Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 25th November 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Lachit Borphukan:
- Report on National Nutrition Mission: NITI Aayog:
- Northeast monsoon :
- U.P. Unlawful Religious Conversion Prohibition Ordinance, 2020::
- Other important current affairs:
1.Lachit Borphukan:

PM pays tribute to Lachit Borphukan on Lachit Diwas.
Lachit Borphukan:
- He was a commander in the Ahom kingdom.
- Known for his leadership in the 1671 Battle of Saraighat that thwarted a drawn-out attempt by Mughal forces under the command of Ramsingh I to take over Ahom kingdom.
- The battle of Saraighat was fought on the banks of the Brahmaputra in Guwahati.
- The National Defence Academy (NDA), ever since 1999 has been conferring the best passing out cadet with the Lachit Borphukan gold medal.
Background:
- During the last phase of the Battle of Saraighat 1671, when the Mughals attacked the Assamese forces through the river in Saraighat, many Assamese soldiers began losing their will to fight.
- It was Lachit’s clarion call to all the soldiers that made them fight till their last breath, ultimately resulting in the defeat of the Mughals.
2.Report on National Nutrition Mission: NITI Aayog:
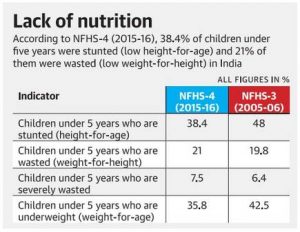
The NITI Aayog has released “Accelerating Progress On Nutrition In India: What Will It Take”, the third progress report on the National Nutrition Mission or the Poshan Abhiyaan.
About the Report:
- The third progress report (October 2019-April 2020) takes stock of the roll-out status on the ground and implementation challenges encountered at various levels through large scale datasets.
- These datasets are the NFHS-4 and Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey (CNNS).
- The initial Reports I and II, focused majorly on the mission’s preparedness and implementation by States and UTs, respectively.
- The review report was drafted in March 2020 and does not factor worsening poverty and hunger levels since then, which are expected to have gone down further due to the Covid-19.
- On stunting, India’s targets are conservative as compared to the global target defined by the World Health Assembly (WHA), which is a prevalence rate of 5% of stunting as opposed to India’s goal of reducing stunting levels to 13.3% by 2022.
- The target of reducing prevalence levels of anaemia among pregnant women from 50.3% in 2016 to 34.4% in 2022 and among adolescent girls from 52.9% in 2016 to 39.66%, is also considered to be conservative as compared to the WHA’s target of halving prevalence levels.
- In the wake of the pandemic, experts warn that deepening poverty and hunger may delay achieving the goals defined under the Mission.
National Nutrition Mission:
- Launched in 2018, it is the Government of India’s flagship program to improve nutritional outcomes for children, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- It is backed by a National Nutrition Strategy prepared by the NITI Aayog with the goal of attaining “Kuposhan Mukt Bharat” or malnutrition-free India, by 2022.
- Aims:
- To reduce stunting, undernutrition, anemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum respectively. To address the problem of malnutrition in a mission-mode.
- 50% of the total budget comes from the World Bank or other multilateral development banks and the rest of the 50% is through Centre’s budgetary support.
- The Centre’s budgetary support is further divided into 60:40 between the Centre and the States, 90:10 for the north-eastern region and the Himalayan States and 100% for the Union Territories (UTs) without legislature.
3.Northeast monsoon :
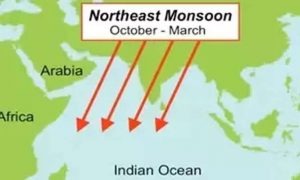
The Northeast monsoon has remained subdued this year. Rainfall over the Southern peninsular region has been deficient so far. The reason is a prevalent La Niña condition, along with a low-pressure belt that is currently lying to the north of its normal position.
- India receives rainfall during two seasons. About 75 percent of the country’s annual rainfall is received from the Southwest monsoon between June and September.
- The Northeast monsoon, on the other hand, occurs from October to December and is a comparatively small-scale monsoon, which is confined to the Southern peninsula.
- Also called the winter monsoon, the rainfall associated with the Northeast monsoon is important for Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karaikal, Yanam, coastal Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, north interior Karnataka, Mahe and Lakshadweep.
- While La Niña conditions enhance the rainfall associated with the Southwest monsoon, it has a negative impact on rainfall associated with the Northeast monsoon.
- during La Niña years, the synoptic systems — low pressure or cyclones — formed in the Bay of Bengal remain significantly to the north of their normal position.
- Besides, instead of moving westwards, these systems recurve. As they lie to the north of their normal position, not much rainfall occurs over southern regions like Tamil Nadu.
4.U.P. Unlawful Religious Conversion Prohibition Ordinance, 2020::

Cleared by the Uttar Pradesh government recently.
- It makes religious conversion for marriage a non-bailable offence.
- The onus will be on the defendant to prove that conversion was not for marriage.
- The notice period to the district magistrate for the religious conversion is two months.
- In case of conversion done by a woman for the sole purpose of marriage, the marriage would be declared null and void.
- Penalties:
- Violation of the provisions of the law would invite a jail term of not less than one year extendable to five years with a fine of ₹15,000.
