Provincial Status To Gilgit-Baltistan: Pakistan
It has been reported that, Pakistani authorities have finalised a law (26th Constitutional Amendment Bill), to award provisional provincial status to strategically located Gilgit-Baltistan.
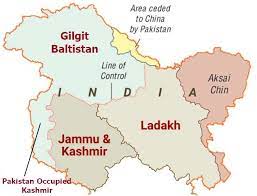
About Gilgit-Baltistan:
- Gilgit-Baltistan is one of the disputed territories of India.
- It is a chunk of high-altitude territory located on the north western corner of the Union Territory of Ladakh.
- It is located strategically as it borders Pakistan, Afghanistan and China.
- The region is claimed by India as part of the erstwhile princely state of Jammu & Kashmir as it existed in 1947 at its accession to India.
- Maharaja Hari Singh, the last Dogra ruler of J&K, had signed the Instrument of Accession with India on 26th October 1947.
- However, it has been under Pakistan’s control since 4th November, 1947, following the invasion of Kashmir by tribal militias and the Pakistan army.
- Following this invasion, India moved to the United Nations Security Council to raise the issue of Pakistan’s invasion, on 1st January 1948.
The UN Security Council passed a resolution:
- Calling for Pakistan to withdraw from all of Jammu and Kashmir and then India had to reduce its forces to the minimum level following which a plebiscite would be held to ascertain people’s wishes.
- However, no withdrawal was ever carried out and it remains a point of contention between two countries.
Current Status:
- Gilgit-Baltistan is an autonomous region now and after the bill is passed, it will become the 5th province of the country.
- Currently, Pakistan has four provinces namely Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Punjab, and Sindh.
- Presently, it has been ruled mostly by executive orders.
- Until 2009, the region was simply called Northern Areas.
- It got its present name only with the Gilgit-Baltistan (Empowerment and Self-Governance) Order, 2009, which replaced the Northern Areas Legislative Council with the Legislative Assembly.




