Pacific Decadal Oscillation:
A recent study revealed that a cyclical event called the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, which repeats every 20-30 years, could make cyclones that originate near the Equator more frequent in the coming years.
- Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is a long-term ocean fluctuation in the Pacific Ocean.
- The term PDO was coined in about 1996 by Steven Hare at the University of Washington.
- It can be known only after several years of measuring ocean temperatures and their interaction with the atmosphere.
- The PDO waxes and wanes approximately every 20 to 30 years.
- From ocean surface topography data, together with other ocean and atmospheric data, scientists can determine whether we are in a ‘cool’ phase or a ‘warm’ phase.
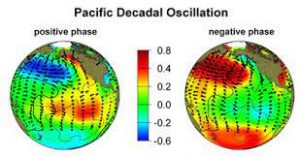
- Cool phase is characterised by a cool wedge of lower-than-normal sea-surface heights/ocean temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific and a warm horseshoe pattern of higher-than-normal sea-surface heights connecting the north, west and southern Pacific.
- Warm’ or ‘positive’ phase occurs when the west Pacific Ocean becomes cool, and the wedge in the east warms.
- The change in location of the cold and warm water masses alters the path of the jet stream.
- The jet stream in the northern hemisphere delivers storms across the United States.




