Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:11th March 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR).
- Right to receive foreign funds for using “legitimate forms of dissent:
- Mercy plea
- ‘The Haryana Scheduled Castes (Reservation in Admission in Educational Institutions) bill, 2020.
- Contaminated sites:
- Input Tax Credit (ITC):
- GI certificates
- WION’s global summit was held in Dubai
- Long Term Reverse Repo Operation (LTROs)
- National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems:
- National Judicial Pay Commission:
- 43rd Annual Day of the National Institute of Health & Family Welfare (NIHFW)
- 130th Foundation Day of National Archives of India
- Other important current affairs:
1. Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR).:

As much as 67% of donations to national parties in 2018-19 came from “unknown sources,” an increase from 53% in the previous financial year, said a report released by the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR).
- The ADR analyzed the income tax returns and donation statements submitted to the Election Commission by the BJP, the Congress, the Trinamool, the Communist Party of India, the Communist Party of India (Marxist), the Nationalist Congress Party and the Bahujan Samaj Party.
- The total income of the parties was ₹3,749.37 crore, of which ₹951.66 crore was from known donors. Of the total income from unknown sources, 64% went to the BJP and 29% to Congress.
- Electoral bonds accounted for 78% of the ₹2,512.98-crore income from unknown sources.
- While parties are required to give details of all donations above ₹20,000, donations under ₹20,000 and those through electoral bonds remain anonymous.
2.Right to receive foreign funds for using “legitimate forms of dissent:

The Supreme Court held that the Central government cannot brand an organization ‘political’ and deprive it of its right to receive foreign funds for using “legitimate forms of dissent” like bandh, hartal, road roko or jail ‘bharo’ to aid a public cause.
- The verdict came on a petition challenging certain provisions of the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), 2010 and the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Rules of 2011, both of which confer the Centre with “unguided and uncanalised power” to brand organizations‘ political’ and shut down their access to foreign funds.
- The provisions under challenge before the court included Section 5 (1) of the FCRA.
- This provision allowed the Centre a free hand to decide whether a seemingly non-political organization was actually political in nature.
- INSAF argued that Section 5(1) was vague and thus unconstitutional.
3.Mercy plea:

The mercy plea filed by one of the four convicts in the 2012 Delhi gangrape case was recently rejected by the President. Now, they will be hanged on March 20.
- The fresh date is in line with the requirement of a gap of 14 days between the date of rejection of the mercy petition and the date of hanging.
- The regular legal procedure followed in death penalty cases: The legal procedure by which a convict is sent to his death is complex, and packed with safeguards.
- First, a trial court may pronounce the death sentence only in the “rarest of the rare” cases.
- Such a sentence is automatically referred to the High Court for confirmation. A warrant of execution may only be issued once the sentence has been confirmed by the High Court.
- Next, the convict has the option of approaching the Supreme Court against the High Court’s decision.
- After the Supreme Court’s decision, the convict may file a review petition and a separate curative petition before the Supreme Court. Both are standard legal processes, meant to rectify egregious errors in judgments.
- Thereafter, a mercy petition before the President may be filed. Such a petition is disposed of after a process involving a recommendation from the relevant state government, and sanction from the Home Ministry.
- The convict may then approach the Supreme Court again by filing a petition questioning the legitimacy of the President’s decision in the mercy petition.
- Finally, the disposal of this petition ends the process, and the death sentence may be executed thereafter.
4.‘The Haryana Scheduled Castes (Reservation in Admission in Educational Institutions) bill, 2020.’:

The Haryana cabinet has recently approved the draft bill ‘The Haryana Scheduled Castes (Reservation in Admission in Educational Institutions) bill, 2020.’
- This bill provides quota within quota for SCs in the state.
- The bill provides reservation of 50% seats to the deprived scheduled castes, out of the total 20% reserved for SC in the graduation and postgraduation courses.
- This will cover all educational institutions maintained by the government or receiving aid out of the state funds.
- It also includes government and government-aided technical and professional institutions.
- Here, deprived SC includes all 36 castes which were part of Block A including Valmiki, Bazigar, Sansi, Deha, Dhanak, and Sapera.
- Article 15(5) of the Constitution authorizes the State to make special provisions for the advancement of any socially and educationally backward classes of citizens or for SCs/STs for admission to educational institutions.
5.Contaminated sites:

There are 128 sites in India contaminated by toxic and hazardous substances, according to a March update by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- West Bengal led the list with 27 sites followed by Odisha at 23.
- Including those, there are 324 sites that may be contaminated, with 196 still awaiting an investigation and confirmation.
- Twenty sites in 6 States have seen agencies prepare detailed project reports, or a plan of action, to clean up sites. Such action follows orders by the National Green Tribunal (NGT).
- These incidents include
- oil contamination due to leakage of underground oil pipelines of Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited in Tamil Nadu,
- pesticide and heavy metal contamination in creeks at Eloor, Kerala,
- chromium contamination at Rania,
- improperly disposed of electronic waste lying on the banks of river Ramganga, Moradabad and
- mercury contamination of the soil at Kodaikanal, Tamil Nadu, and Ganjam, Odisha.
6.Input Tax Credit (ITC):
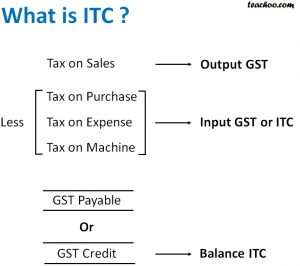
Restrictions imposed on the input tax credit, used by business establishments to reduce their tax liability, on inward supplies under the Central Goods and Services Tax Act have been challenged in the Rajasthan High Court with the plea that the amendment made to a rule to introduce the provision had imposed “unreasonable and arbitrary” conditions.
- The amended Rule 36 (4) of the CGST Rules, 2017, provides that the input tax credit can be availed only when a supplier of goods updates and uploads online the details of supplies through each of the bills.
- The petition now contended that the right to avail of credit could not be taken away by imposing the restrictions contained in the provisions of Section 43A of the Act, which was yet to be notified, through rules.
Input Tax Credit (ITC):
- It is the tax that a business pays on a purchase and that it can use to reduce its tax liability when it makes a sale.
- Exceptions: A business under composition scheme cannot avail of input tax credit. ITC cannot be claimed for personal use or for goods that are exempt.
7.GI certificates:

Two GI certificates of registration for the same product cannot be issued.
- The petitioners have an alternative and efficacious remedy available by filing an application to the registrar of trademark seeking to cancel or vary the GI certificate issued to APEDA.
- In May 2010, GI status was given to basmati grown only in Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Uttrakhand and parts of western Uttar Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir.
- But, Madhya Pradesh demanded that its 13 districts be recognized as traditional Basmati growing regions.
- However, the GI registry had rejected Madhya Pradesh’s claim as being the original and unique basmati growing region.
- It had observed that the documents and evidence filed by Madhya Pradesh show the importance, special characters of rice cultivated in Madhya Pradesh but not the basmati cultivation in the traditional growing area.
- Madhya Pradesh says non-inclusion of the state in the basmati growing areas would have an adverse effect on the lives of farmers who mainly depend upon basmati cultivation and it will also affect the export potential, which will indirectly reduce the country’s turnover from the export of basmati.
8. WION’s global summit was held in Dubai:

The third edition of WION’s global summit was held in Dubai recently.
- Theme: “Navigating and negotiating global imperatives”.
- Several topics, including balancing and recalibrating Pakistan’s diplomatic strategy and getting the youth to participate in democracy, were discussed at the summit.
- At the event, Former Pakistan Minister Kasuri recalled the plan for Sir Creek pact.
- Sir Creek is a 96-km strip of water disputed between India and Pakistan in the Rann of Kutch marshlands.
- Originally named Ban Ganga, Sir Creek is named after a British representative.
- The Creek opens up in the Arabian Sea and roughly divides the Kutch region of Gujarat from the Sindh Province of Pakistan.
9.Long Term Reverse Repo Operation (LTROs):

