Today Current Affairs: 18th May 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Covid Drug Released:

The first batch of the indigenously developed anti-Covid-19 drug, 2-deoxy-D-glucose or ‘2-DG’, has been released.
- Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI), had cleared the formulation on May 1 for emergency use as an adjunct therapy in moderate to severe Covid-19 patients.
About 2- DG:
- 2-DG has been developed by the Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Allied Sciences (INMAS), New Delhi, a lab of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), in collaboration with Hyderabad-based pharma company Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories (DRL).
- The drug accumulates in virus-infected cells and prevents the growth of the virus by stopping viral synthesis and energy production.
- Its selective accumulation in virally infected cells makes this drug unique.
- The molecule helps in faster recovery of patients hospitalised with Covid-19 and reduces their dependence on supplemental oxygen.
- 2-DG being a generic molecule and an analog of glucose, it can be easily produced and made available in large quantities.
Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS):

Ministry of Tribal Affairs and Microsoft sign MoU on Joint initiative for Digital Transformation of Tribal Schools such as Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) and Ashram Schools.
- Under the affirmative action initiative, Microsoft will make AI curriculum available to tribal students in both English and Hindi at all EMRS schools under the Ministry to skill educators and students in next-generation technologies including Artificial Intelligence.
- Under this program in the first phase, 250 EMRS schools have been adopted by Microsoft out of which 50 EMRS schools will be given intensive training and 500 master trainers would be trained in the first phase.
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) started in the year 1997-98 to impart quality education to ST children in remote areas in order to enable them to avail of opportunities in high and professional education courses and get employment in various sectors.
- In order to give further impetus to EMRS, it has been decided that by the year 2022, every block with more than 50% ST population and at least 20,000 tribal persons, will have an EMRS.
Diplomatic Immunity To Avoid Criminal Charges:

After she allegedly hit two staff members at a boutique in Seoul last month, the wife of Belgium’s ambassador to South Korea will now be exercising her diplomatic immunity to avoid criminal charges.
- Diplomatic immunity is a privilege of exemption from certain laws and taxes granted to diplomats by the country in which they are posted.
- The custom was formed so that diplomats can function without fear, threat, or intimidation from the host country.
- Diplomatic immunity is granted on the basis of two conventions, popularly called the Vienna Conventions — the Convention on Diplomatic Relations, 1961, and the Convention on Consular Relations, 1963.
- They have been ratified by 187 countries, including South Korea, which means, it is a law under that country’s legal framework and cannot be violated
- According to the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, 1961, the immunity enjoyed by a diplomat posted in the embassy is “inviolable”. The diplomat cannot be arrested or detained and his house will have the same inviolability and protection as the embassy.
- It is possible for the diplomat’s home country to waive immunity but this can happen only when the individual has committed a ‘serious crime’, unconnected with their diplomatic role or has witnessed such a crime.
- Alternatively, the home country may prosecute the individual.
The West Bengal Government Will Set Up A Legislative Council (Vidhan Parishad):

The West Bengal government will set up a Legislative Council (Vidhan Parishad), as per a decision taken up at the recent Cabinet meeting.
- For setting up the Council, a Bill has to be introduced in the Assembly, and then a nod from the Governor is required. The Upper House existed till 1969.
- India has a bicameral system i.e., two Houses of Parliament. At the state level, the equivalent of the Lok Sabha is the Vidhan Sabha or Legislative Assembly; that of the Rajya Sabha is the Vidhan Parishad or Legislative Council.
- Under Article 169 of the constitution, Parliament may by law create or abolish the second chamber in a state if the Legislative Assembly of that state passes a resolution to that effect by a special majority.
- As per article 171 clause (1) of the Indian Constitution, the total number of members in the legislative council of a state shall not exceed one-third of the total number of the members in the Legislative Assembly of that state and the total number of members in the legislative council of a state shall in no case be less than 40.
Independent Collegium:

A petition was filed in the Supreme Court seeking the constitution of an independent collegium to appoint members of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- The petition was filed by the Association for Democratic Reforms.
- The petition states that the present process of appointing members to the Election Commission, solely by the executive, is incompatible with Article 324(2) of the Constitution.
- The appointment of members of Election Commission on the “pick and choose” of the executive violates the very foundation for which it was created, thus, making the Commission a branch of executive.
- Democracy is a facet of the basic structure of the constitution and in order to ensure free and fair elections and to maintain healthy democracy in our country, the Election Commission should be insulated from political and/or executive interference.
Recommendations are given by various expert committees:
- 255th Law Commission Report recommended that the appointment of all the Election Commissioner should be made by the President in consultation with a three-member collegium or selection committee, consisting of the Prime Minister, the Leader of the Opposition of the Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India.
- 4th Report submitted by the Second Administrative Reform Commission in January 2007 also recommended for the constitution of a neutral and independent collegium headed by the Prime Minister with the Speaker of the Lok Sabha, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, the Law Minister and the Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha as it’s members.
- Dr. Dinesh Goswami Committee in its Report of May 1990 recommended for the effective consultation with neutral authorities like Chief Justice of India and the Leader of the Opposition for the appointment in Election Commission.
- Justice Tarkunde Committee in its Report of 1975 recommended that the members of the Election Commission should be appointed by the President on the advice of a Committee consisting of the Prime Minister, the Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India.
Monoclonal antibody Therapies:
India is facing shortages of the monoclonal antibody therapy
Monoclonal antibodies:
- They are artificially created antibodies that aim to aid the body’s natural immune system.
- They target a specific antigen — a protein from the pathogen that induces an immune response.
- Monoclonal antibodies can be created in the lab by exposing white blood cells to a particular antigen.
- To increase the number of antibodies produced, a single white blood cell is cloned, which in turn is used to create identical copies of the antibodies.
- In the case of Covid-19, scientists usually work with the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which facilitates the entry of the virus into the host cell.
- In a healthy body, the immune system is able to create antibodies — tiny Y-shaped proteins in our blood that recognise microbial enemies and bind to them, signalling the immune system to then launch an attack on the pathogen.
- However, for people whose immune systems are unable to make sufficient amounts of these antibodies, scientists provide a helping hand- using monoclonal antibodies.
- The idea of delivering antibodies to treat a disease dates as far back as the 1900s, when Nobel-prize winning German immunologist Paul Ehrlich proposed the idea of a ‘Zauberkugel‘ (magic bullet), a compound that selectively targets a pathogen.
- From then, it took eight decades of research to finally arrive at Muromonab-CD3, the world’s first monoclonal antibody to be approved for clinical use in humans.
- Muromonab-CD3 is an immunosuppressant drug given to reduce acute rejection in patients with organ transplants.
- Monoclonal antibodies are now relatively common. They are used in treating Ebola, HIV, psoriasis etc.
Plasma Therapy:

