Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 3rd June 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
A3i (Type of coronavirus):
World Bank has released a part of the Global Economic Prospects (GEP) June 2020 report
Electronics incentive schemes launched:
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC):
WHO Funding:
1.A3i (Type of coronavirus):
Scientists at multiple CSIR laboratories have identified a type of coronavirus that maybe the second most prevalent in India and may comprise 3.5% of the genomes globally.
- The most dominant coronavirus clade in India is the A2a, and of 213 genomes analyzed by the group, 62% of them were A2a.
- The newly identified type, that the scientists have christened A3i, comprised 41% of those analyzed.
- With this, there are 11 SARS-CoV-2 types identified globally, with at least six of them identified in India.
- The coronavirus type, or clade, is a cluster of SARS-CoV-2 viruses that share evolutionary similarities.
- Such classifications are useful in establishing whether certain strains are particularly virulent, spread more easily, how they are likely to evolve over time, and whether some could be less vulnerable to certain kinds of vaccines.
2. World Bank has released a part of the Global Economic Prospects (GEP) June 2020 report.:

Recently, the World Bank has released a part of the Global Economic Prospects (GEP) June 2020 report.
- The report highlighted that the Covid-19 pandemic will be having a “severe” short and long term effects on economic growth.
Key Findings
- Impact on Global Poverty:
- The Covid-19 pandemic and economic shutdowns have devastated the poor around the world which is unprecedented in modern times.
- It has been estimated that 60 million people could be pushed into extreme poverty in 2020. These estimates are likely to rise further, with the reopening of advanced economies.
- These economic lockdowns have also damaged the multiple channels, including lower investment and innovation, erosion of the human capital, and a retreat from global trade and supply linkages.
It has also lowered the potential growth and labor productivity.
- Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs):
- EMDEs are most vulnerable and may face health crises, restrictions, and external shocks like falling trade, tourism, and commodity prices, as well as capital outflows.
- These countries are expected to have a 3-8% output loss in the short term.
- But in the long term, these countries will experience a drop in the level of output with a lowering of potential output growth.
- Growth is likely to slow more in commodity-exporting EMDEs than in commodity-importing ones.
Spillover Effect over EMDEs: - EMDEs are also expected to witness the spillover effects of the U.S., the Euro Area and China, which represent almost half of global output.
- As these countries are unlikely to return to pre-pandemic levels of output before the end of 2021.
- Issue of Loan Repayments:
- Earlier, G20 countries and commercial creditors had agreed to freeze loan repayments for low-income countries (starting 1st May 2020) till year-end. But these creditors had not yet implemented the same.
- The delay by commercial creditors to freeze loan repayment is deepening poverty in the debtor country.
Most creditors are in advanced economies like the U.S., Europe, Japan, China, and the Gulf.
- Energy-Exporting Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs):
- The Energy-Exporting Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs) are facing a dual problem of the public health crisis with strained fiscal positions due to the recent collapse in oil revenues.
- The collapse in oil demand due to the worldwide economic lockdowns and a surge in oil inventories have made the steepest one-month decline in oil prices on record.
3. Electronics incentive schemes launched:

The government has launched three incentive schemes with a total outlay of about ₹48,000 crores to boost the large-scale manufacturing of electronics in the country.
The schemes are:
Production Linked Incentive:
- Targeted at mobile phone manufacturing and specified electronic components.
- The government initially plans to incentivize 10 firms five global and five local.
- This Scheme shall extend an incentive of 4% to 6% on incremental sales (over the base year) of goods manufactured in India and covered under the target segments, to eligible companies, for a period of five years subsequent to the base year.
Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors (SPECS):
- It shall provide a financial incentive of 25% on capital expenditure for the identified list of electronic goods, i.e., electronic components, semiconductor/ display fabrication units, Assembly, Test, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP) units, specialized sub-assemblies and capital goods for manufacture of aforesaid goods.