According to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the response to the Long Term Reverse Repo Operation (LTROs) has been highly encouraging.
- Long Term Reverse Repo Operation (LTRO) is a mechanism to facilitate the transmission of monetary policy actions and the flow of credit to the economy.
- This helps in injecting liquidity into the banking system.
- Funds through LTRO are provided at the repo rate. This means that banks can avail one year and three-year loans at the same interest rate of one day repo.
- But usually, loans with higher maturity period (here like 1 year and 3 years) will have a higher interest rate compared to short term (repo) loans.
- According to the RBI, the LTRO scheme will be in addition to the existing Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) and the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) operations.
- The LAF and MSF are the two sets of liquidity operations by the RBI with the LAF having a number of tools like repo, reverse repo, term repo, etc.
- The central bank has been conducting LTROs for one- and three-year tenors of appropriate sizes for up to a total amount of Rs 1,00,000 crore at the policy repo rate from the fortnight beginning February 15, 2020.
- The central bank received total bids of ₹1.94 lakh crore, for the three-year repo, compared with the notified amount of ₹25,000 crores.
- In yet another (LTROs) ₹48,856 crores worth of bids were conducted for an amount of ₹25,000 crores with a three-year tenor.
LTROs are conducted on Core Banking Solution (E-KUBER) platform.
- The operations would be conducted at a fixed rate.
- The minimum bid amount would be Rs 1 crore and multiples thereof.
- There will be no restriction on the maximum amount of bidding by individual bidders.
10.National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems:

Department of Science and Technology (DST) has sanctioned Rs 7.25 crore to IIT Mandi to establish a Technology Innovation Hub (TIH) at the Institute.
- DST has sanctioned the funds under its National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- The TIH will develop tools, education material, hands-on experiments with specialized tool kits, connecting with existing innovation ecosystems.
- It will inter-link with different stakeholders and connect with other initiatives of the Government of India by providing an innovation platform for schools, colleges and advanced technical training institutes in the targeted areas.
- The deliverables include:
- Technology Deliverables: To develop technology interface for challenges concerning landslides, environment (including climate change), air pollution, agriculture, cybersecurity, defense forces, healthcare, and forensics.
- Human Resource and Skill Development Deliverables: To generate skilled manpower in the HCI area at graduate, post-graduate, doctoral, post-doctoral and faculty levels by organizing workshops and seminars.
- International Collaborations Deliverables: To develop and sustain existing and new collaboration with universities and organizations in India and abroad.
- Entrepreneurship and Startup Deliverables: To create a startup ecosystem by working with the technology-business incubator of IIT Mandi, Catalyst, with an approach of Knowledge Generation Technology Development Technology Translation Technology Commercialisation.
National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS):
- To harness the potential of this new wave of technology and make India a leading player in CPS, the Union Cabinet approved the launch of the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS) in 2018.
- It had a total outlay of INR 3,660 crores for a period of five years.
11.National Judicial Pay Commission:

Recently, a Supreme Court Bench has made it clear to the States and Union Territories (UTs) that recommendations made by the Second National Judicial Pay Commission to nearly triple the pay and allowances for subordinate judiciary should be implemented proactively.
- The Supreme Court highlighted, in its February 28, 2020 order, that a financially self-sufficient subordinate judiciary was pivotal for the existence of an independent judiciary.
- Second National Judicial Pay Commission
- The Commission was constituted in 2017 pursuant to the order of the Supreme Court in All India Judges Association case, under Article 32 (Constitutional Remedies) of the Constitution.
- It is headed by former Judge of Supreme Court Justice P. Venkatrama Reddi.
- Few of the objectives of the Commission are:
- To evolve the principles governing the pay structure and emoluments of Judicial Officers belonging to the Subordinate Judiciary all over the country.
- To examine the present structure of emoluments and conditions of services of Judicial Officers in the States and Union Territories and to make suitable recommendations including post-retirement benefits such as a pension, etc.
- To consider and recommend such interim relief as the Commission considers just and proper to all categories of Judicial Officers.
- To make recommendations regarding setting up of a permanent mechanism to review the pay and service conditions of members of Subordinate Judiciary periodically by an independent Commission.
- The Supreme Court observed that the Commission may consider, if necessary, sending reports on any of the matters as and when recommendations are finalized.
- The Commission has been empowered to devise its own procedure and formulate the modalities necessary for accomplishing the task.
12.43rd Annual Day of the National Institute of Health & Family Welfare (NIHFW):

