Open-RAN (Radio Access Network):
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Chairman said that use of Open-RAN (Radio Access Network) and software-defined telecom networks will open new opportunities for Indian entities to enter into the network equipment market.
- Open-RAN is not a technology, but rather an ongoing shift in mobile network architecture that allows networks to be built using subcomponents from a variety of vendors.
- O-RAN has an open, multi-vendor architecture for deploying mobile networks, as opposed to the single-vendor proprietary architecture.
- O-RAN uses software to make hardware manufactured by different companies work together.
- The key concept of Open RAN is “opening” the protocols and interfaces between the various subcomponents (radios, hardware and software) in the RAN.
Radio Access Network (RAN):
- It is the part of a telecommunications system that connects individual devices to other parts of a network through radio connections.
- A RAN resides between user equipment, such as a mobile phone, a computer or any remotely controlled machine, and provides the connection with its core network.
- As a technical matter this is what the industry refers to as a disaggregated RAN.
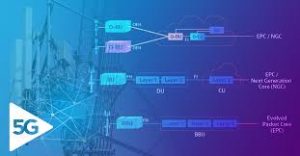
Elements of RAN:
- The Radio Unit (RU) is where the radio frequency signals are transmitted, received, amplified and digitized.
- The RU is located near, or integrated into,the antenna.
- The Distributed Unit (DU) is where the real-time, baseband processing functions reside. The DU can be centralized or located near the cell site.
- The Centralized Unit (CU) is where the less time-sensitive packet processing functions typically reside.
The functioning of Open RAN:
- It is the interface between the RU, DU, and the CU that are the main focus of Open RAN.
- By opening and standardizing these interfaces (among others in the network), and incentivizing the implementation of the same, networks can be deployed with a more modular design without being dependent upon a single vendor.
- Making these changes can also allow the DU and CU to be run as virtualized software functions on vendor-neutral hardware.




