Today Current Affairs: 20th November 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Cairn’s Offer On Retrospective Tax:

Moving quickly towards ending a retrospective tax dispute with a firm that gave India its largest oilfield, the government has accepted Cairn Energy PLC undertakings which would allow for the refund of taxes.
- The company will now be issued a ₹7,900 crore refund.
- In December 2020, a three-member international arbitral tribunal at the Permanent Court of Arbitration in the Netherlands ruled unanimously that the Indian government was “in breach of the guarantee of fair and equitable treatment”, and against the India-UK Bilateral Investment Treaty, and that the breach caused a loss to the British energy company and ordered compensation of $1.2 billion.
- Cairn had challenged the Indian government seeking taxes over an internal business reorganisation using the 2012 retrospective tax law, under the UK-India Bilateral Investment Treaty.
- In 2014, the Indian tax department had demanded Rs 10,247 crore in taxes.
- In 2015, Cairn Energy Plc commenced international arbitration proceedings against the Indian government.
Retrospective taxation:
- It allows a country to pass a rule on taxing certain products, items or services and deals and charge companies from a time behind the date on which the law is passed.
- Countries use this route to correct any anomalies in their taxation policies that have, in the past, allowed companies to take advantage of such loopholes.
- Retrospective Taxation hurts companies that had knowingly or unknowingly interpreted the tax rules differently.
59th Anniversary Of The Battle Of Rezang La:

November 18 marks the 59th anniversary of the Battle of Rezang La. A memorial was inaugurated on the occasion.
- Rezang La is a mountain pass on the Line of Actual Control in Ladakh.
- It is located between village of Chushul and the Spanggur Lake that stretches across both Indian and Chinese territories.
- It had also been the site of a heroic battle on 18 November 1962.
About the battle:
- Troops from the 13 Kumaon Regiment defeated several waves of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army in 1962.
- Despite being heavily outnumbered, soldiers of the regiment fought to the last man standing, under freezing temperatures, and with limited ammunition.
Significance of the region:
- Rezang La is vital for the defence of the crucially important Chushul. Any invader reaching there would have had a free run to Leh.
India Becomes The Highest Recipient Of Remittances:

According to the World Bank’s Migration and Development Brief, India has become the world’s largest recipient of Remittances, receiving USD 87 billion (a gain of 4.6 % from previous year) in 2021.
- India is followed by China, Mexico, the Philippines, and Egypt.
- The United States being the biggest source, accounting for over 20% of all Remittances.
- Factors for Remittance Growth:
- Migrants’ determination to support their families in times of need, aided by economic recovery in Europe and the United States which in turn was supported by the Fiscal Stimulus and employment support programs.
- In the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries and Russia, the recovery of outward remittances was also facilitated by stronger oil prices and the resulting pickup in economic activity.
- The severity of Covid-19 caseloads and deaths during the second quarter (well above the global average) played a prominent role in drawing substantial flows (including for the purchase of oxygen tanks) to the country.
- Flows from migrants have greatly complemented government cash transfer programs to support families suffering economic hardships during the Covid-19 crisis.
- Projection for 2022:
- Remittances are projected to grow 3% in 2022 to USD 89.6 billion, because of a drop in overall migrant stock, as a large proportion of returnees from the Arab countries await return.
Protection Of Children From Sexual Offences Act (POCSO):