Recently, the 43rd Annual Day of the National Institute of Health & Family Welfare (NIHFW) was organized.
On the occasion, the Union Health Minister emphasized that synergy and cooperation between institutions needed to counter India’s Public Health challenges.
- The National Institute of Health & Family Welfare (NIHFW) is situated in Delhi and was established in 1977.
- NIHFW is the premier organization under Ministry Of Health and Family Welfare for capacity building through training of health professionals, frontline health workers such as Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) and Auxiliary Nurse Midwife (ANMs) and other central and state officers & healthcare staff.
Accredited Social Health Activist
- An Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) is a community health worker instituted by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) as a part of the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM).
- The mission began in 2005.
- ASHAs must primarily be female residents of the village that they have been selected to serve, who are likely to remain in that village for the foreseeable future.
Auxiliary Nurse Midwife
- Auxiliary nurse midwife, commonly known as ANM, is a village-level female health worker in India who is known as the first contact person between the community and the health services.
13.130th Foundation Day of National Archives of India:

Recently, on the occasion of 130th Foundation Day of National Archives of India, an exhibition “Jallianwala Bagh” was inaugurated, to mark the Jallianwala Bagh massacre centenary.
- The present exhibition is primarily presented with the help of original and digital copies of archival documents relating to the Jallianwala Bagh Massacre available in the National Archives of India.
- This is an attempt to portray the relentless struggle of the Indian people against the British tyranny through our record holdings.
- The National Archives of India is an attached office under the Ministry of Culture. It was established on 11 March 1891 at Kolkata (Calcutta) as the Imperial Record Department.
Other important current affairs:
1. Union Minister Prakash Javadekar on Sunday said the Centre would make it mandatory for sanitary napkin companies to provide bio-degradable disposal bags from January 2021.
- He said that the possibility of getting infected because of handling used Sanitary Napkins thrown in the garbage was brought to notice by many of the women garbage collectors.
- That’s why Environment Ministry has taken the decision to ask Makers of Sanitary Napkins to provide biodegradable bags so that Napkins can be wrapped in these bags before being thrown in the garbage.
2. According to a report released by Network of Women in Media, India (NWMI), over 70% of respondents who had approached an internal committee to report sexual harassment at the workplace were not completely satisfied with the outcome.
- The survey found that 36% of all respondents reported having experienced sexual harassment at the workplace. Of the respondents who experienced such harassment at work, 53% did not report it.
- A small percentage made a report to the internal committee (IC) of their media houses. But 70% of those who made a complaint was not completely satisfied with the outcome.
- Among the women who said that their organization did not have a mechanism to deal with sexual harassment, 47% had faced sexual harassment.
3. Aimed at collating government data, scattered across multiple sources for the consumption of policymakers, researchers, students, and journalists, the Indian School of Business (ISB) have developed a one-stop open data portal.
- India Data Portal (IDP) incubated at ISB’s Bharti Institute of Public Policy is a platform that has data from multiple disciplines, subjects, and areas.
- In the first phase, the focus is on agriculture data, and in later phases, the portal will diversify to include datasets on financial inclusion, rural development, etc.
4. The Government of India is set to launch a mahua-based alcoholic beverage in the market for the first time.
- Called Mahua Nutribeverage, it will be available as early as next month for Rs 700 for a 750 ml bottle and will come in six fruit-based flavors.
- The beverage has a high nutritional value and relatively low alcohol content, at 5 percent.
