Metal-Organic Frameworks:
Researchers have carried out an in-depth analysis of the mechanisms underlying the flexibility of crystals of Metal-Organic frameworks (MOFs) and introduced a novel quantitative measure of mechanical flexibility for crystals.
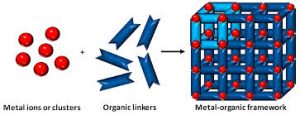
- Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are a class of porous, crystalline materials with a broad range of applications.
- They are composed of metal ions or clusters, which act as the joints, bound by multidirectional organic ligands, which act as linkers in the network structure.
- These crystalline materials possess the remarkable ability to absorb gases, such as carbon dioxide, and store them as well as act as filters for crude oil purification.
- MOFs derive their ability from the presence of nanopores, enhancing their surface areas that, in turn, make them adept at absorbing and storing gases.
- Flexibility in crystals has been assessed in terms of a parameter called elastic modulus, which is a measure of a material’s resistance to strain-induced deformation.