The Supreme Court quashed a Bombay High Court decision to acquit a man charged with assault under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO) solely on the grounds that he groped the child over her clothes without “skin-to-skin” contact.
- “The act of touching a sexual part of the body with sexual intent will not be trivialised and not excluded under Section 7 of the POCSO Act,” the Bench held.
- Section 7 mandates that “whoever with sexual intent touches the vagina, penis, anus or breast of the child or makes the child touch the vagina, penis, anus or breast of such person or any other person, or does any other act with sexual intent which involves physical contact without penetration is said to commit sexual assault”.
- It also observed that the “purpose of law is not to allow the offender to sneak out of the mesh of law”.
- The court said limiting the ambit of “touch” to a narrow and pedantic” definition would lead to an “absurd interpretation”. The Bench noted that the most important ingredient in Section 7 was the sexual intent of the offender and not skin-to-skin contact.
- The conclusion that “sexual intent” mentioned in the provision should be ex facie skin to skin would defeat the object of the provision.
- It would, rather than giving effect to the rule, destroy it.
Shale Oil And Gas:
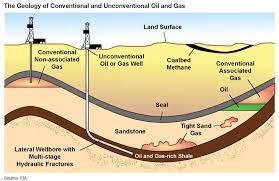
Cairn India will partner US-based Halliburton to start shale exploration in the Lower Barmer Hill formation, Western Rajasthan.
Shale Oil and Gas:
- Tight Oil: The key difference between shale oil and conventional crude is that the former, also called ‘tight oil’, is found in smaller batches, and deeper than conventional crude deposits.
- Shale Gas: Unlike conventional hydrocarbons that can be extracted from the permeable rocks easily, shale gas is trapped under low permeable rocks.
- Extraction Process: Extraction requires creation of fractures in oil and gas rich shale to release hydrocarbons through a process called hydraulic fracking/fracturing.
- It requires a mixture of ‘pressurised water, chemicals, and sand’ (shale fluid) to break low permeable rocks and have access to the shale gas reserves.
- Top Producers: Russia and the US are among the largest shale oil producers in the world, with a surge in shale oil production in the US having played a key role in turning the country from an importer of crude to a net exporter in 2019.
- Associated Concerns: Shale oil and gas exploration faces several challenges other than environmental concerns around massive water requirements for fracking and potential for groundwater contamination.
- Shale rocks are usually found adjacent to rocks containing usable/ drinking water known as ‘aquifers’.
- While fracking, the shale fluid could possibly penetrate aquifers leading to methane poisoning of groundwater used for drinking and irrigation purposes.
Coal : Sustainable Development Plan

Union Ministry of Coal of India has moved forward with a comprehensive Sustainable Development Plan.
- A full-fledged Sustainable Development Cell (SDC) in Ministry of Coal has been established to advice, mentor and plan action to minimise the adverse impact of mining.
- In line with the commitment of our country to reduce the total projected carbon emissions by one billion tonnes from now onwards till 2030, Bio-Reclamation of mined out land has already been taken up on a big scale by all coal companies through massive tree plantation drive.
- Coal & Lignite companies have planned to install additional 5560 MW of renewable capacity with an investment of over Rs. 15000 Crores.
- This will take the total installed capacity to 7 GW. Coal India alone has planned to install 3 GW of solar Power in next 5 years to achieve its net zero target.
- First Mile Connectivity (FMC) is other major initiative by coal companies to minimise environmental pollution, where coal is being transported through conveyor belt from Coal Handling Plants to Silo for loading.
- This process eliminates movement of coal through road.
- Similarly, Surface Coal Gasification Projects have been planned for Syn Gas production to be used further either for production of Methanol/Ethanol, Urea or Petrochemicals.
- This will be a way forward for use of dry fuel as green coal with relatively lesser carbon footprint and environmental pollution.
Wings India, 2022:

Jyotiraditya M. Scindia, Union Minster of Civil Aviation here today inaugurated a curtain raiser event about Wings India, 2022 which is Asia’s largest event on Civil Aviation (Commercial, General and Business Aviation).
- The minister appreciated the efforts the Civil Aviation Ministry, AAI and FICCI with the support of MEA and states government in organising this important event i.e. Wings India 2022, Hyderabad with the apt theme India@75: “New Horizon for Aviation Industry”.
- It aims to bring together the key stakeholders of the Global Aviation market, International regulators, States Governments and business associations as a group representing airlines, to facilitate direct interaction with various airlines, airport operators, cargo operators and other players at a common platform.
The Indian Civil Aviation industry
- India today handles the third largest domestic traffic after the USA and China.
- Government of India had announced Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) – UDAN (UdeDesh Ka Aam Nagrik) on 21st October 2016.
- As on date, 387 routes connecting 62 Airports including 6 Heliports and 2 Water Aerodromes have been made operational under RCS-UDAN Scheme.
Panchayats Extension To Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act 1996:

The Union Minister of Tribal Affairs Arjun Munda and the Union Minister for Rural Development & Panchayati Raj Giriraj Singh jointly inaugurated the one-day National Conference on provisions of the Panchayats Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act 1996 (PESA) in New Delhi.
- PESA seeks to protect the principle of Jal, Jungle , Jameen (Water, forest and land) for the tribals.
- Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 or PESA is a law enacted by the Government of India to cover the “Scheduled areas”, which are not covered in the 73rd amendment or Panchayati Raj Act of the Indian Constitution.
- It was enacted on 24 December 1996 to enable Gram Sabhas to self-govern their natural resources. It is an Act to provide for the extension of the provisions of Part IX of the Constitution relating to the Panchayats to the Scheduled Areas.
- “Scheduled Areas” means the Scheduled Areas as referred to in Clause (1) of Article 244 of the Constitution. The Act extended the provisions of Panchayats to the tribal areas of states that have Fifth Schedule Areas.
- A state legislation on panchayats in the scheduled area should take care of the customs, religious practices and traditional management practices of community resources
- Every village shall contain a grama sabha whose members are included in the electoral list for the panchayats at village level
- The recommendation of the gram sabha is mandatory for granting mining licenses in the scheduled areas
- Planning and management of minor water bodies are entrusted to the panchayats
Digital Lending:

A Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Working Group (WG) on digital lending, including lending through online platforms and mobile apps has submitted its recommendations.
Key recommendations:
- A separate legislation should be enacted to oversee such lending.
- Setup a nodal agency to vet the Digital Lending Apps.
- A Self-Regulatory Organisation should be set up for participants in the digital lending ecosystem.
- Develop certain baseline technology standards and compliance with those standards as a pre-condition for offering digital lending solutions.
- Disbursement of loans should be made directly into the bank accounts of borrowers and servicing of loans should be done only through the bank accounts of the digital lenders.
- All data collection must require the prior consent of borrowers and come ‘with verifiable audit trails’ and the data itself ought to be stored locally.
- Digital lending has the potential to make access to financial products and services more fair, efficient and inclusive.
- From a peripheral supporting role a few years ago, FinTech-led innovation is now at the core of the design, pricing and delivery of financial products and services.
The Sydney Dialogue:

The Prime Minister delivered the keynote at the inaugural Sydney Dialogue via video conferencing.
- He spoke on the theme of India’s technology evolution and revolution.
Highlights of the Address:
- The international order should ensure cryptocurrencies do not end up in the wrong hands.
- Citing the unregulated nature of the crypto market, recently, the PM called for taking progressive and forward-looking steps.
- India’s space sector is open to private investment and the agriculture sector is reaping the benefits of the digital revolution.
- In 2020, the government opened Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe) to provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
- Highlighted the leaps in India’s digital revolution that has redefined politics, economy and society.
- However, the digital age is raising new questions on sovereignty, governance, ethics, law, rights and security.
Sydney Dialogue:
- It is an initiative of the Australian Strategic Policy Institute.
- It is an annual summit of cyber and critical technologies to discuss the fallout of the digital domain on the law and order situation in the world.
Shakti:

Advanced Electronic Warfare (EW) System ‘Shakti’ has been designed and developed by Defence Electronics Research Laboratory (DLRL) Hyderabad a laboratory of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for Capital Warships of the Indian Navy for the interception, detection, classification, identification and jamming of conventional and modern Radars.
- The Shakti EW system will provide an electronic layer of defence against modern radars and anti-ship missiles to ensure electronic dominance and survivability in the maritime battlefield.
- This system will replace the earlier generation EW Systems of the Indian Navy.
- The system has been integrated with the wideband Electronic Support Measures (ESM) and Electronic Counter Measure (ECM) for the defence of Indian Navy Ships against missile attacks.
- The ESM of the system helps in finding accurate direction and interception of modern radars. The system has a built-in radar fingerprinting and data recording replay feature for post-mission analysis.
- First Shakti system has been installed on-board INS Visakhapatnam and is being installed on-board Indigenous Aircraft Carrier, INS Vikrant.
- Twelve Shakti Systems are under production at Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) supported by more than fifty MSMEs at a total cost of Rs 1805 Crores.
- These systems are scheduled to be installed on-board capital warships under production, including P-15B, P-17A and Talwar class follow-on ships.