- It has been developed by IIT-Delhi after two years of research in collaboration with TRIFED (Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India).
- The marketing is being undertaken under the Tribal Affairs Ministry’s Van Dhan Vikas Karyakram.
- Mahuwa (Madhuca Indica) is a prominent forest tree in tribal areas of Bastar and plays an important role in the rural economy.
- The mahuwa flowers are a rich source of sugars and are said to contain vitamins, minerals, and calcium.
- The flowers are fermented and distilled yielding spirituous liquor also known as ‘country beer’.
- An estimated 90 percent of the annual production of Mahuwa flower is used in the process of brewing beverages.
5. Enrolment of students from marginalized communities, mainly the Scheduled Castes (SC) and the Scheduled Tribes (ST), was abysmally low in Ph.D. programs in the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) from 2015 to 2019, data presented in the Rajya Sabha.
- Of the 25,007 Ph.D. scholars admitted in the 23 IITs over the five-year period, only 9.1% were from the SC communities and 2.1% from the STs. This is lower than the 15% seats reserved for the former and 7.5% for the latter.
- Those from the Other Backward Classes (OBCs) made up 23.2%, which is also lower than the reservation-mandated 27%. Nearly two-thirds of the admissions (65.6%) went to general category students.
- While the Central Educational Institutions (Reservation in Admission) Act, 2006 seems to have helped those from the OBCs marginally, the enrolment from the Scheduled communities remained low.
- Among the 23 IITs, 10 had at least 27% Ph.D. scholars from the OBCs as mandated by the Act.
- In contrast, only the IIT-Dhanbad ((Indian School of Mines) in Jharkhand had a minimum of 15% from SC communities and the IIT-Bhilai in Chhattisgarh met 7.5% reservation for STs.
6. Attukal Pongala’ is one of the largest religious congregations of women.
- Preparing ‘pongala’ (a sweet offering) is considered an auspicious all-women ritual as part of the annual festival of the Attukal Bhagavathy Temple, which is popularly known as the “Women’s Sabarimala”.
- As per local legend, the Pongala festival commemorates the hospitality accorded by women in the locality to Kannagi, the heroine of the Tamil epic Silappadhikaram while she was on her way to Kodungallur in Kerala, after destroying Madurai city to avenge the injustice to her husband Kovalan.
- Attukal Temple is called the “Women’s Sabarimala” as only women perform rituals, just as predominantly men undertake the pilgrimage to the shrine of Lord Ayyappa.
7. The United Nations Conference on Trade, Investment and Development has warned that the Foreign Direct Investment flows all over the world will reduce by 15% due to Corona Virus. According to the organization, the outbreak could cost 2 trillion USD to the global economy.
- The United Nations earlier pointed out that the growth of the global economy will be slow between 0.5% and 1.5% for the year 2020-21.
- With the spread of the virus, the organization has predicted a further decline in economic growth.
8.Anti-HIV drugs used against COVID-19 for the first time in India:
- India for the first time used Lopinavir and Ritonavir combination to treat Italian patients in India infected with COVID-19. The couple were on a tour to India and are currently being treated in Jaipur
- The Indian Council of Medical Research has been authorized to research on COVID-19 drugs. Also, the council has been approved to use the above HIV drug combination during public health emergencies.
- Currently, 70% of HIV positive patients in India are on first-line drugs.
- These medicines are manufactured in India mainly for export purposes. They are exported to African countries predominantly.
- The combination of Lopinavir and Ritonavir drugs is a second-line drug.
9. The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) recently released its report on “Trends in International arms transfers 2019”. According to the report, India is the second-largest arms importer in the world.
- The report says that Russia is the largest supplier to the Indian market between 2015-19. Russia has remained the top supplier in spite of the fact that the Indian Weapons market for Russia declined from 72% to 56%.
- The report also says that the top 5 arms importers in the world include Saudi Arabia, India, Egypt, Australia, and China. These 5 countries accounted for 36% of world arms imports.
