West Nile virus : Outbreak
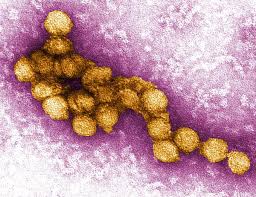
Ukraine is grappling with a severe outbreak of West Nile virus (WNV), with health officials raising alarms as the death toll rises.
- West Nile Virus (WNV) is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the family Flaviviridae.
- It was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- It is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America and West Asia.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it typically spikes between the summer and autumn months of June and September.
- Transmission: Human infection is most often the result of bites from infected mosquitoes. Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds, which circulate the virus in their blood for a few days.
- The virus may also be transmitted through contact with other infected animals, their blood, or other tissues.
- Infection with WNV is either asymptomatic (no symptoms) in around 80% of infected people, or can lead to West Nile fever or severe West Nile disease.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever and symptoms include fever, headache, tiredness, and body aches, nausea, vomiting, occasionally with a skin rash.




