Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease : Causes
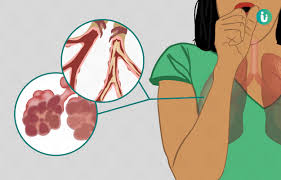
Health experts list the causes of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease beyond smoking, including environmental toxins, genetic predispositions, and occupational hazards.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs.
- There are two main forms of COPD:
- Chronic bronchitis, which involves a long-term cough with mucus.
- Emphysema, which involves damage to the lungs over time.
- Most people with COPD have a combination of both conditions.
- It’s typically caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most often from cigarette smoke.
- Tobacco smoking accounts for over 70% of COPD cases in high-income countries.
- In low- and middle-income countries (LMIC), tobacco smoking accounts for 30–40% of COPD cases, and household air pollution is a major risk factor.
- The most common symptoms of COPD are difficulty breathing, chronic cough (sometimes with phlegm) and feeling tired.
- COPD symptoms can get worse quickly.
- These are called flare-ups.
- These usually last for a few days and often require additional medicine.
- People with COPD are at increased risk of developing heart disease, lung cancer, and a variety of other conditions.
- Treatment:
- COPD isn’t curable, but it can get better by not smoking, avoiding air pollution, and getting vaccines.
- It can be treated with medicines, oxygen, and pulmonary rehabilitation.