10. Gujarat has topped solar rooftop plants across the country. The state government has taken up dedicated schemes in order to achieve renewable power goals.
- There are more than 50,915 rooftop solar plants set up in the state today.
- The state government has adopted the scheme called “Surya Gujarat” in order to increase the use of solar energy at the domestic level.
- The scheme aimed to cover more than 8 lakh domestic consumers by 2022. It had also provided a 40% subsidy to projects with a capacity between 3 KWhr and 10 KWhr.
- After Gujarat, Maharashtra topped with solar rooftop power plant installation with more than 5,513 installations.
- The above information was provided by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy as a written reply in Parliament.
11.. The Hubballi-Ankola railway line project saw stiff opposition from a majority of the board members of the Karnataka State Wildlife Board.
- The proposed 164.44-km railway line passes through forests between two major protected areas — Kali Tiger Reserve and Bedthi Conservation Reserve.
- More than 80% of the line has to pass through the dense forest lands of the Western Ghats, and this entails the diversion of 727 hectares of prime forests.
13. A public interest litigation petition has been filed in the Madras High Court seeking a direction to the Centre and State government to constitute a permanent body for taking serious steps to safeguard the flora, fauna and other natural resources in the Eastern and Western Ghat areas in Tamil Nadu.
- The petition is on the basis of the recommendations made by the Madhav Gadgil and Kasturi Rangan committees.
- Petitioner contended that the natural resources abundantly available in this area are being properly utilized by other regions, except Tamil Nadu.
- They are being misutilised and mismanaged not only by the administrators but also by the public at large.
- Besides, large-scale plantations of coffee, tea and orchards have been raised in the hills of Western Ghats. Aromatic and valuable trees like sandals are removed illegally. Despite the Wildlife Protection Act, hunting takes place in some pockets.
- The forests are getting degraded because of the illicit collection of firewood, illicit grazing and illicit felling of trees.
14. The European Commission (EC) has launched the ‘United for Biodiversity’ coalition.
- It was launched on World Wildlife Day 2020- 3rd March.
- The coalition is made up of zoos, aquariums, botanical gardens, national parks, and natural history and science museums from around the world.
- The coalition offers the opportunity for all such institutions to “join forces and boost public awareness about the nature crisis, ahead of the crucial COP-15 of the Convention on Biological Diversity in Kunming, China in October 2020.
15. The sharing economy, also known as collaborative consumption or peer-to-peer-based sharing, is a concept that highlights the ability of individuals to rent or borrow goods rather than buy and own them.
- The ‘sharing economy’ includes segments such as co-working (Awfis, WeWork India), co-living (Stanza Living, OYO Life, Oxford Caps), shared mobility (Uber, Ola, Shuttl) and furniture rental (Furlenco, Rentomojo.)
- The shared economy in India is estimated to be about $2 billion industry by the end of the current year, according to a recent report by Maple Capital Advisors.
16. India’s coal imports rise:
- India’s thermal coal imports rose 12.6 percent to nearly 200 million tonnes in 2019. This is the second straight year of growth in shipments of the fuel.
- Imports of coking coal – used mainly in the manufacturing of steel – fell marginally, following two straight years of increase.
- Coal is among the top five commodities imported by India, the world’s largest consumer, importer, and producer of the fuel.
17. Bangladesh and India share a 4,156-kilometre-long international border, the fifth-longest land border in the world.
- This includes 262 km in Assam, 856 km in Tripura, 180 km in Mizoram, 443 km in Meghalaya, and 2,217 km in West Bengal.
- According to the recent government data, there has been no unusual increase in the apprehension of illegal infiltrators along the Bangladesh border in 2019 compared to the trend observed in the past six years.