Modified Electronics Manufacturing Clusters (EMC 2.0) Scheme:
- It shall provide support for the creation of world-class infrastructure along with common facilities and amenities, including Ready Built Factory (RBF) sheds / Plug and Play facilities for attracting major global electronics manufacturers, along with their supply chains.
4.China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC):
China under the multi-billion-dollar CPEC will set up a 1,124-megawatt power project- Kohala Hydropower Project- in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir despite India’s objection to it.
- A tripartite agreement has been finalized among China’s Three Gorges Corporation, the authorities in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) and the PPIB to implement the 1,124-megawatt Kohala hydroelectric power project under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) framework.
- The project will be built on the Jhelum River and aims at annually providing more than five billion units of clean and low-cost electricity for consumers in Pakistan.
- This marks one of the largest investments of USD 2.4 billion in an independent power producer (IPP) in the region.
CPEC:
- The CPEC is the flagship project of the multi-billion-dollar Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a pet project of Chinese President Xi Jinping, aimed at enhancing Beijing’s influence around the world through China-funded infrastructure projects.
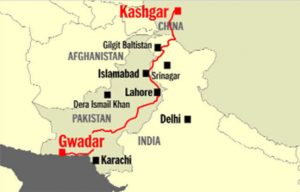
- The 3,000 km-long China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) consists of highways, railways, and pipelines.
- CPEC eventually aims at linking the city of Gwadar in South Western Pakistan to China’s North Western region Xinjiang through a vast network of highways and railways.
- The proposed project will be financed by heavily-subsidized loans, that will be disbursed to the Government of Pakistan by Chinese banks.
- It passes through PoK.
- CPEC rests on a Chinese plan to secure and shorten its supply lines through Gwadar with an enhanced presence in the Indian Ocean. Hence, it is widely believed that upon CPEC’s fruition, an extensive Chinese presence will undermine India’s influence in the Indian Ocean.
- It is also being contended that if CPEC were to successfully transform the Pakistan economy that could be a “red rag” for India which will remain at the receiving end of a wealthier and stronger Pakistan.
- Besides, India shares a great deal of trust deficit with China and Pakistan and has a history of conflict with both. As a result, even though suggestions to re-approach the project pragmatically have been made, no advocate has overruled the principal strands of contention that continue to mar India’s equations with China and Pakistan.
5.WHO Funding:
With President Donald Trump announcing that the US will be “terminating” its relationship with the World Health Organisation (WHO), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) is set to become the biggest funder of the organization.
- A private foundation becoming the biggest funder, and hence the biggest influence, on a United Nations agency, would be a first.
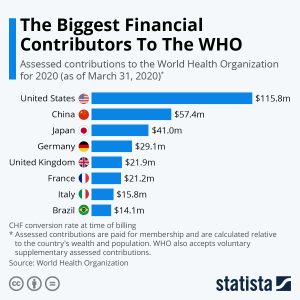
- In fact, though the WHO is meant to be a body accountable to its member countries, among the top 10 donors to the organization only four are member countries and one is the European Commission.
- The rest are all non-state actors or philanthropies.
- When the WHO was constituted, its constitution stipulated that it should primarily be financed through regular contributions from member countries, called “assessed contributions”, relative to the country’s wealth and population.
Other important current affairs:
1. The country’s two power exchanges — Indian Energy Exchange (IEX) and Power Exchange India (PXIL) — commenced real-time electricity market (RTM) on their platforms.
- The RTM enables consumers, including distribution companies (discoms) and captive users, to buy power on exchanges just an hour before delivery.RTM will help consumers purchase electricity just an hour in advance.
- With RTM, both sellers and buyers now get an opportunity to continuously manage their portfolio optimally through a transparent and efficient marketplace.
- In December 2019, the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) approved the framework for RTM trading by power exchanges.
- Till now, the exchanges had day-ahead, week-ahead, and season-ahead markets, as well as renewable energy certificates trading.
- There are two energy exchanges in India — IEX and PXIL — where electricity is traded.
2. Scientists have recently discovered tiny flashes of radio light emanating from all over the Sun, which they say could help in explaining the long-pending coronal heating problem.
