the Government of India like Make in India, Digital India, Swachh Bharat, etc.
- Budget: Rs. 12,000 Crore.
- Implementation :
Centrally Sponsored Centrally Managed (CSCM): This component was implemented by National Skill Development Corporation. 75% of the PMKVY 2016-20 funds and corresponding physical targets have been allocated under CSCM. - Centrally Sponsored State Managed (CSSM): This component was implemented by State Governments through State Skill Development Missions (SSDMs). 25% of the PMKVY 2016-20 funds and corresponding physical targets have been allocated under CSSM.
- Implementation :
- Outcome: More than 1.2 Crore youth have been trained/oriented through an improved standardized skilling ecosystem in the country under PMKVY 1.0 and PMKVY 2.0.
PMKVY 3.0:
- Launched in 717 districts, 28 States/eight UTs, PMKVY 3.0 is a step towards ‘Atmnanirbhar Bharat’.
- It will be implemented in a more decentralized structure with greater responsibilities and support from States/UTs and Districts.
- District Skill Committees (DSCs), under the guidance of State Skill Development Missions (SSDM), shall play a key role in addressing the skill gap and assessing demand at the district level.
Data Released By The Union Agriculture Ministry:

According to the data released by the Union Agriculture Ministry, the decrease in the area of paddy cultivation is 22.90 lakh hectares, 5.62% less than the area covered in 2021.
- States such as Jharkhand (decrease of 9.80 lakh hectares), Madhya Pradesh (6.32 lakh hectares), West Bengal (4.45 lakh hectares), Chhattisgarh (3.91 lakh hectares), Uttar Pradesh (2.61 lakh hectares) and Bihar (2.18 lakh hectares) are the major contributors for the decrease in the cultivated area of paddy in this kharif season.
- Meanwhile, States such as Telangana (increase of 4.71 lakh hectares), Haryana (0.94 lakh hectares), Nagaland (0.78 lakh hectares) and Gujarat (0.55 lakh hectares) showed an increase in the area of cultivation of paddy.
- The coverage of pulses too witnessed a marginal decrease.
- Increase in area in cultivation is reported from States such as Madhya Pradesh (4.08 lakh hectares), Uttar Pradesh (0.22 lakh hectares) and Assam (0.11 lakh hectares) while Maharashtra (decrease of 3.23 lakh hectares), Telangana (1.70 lakh hectares), Jharkhand (1.33 lakh hectares) and Karnataka (0.94 lakh hectares).
- Tur/arhar cultivation was down marginally at 44.86 lakh hectares as against 47.56 lakh hectares in 2021.
- Oilseeds have been cultivated in 188.51 lakh hectares in the country, slightly less than 189.66 lakh hectares of 2021.
- In the case of sugarcane, the cultivation is 55.65 lakh hectares, a slight increase in the production as compared to 54.70 lakh hectares in 2021 kharif.
INS Vikrant:

The commissioning of India’s first Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC-1) into the Navy as INS Vikrant marks a defining moment.
- The first ever aircraft carrier to be indigenously designed and constructed, INS Vikrant will strengthen the country’s standing as a ‘Blue Water Navy’ a maritime force with global reach and capability to operate over deep seas.
- With it, India also joins the elite group of nations – the US, Russia, France, the UK and China – who are capable of designing and constructing aircraft carriers.
- Also, with a displacement of 43,000 tonnes when fully loaded, INS Vikrant is set to be the seventh largest among the carriers or carrier classes in the world.
- INS Vikrant, with pennant number R11, was the first-ever aircraft carrier that was operated by the Indian Navy.
- The ship was officially laid down in 1943
- The plan for building an indigenous aircraft carrier started taking shape as the old INS Vikrant neared its decommissioning in the late 1990s.
Raksha Or SPARSH:

Defence Ministry has said that System for Pensions Administration – Raksha or SPARSH has disbursed more than three thousand ninety crore rupees to Defense Pensioners digitally in the month of August this year.
- More than five lakh sixty-two thousand Defence Pensioners migrated successfully on the digital platform of SPARSH in August.
- SPARSH is a web-based system processing pension claims and crediting the pension directly into the bank accounts of defence pensioners without any external intermediary.
- It has grown exponentially with more than 11 thousand 600 crore rupees disbursed in 2021-22, from just about 57 crore rupees in 2020-21.
Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (IAD):

Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully demonstrated a new technology with Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (IAD).
- Designed and developed by ISRO’s Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), IAD is a game-changer with multiple applications for future missions including to Mars and Venus.
- The IAD was successfully test flown in a ‘Rohini’ sounding rocket from Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station.
- Rohini sounding rockets are routinely used for flight demonstration of new technologies being developed by ISRO as well as by scientists from India and abroad.
- The IAD was initially folded and kept inside the payload bay of the rocket. At around 84 km altitude, the IAD was inflated and it descended through the atmosphere with the payload part of a sounding rocket.
- The IAD has systematically reduced the velocity of the payload through aerodynamic drag and followed the predicted trajectory.
India Economy:
India is set to become the third largest economy in the world by 2029.
- A State Bank of India report said India will surpass Germany in 2027 and most likely Japan by 2029 at the current rate of growth.
- The report said that the country has undergone a large structural shift since 2014 and is now the 5th largest economy overtaking the United Kingdom.
- The path taken by India since 2014 reveals the country is likely to get the tag of 3rd largest economy in 2029, a movement of 7 places upwards since 2014 when India was ranked 10th, it said.
- The report is authored by Soumya Kanti Ghosh, group chief economic adviser, SBI.
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman said, the International Monetary Fund’s own forecasts show India overtaking the UK in dollar terms on an annual basis this year.
- This has put India, the Asian powerhouse, just behind the US, China, Japan and Germany.
Section 437 Of The Code Of Criminal Procedure:

Chief Justice of India, U.U. Lalit, in its order on activist Teesta Setalvad on September 2, made an oral observation that under Section 437 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), a woman is entitled to favourable treatment.
- He was referring to a provision that says being a woman is a possible ground for granting bail, even when otherwise it cannot be considered.
- Section 437 of the CrPC deals with bail in case of non-bailable offences.
- It says a person shall not be released on bail if there is reasonable ground to believe that he has committed an offence punishable with death or life imprisonment; or, if he has been previously been convicted for an offence punishable with death, life imprisonment, or for a term of seven years or more; or been convicted on two or more occasions on other offences with a term between three and seven years.
- However, it also contains exceptions in a proviso that says the court may grant bail even in these cases, “if such person is under the age of 16 or is a woman or is sick or infirm”.
- There are several provisions in criminal law that give special consideration to women.
- For instance, when a police officer requires the attendance of any person who he believes is acquainted with a case under investigation, the person has to appear before the officer (Section 160).
- However, no woman shall be required to do so at any place other than the place in which she resides.




