CRISPR:
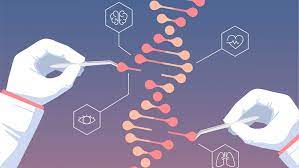
Over the last 3 years, the gene-editing technology with near unlimited potential has produced flawless results in clinical trials.
- India has approved a 5-year project to develop CRISPR to cure sickle cell anaemia.
- CRISPR is short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, which is a reference to the clustered and repetitive sequences of DNA found in bacteria, whose natural mechanism to fight some viral diseases is replicated in this gene-editing tool.
- Its mechanism is often compared to the ‘cut-copy-paste’, or ‘find-replace’ functionalities in common computer programmes.
- A bad stretch in the DNA sequence, which is the cause of disease or disorder, is located, cut, and removed and then replaced with a ‘correct’ sequence.
- And the tools used to achieve this are not mechanical, but biochemical specific protein and RNA molecules.
- The technology replicates a natural defence mechanism in some bacteria that uses a similar method to protect itself from virus attacks.