The use of convalescent plasma has been dropped from the recommended treatment guidelines for COVID-19, according to an advisory from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- Though a trial by the ICMR on 400 patients last year called the PLACID trial had found no significant benefit from the use of plasma, it continued to find a place in the recommended guidelines.
- Some experts have said the use of such plasma may have even played a role in facilitating new worrisome mutations to the virus.
Plasma therapy:
- Blood plasma is a yellowish liquid component of blood that holds the blood cells of whole blood in suspension.
- It is the liquid part of the blood that carries cells and proteins throughout the body. It makes up about 55% of the body’s total blood volume.
- This plasma contains viral antibodies that have treatment potential for severe cases of the disease.
- Plasma therapy is a medical procedure that uses the blood of a recovered patient to create antibodies on those infected individuals.
- Medically known as convalescent plasma therapy, this treatment uses antibodies found in the blood taken from a recovered Covid-19 patient.
- It is then used to treat those with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection to aid recovery.
Farzad-B Gas Field:
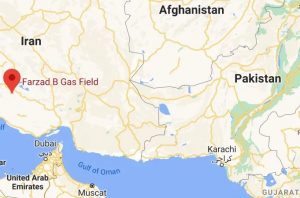
Iran gave the Farzad-B Gas Field to Petropars, a domestic gas producer.
- This is a setback for India’s energy ties with Iran as ONGC Videsh Ltd (OVL) had discovered the gas field in 2008 and has been part of the ongoing cooperation on that front.
Farzad-B Gas Field:
- It is located in the Persian Gulf (Iran).
- The contract for exploration of the field was signed in 2002 by an Indian consortium comprising ONGC Videsh, Indian Oil Corporation, and Oil India.
- The contract expired in 2009 after the declaration of commerciality of the field, based on the gas discovery.
- It has gas reserves of more than 19 trillion cubic feet.
- ONGC has invested approximately USD 100 million.
- Since then, the consortium has been trying to secure the contract for the development of the field.
- The major dispute between India and Iran was over setting up of two pipelines, and also over money to be quoted on the development plan.
- Around 75% of the deal was finalized by May 2018, when the US unilaterally withdrew from the nuclear deal and announced sanctions on Iran.
- In January 2020, India was informed that in the immediate future, Iran would develop the field on its own and would like to involve India appropriately at a later stage.
ELDERLINE:

The Ministry of Social Justice has started state-wise call centers in five major states to address the problems faced by elderly people in the wake of the covid pandemic.
- The toll-free helpline for elderly persons called ELDERLINE is expected to become operational in all states by the end of May 2021.
- The states covered are Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Rajasthan.
- It was already working in Telangana for one year.
- The toll-free number by which the call centers can be reached is 14567.
SAMVEDNA:

With the objective of providing psychological first-aid and emotional support to children affected during the COVID-19 Pandemic, the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR)is providing Tele-Counselling to children through SAMVEDNA.
- SAMVEDNA stands for Sensitizing Action on Mental Health Vulnerability through Emotional Development and Necessary Acceptance.
- It is a Toll-Free Helpline launched to provide psycho-social mental support for Children affected during COVID 19 Pandemic.
- This service is available on a toll-free No: 1800-121-2830 from Monday to Saturday from 10 a.m. to 1 p.m. and 3 p.m. to 8 p.m.
- Tele counseling is provided to the children under three categories:
- Children who are in Quarantine/isolation/COVID Care centers.
- Children who have COVID positive parents or family members and near ones.
- Children who have lost their parents due to Covid-19 Pandemic.
Proposal For Gold Exchange:

The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has proposed a framework for setting up a spot gold exchange.
- The spot exchange is where financial instruments, such as commodities, currencies, and securities, are traded for immediate delivery.
- SEBI is a statutory body established in April 1992 in accordance with the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
The framework of Gold Exchange:
- In the first tranche, an entity desirous of delivering gold, locally manufactured or imported, on the exchange platform would have to approach a SEBI regulated vault manager and deposit physical gold meeting quality and quantity parameters with it.
- Against this, the vault manager will issue an EGR (Electronic Gold Receipt), which will be tradeable on the exchanges, in the second tranche.
- A beneficial owner will surrender the EGR to a vault manager and take delivery of the gold in the third tranche.
- A common interface will be developed between vault managers, depositories, clearing corporations, and stock exchanges to enable seamless execution of the three tranches.
- The proposed denominations – reflecting underlying physical gold – of EGRs are 1 kilogram, 100 gram, 50 gram, and subject to conditions, those can also be even for 5 and 10 gram.
- STT (Security Transaction Tax) will be levied on the trading of the EGR and IGST (Integrated Goods and Services Tax) at the time of delivery.