- The data was collected with the help of the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) radio telescope.
- The radio lights or signals under study result from beams of electrons accelerated in the aftermath of a magnetic explosion on the Sun.
- These observations are the strongest evidence to date that the tiny magnetic explosions, originally referred to as ‘nanoflares’ by eminent American solar astrophysicist Eugene Parker.
- Researchers believe that these explosions could indeed be heating up the corona.
- The Sun’s corona is the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere. The corona is usually hidden by the bright light of the Sun’s surface. That makes it difficult to see without using special instruments. However, the corona can be viewed during a total solar eclipse.
- The corona is about 10 million times less dense than the Sun’s surface. This low density makes the corona much less bright than the surface of the Sun.
3. Three more States included in the One Nation One Card scheme- Odisha, Sikkim, and Mizoram. The facility so far is enabled in 17 States/UTs.
- One Nation One Ration Card (RC) will ensure all beneficiaries especially migrants can access PDS across the nation from any PDS shop of their own choice.
- Benefits: no poor person is deprived of getting subsidized foodgrains under the food security scheme when they shift from one place to another. It also aims to remove the chance of anyone holding more than one ration card to avail benefits from different states.
- This will provide freedom to the beneficiaries as they will not be tied to anyone PDS shop and reduce their dependence on shop owners and curtail instances of corruption.
4. Union Minister of Rural Development chaired the 21st meeting of the Central Employment Guarantee Council.
- The Central Employment Guarantee Council was constituted under Section 10 of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (Mahatma Gandhi NREGA), 2005.
- Addressing the participants, rural development minister said that for the Financial Year 2020-21, Rs.61,500 crore has been allocated for this program which is an all-time high.
- An additional provision of Rs.40,000 crore has been made for this program under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan to provide employment to the needy workers during this difficult period arising of COVID-19.
5. Majority producers in the Malayalam film industry declared that they do not prefer online release for their movies amid the COVID-19 outbreak.
- As the theatres remain closed amid the pandemic, the release of many movies was postponed for over three months. Following this, a few producers announced the OTT release for their movies.
- The announcement irked theatre owners and they declared that they will boycott movies of the producer and actor if they go with the online release.
- An “over-the-top” media service is any online content provider that offers streaming media as a standalone product. The term is commonly applied to video-on-demand platforms, but also refers to audio streaming, messaging services, or internet-based voice calling solutions.
- OTT services circumvent traditional media distribution channels such as telecommunications networks or cable television providers.
- As long as you have access to an internet connection — either locally or through a mobile network — you can access the complete service at your leisure.
6. Recently, the Jammu and Kashmir administration has approved a Media Policy-2020.
- The policy seeks to create a sustained narrative on the functioning of the government in the media and promote the highest standard of journalism in the Union Territory.
- The media policy aims to put in place a Standard Operating Procedure for reaching out to the people in situations of crisis like health issues and natural disasters.
7. Depsang:
- There have been reports of a heavy Chinese presence at Depsang.
- The “Depsang plain” is one of the few places in the Western Sector where light armor (vehicles) would have ease of maneuver, so any Chinese buildup there is a cause for concern.
- It is an area at a crucial dip (called the Bulge) on the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- The Chinese Army occupied most of the plains in 1962.
- India controls the western portion of the plains as part of Ladakh, whereas the eastern portion is part of the Aksai Chin region, which is controlled by China and claimed by India.
7. Bimal Julka committee:
- An Expert Committees on Rationalisation of Film Media Units and Review of Autonomous Bodies submitted its report to the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting. The Committee was chaired by Bimal Julka.
- The committee has found overlapping activities being undertaken by multiple institutes.
- It has suggested an umbrella configuration with 4 broad verticals under which institutes should work.
- They are – Production, Festival, Heritage, and Knowledge. It has recommended that these verticals be headed by professionals.
- It has also recommended the creation of a Film Promotion Fund for independent filmmakers for making commercial films.