- If a minor woman or a woman from the Scheduled Caste or Scheduled Tribes communities was converted through the said unlawful means, the jail term would be a minimum of three years and could be extended to 10 years with a fine of ₹25,000.
- The ordinance also lays down strict action, including cancellation of registration of social organizations conducting mass conversions.
- The ordinance comes days after the Allahabad high court said in a verdict (Salamat Ansari-Priyanka Kharwar case) that the right to choose a partner or live with a person of choice was part of a citizen’s fundamental right to life and liberty.
- The verdict also said earlier court rulings that ‘religious conversion for marriage was unacceptable’ was not good in law.
- The law has come under sharp criticism from several legal scholars who had contended that the concept of ‘love jihad’ did not have any constitutional or legal basis.
- They have pointed to Article 21 of the constitution which guarantees individuals the right to marry a person of one’s choice.
- Also, under Article 25, freedom of conscience, the practice, and conversion of the religion of one’s choice including not following any religion, are also guaranteed.
The Supreme Court of India, in both the Lily Thomas and Sarla Mudgal cases, has confirmed that religious conversions carried out without a bona fide belief and for the sole purpose of deriving some legal benefit do not hold water.
Other important current affairs:
1.Germany is planning to impose a mandatory quota for the number of women working in senior management positions in the country’s listed firms.
- This historic move is being seen as the next step in narrowing the gap of sexual inequality in the country.
What is Germany’s new boardroom quota for women? - In case executive boards of listed companies have more than three members, one of them must be a woman.
- Companies in which the federal government has a stake will require a supervisory board quota of at least 30 per cent and minimum participation in executive boards.
- Since 2015, Germany, which is Europe’s biggest economy, has had a voluntary quota of 30 per cent for women on supervisory boards.
- However, various studies have indicated this did little to improve the proportion of senior executive positions held by women.
2.The government of India has blocked 43 new mobile apps, mostly Chinese, in the country, including shopping website AliExpress.
- This is in addition to a total of 177 Chinese apps banned till now.
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology banned these mobile apps under Section 69A of the Information Technology Act (IT Act), 2000.
- Section 69A of the Information Technology Act, 2000, was introduced by an amendment to the Act in 2008.
- It gives the Central government the power to block public access to any information online whether on websites or mobile apps.
- Under Section 69A, if a website threatens India’s defence, its sovereignty and integrity, friendly relations with foreign countries and public order, the government can ban it, after following due procedure.
- Detailed procedures to do so are listed under the Information Technology (Procedure and Safeguards for Blocking Access of Information by Public) Rules, 2009.
3.At the Afghanistan 2020 Conference, India has announced about 150 projects worth USD 80 million.
- Afghanistan’s President, officials from the United Nations (UN) and the European Union (EU) officials, besides representatives of other countries, attended the conference.
- Also, the USA has decided to reduce its troop presence in Afghanistan to about 2,500 by January 2021.
- India will launch phase-IV of high-impact community development projects, which include around 150 projects worth USD 80 million.
- It has signed an agreement for building the Shahtoot dam, which would provide safe drinking water to 2 million residents of Kabul city.
- It builds on the 202 km Pul-e-Khumri transmission line of 2009, through which India provides power to the city
4.The Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) of the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) has recognized the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) as a component of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) during its 102nd session held virtually.
- The IMO is the United Nations specialized agency responsible for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine and atmospheric pollution by ships.
- India has become the fourth country in the world to have its independent regional navigation satellite system recognized by the IMO as a part of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS).
- The other three countries that have its navigation systems recognized by the IMO are the USA, Russia, and China.
5.India has successfully test-fired a land-attack version of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The test by the Army comes over a month after the Naval version of BrahMos was successfully test fired from the Indian Navy’s indigenously-built stealth destroyer INS Chennai.
- Features of New Land-attack Version:
- The range of the missile has been extended to 400 km from the original 290 km but its speed has been maintained at 2.8 Mach or almost three times the speed of sound.
- The test was done in a “top-attack” configuration.
- Most modern missiles, including BrahMos, can be fired in both top-attack and direct attack modes.
- In top attack mode, the missile is required to climb sharply after launch, travel at a certain altitude and then fall on top of the target.
- In direct attack mode, the missile travels at a lower altitude, directly striking the target.
6.Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid tribute to Sir Chotu Ram Ji on his birth anniversary.
- Sir Chhotu Ram, (1881 – 1945) was a prominent politician in British India’s Punjab Province.
- He belonged to the Jat community and championed the interest of oppressed communities of the Indian subcontinent. For this feat, he was knighted in 1937.
- On the political front, he was a co-founder of the National Unionist Party which ruled the United Punjab Province in pre-independent India and kept Congress and the Muslim League at bay.
- His birth name was Ram Richpal and was popularly known as Deen Bandhu (in Urdu as Rahbare Azam, which translates as the messiah of the poor).
7.Union Agriculture Minister unveiled ‘Sahakar Pragya’ to impart training to primary cooperative societies in rural areas.
- The 45 new training modules of Sahakar Pragya of the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) will impart training to primary cooperative societies in rural areas along with Lakshmanrao Inamdar National Cooperative Research and Development Academy(LINAC).
- Sahakar Pragya embodies enhancing NCDC’s training capacity by 18-fold through an elaborate network of 18 Regional Training Centres across the country by the dedicated LINAC set up and fully funded by NCDC.




