Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 5th October 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Chardham Project:
- Postal ballot
- Narco and Polygraph Tests:
- Compensatory Afforestation:
- Belt & Road Initiative.:
- POCSO Act:
- Other important current affairs
1. Chardham Project:
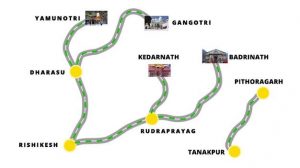
The chairman of a Supreme Court-appointed expert committee has alleged violations of the court orders in the execution of the Chardham road project — a 900 km, ₹12,000 crore enterprise to connect pilgrimage spots in Uttarakhand.
- A controversial aspect was the proposed width of the two-lane highways envisaged.
- The top court ruled last month that a width of 5.5 metres be enforced as it was in conformity with a 2018 recommendation of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) for mountain roads.
The Chardham Project:
- The project comprises improvement as well as the development of 889 km length of national highways.
- The project will connect Badrinath Dham, Kedarnath Dham, Gangotri, Yamunotri, and part of the route leading to Kailash Mansarovar yatra.
2. Postal ballot :

Seeking to make the procedure to opt for postal ballot more convenient for those above 80 years of age and people with disabilities, the Election Commission has come out with a set of new instructions.
- EC announces new rules for the postal ballot.
- The rules aim to make it more convenient for those above 80 years of age and people with disabilities to vote.
New rules:
- The returning officer would deploy polling teams, which will deliver and collect the postal ballot on pre-informed dates and then deposit it with the returning officer.
- The form required to opt for the postal ballot would be delivered at the residence of all those aged above 80 and people with disabilities by the booth level officer under his polling station.
Postal voting:
- A restricted set of voters can exercise postal voting.
- Through this facility, a voter can cast her vote remotely by recording her preference on the ballot paper and sending it back to the election officer before counting.
- Members of the armed forces like the Army, Navy and Air Force, members of the armed police force of a state (serving outside the state), government employees posted outside India and their spouses are entitled to vote only by post.
- The exception to the above-mentioned category of voters is provided under Section 60 of the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
3.Narco and Polygraph Tests:

The Uttar Pradesh government decided to conduct polygraph and narcoanalysis tests of the accused and all involved police personnel as part of the investigation into the alleged gangrape and murder of a 19-year old in Hathras last month.
Polygraph or Lie Detector Test:
- It is a procedure that measures and records several physiological indicators such as blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and skin conductivity while a person is asked and answers a series of questions.
- This test is based on the assumption that physiological responses that are triggered when a person is lying are different from what they would be otherwise.
- A numerical value is assigned to each response to conclude whether the person is telling the truth, is deceiving, or is uncertain.
- A test similar to Polygraph was first done in the 19th century by the Italian criminologist Cesare Lombroso, who used a machine to measure changes in the blood pressure of criminal suspects during interrogation.
Narcoanalysis Test:
- It involves the injection of a drug, sodium pentothal, which induces a hypnotic or sedated state in which the subject’s imagination is neutralized, and they are expected to divulge information that is true.
- The drug, also referred to as truth serum, was used in larger doses as anesthesia during surgery, and is said to have been used during World War II for intelligence operations.
- Recently, investigating agencies have sought to employ these tests in the investigation, and are sometimes seen as being a softer alternative to torture or “third degree” to extract the truth from suspects.
Brain Mapping Test or P-300 test:
- In this test, the activity of the brain of a suspect is measured during interrogation to find out whether he is concealing any information.
None of these methods has been proven scientifically to have a 100% success rate, and remain contentious in the medical field as well.
- The consequences of such tests on individuals from weaker sections of society who are unaware of their fundamental rights and unable to afford legal advice can be adverse.
- It may involve future abuse, harassment, and surveillance, even leakage of the video material to the Press for a trial by the media.
4.Compensatory Afforestation:

A recent study on compensatory afforestation in lieu of forest diversion for development of projects in Himachal Pradesh’s Kinnaur district, only 10% of saplings said to be planted were actually found on the site and their survival rate was as low as 3.6%.
- The study has been carried out by Himdhara Environment Research and Action Collective. It is based on government data and ground research and was conducted between 2012 and 2016.
Data Analysis:
- As of 31st March 2014, the total area demarcated for compensatory afforestation was 1,930 ha in lieu of 984 ha of forest land diverted for non-forest activities, including roads, hydro-projects, transmission lines, etc.
- The total diverted forest land in Kinnaur had 11,598 standing trees, belonging to 21 species.
- The majority of the trees felled were coniferous, dominated by cedar (3,612 felled) and near-threatened chilgoza pines (2,743).
- Between 2002 and 2014, of the Rs.162.82 crore collected under Catchment Area Treatment (CAT) plan funds of Kinnaur’s projects, only 36% had been spent till 31st March 2014.
- CAT plan funds are budgeted as mitigation measures for hydroelectric power projects.
- More than 90% of the diversion of forest in Kinnaur takes place for the development of hydropower projects and transmission lines.
- Himachal Pradesh has the highest installed capacity of hydropower projects of 10,000 MW in the country and located in the Sutlej basin, Kinnaur is the state’s hydropower hub with 53 planned hydropower projects.
Compensatory Afforestation:
- According to Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) rules, for every hectare of forest land diverted, double the area of ‘degraded’ lands are used as sites for ‘compensatory afforestation’.
- Every time forest land is diverted for non-forest purposes such as mining or industry, the user agency pays for planting forests over an equal area of non-forest land, or when such land is not available, twice the area of degraded forest land.
- As per the rules, 90% of the Compensatory Afforestation Fund (CAF) money is to be given to the states while 10% is to be retained by the Centre.
- The funds are used for CAT, assisted natural generation, forest management, wildlife protection and management, relocation of villages from protected areas, managing human-wildlife conflicts, training and awareness generation, the supply of wood saving devices and allied activities.
5. Belt & Road Initiative.:
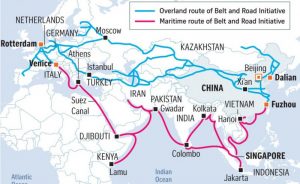
Xi hails ‘steady’ China-Bangladesh friendship, seeks the joint promotion of Belt & Road Initiative.
- The Belt and Road Initiative, reminiscent of the Silk Road, is a massive infrastructure project that would stretch from East Asia to Europe.
- It was launched in 2013.
- The plan is two-pronged: the overland Silk Road Economic Belt and the Maritime Silk Road- The two were collectively referred to first as the One Belt, One Road initiative but eventually became the Belt and Road Initiative.
- The project involves creating a vast network of railways, energy pipelines, highways, and streamlined border crossings.
- To date, more than sixty countries—accounting for two-thirds of the world’s population—have signed on to projects or indicated an interest in doing so.
- Analysts estimate the largest so far to be the estimated $60 billion China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, a collection of projects connecting China to Pakistan’s Gwadar Port on the Arabian Sea.
Original Silk Road:
- The original Silk Road arose during the westward expansion of China’s Han Dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), which forged trade networks throughout the Central Asian countries, as well as modern-day India and Pakistan to the south. Those routes extended more than four thousand miles to Europe.
6.POCSO Act:

The Delhi High Court has ruled that the presumption of guilt engrafted in Section 29 of the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012 gets triggered and applies only once the trial begins, that is after charges are framed against the accused.
Section 29 of the POCSO Act:
- It says that when a person is prosecuted for committing an offense of sexual assault against a minor, the special court trying the case “shall presume” the accused to be guilty.
- The question of whether the presumption of guilt applies only at the stage of trial or does it also apply when a bail plea is being considered cropped up while hearing the bail plea of a 24-year-old man arrested for alleged sexual assault of a minor.
Rulings:
- It was clarified that if a bail plea is being considered before charges have been framed, Section 29 has no application.
- ‘Trial’ commences when charges are framed against an accused and not before that.
- Only at the stage when charges are framed does the court apply its judicial mind to whether there is enough evidence on record to frame a precise allegation, which the accused must answer.
- The Court held that an accused cannot be asked to disprove their guilt even before the foundational allegations with supporting evidence that suggests guilt are placed by the prosecution before the court.
- It is only once charges are framed that the accused know exactly what they are alleged to be guilty of; and therefore, what guilt they are required to rebut (deny).
- It would be disgraceful to fundamental criminal jurisprudence to ask the accused to disclose their defense; or, worse still, to present evidence in their defense even before the prosecution has marshaled its evidence.
- Earlier, the reverse burden on the accused to prove his innocence was incorporated in the POCSO Act keeping in view the low conviction rate of sexual offenses against children.
- Reverse burden means that persons charged with an offense would have to rebut the presumption against them and the burden of proof would lie on them to show that they have not committed the act constituting an offense.
- The Court also set out fresh norms while deciding a bail plea at the post-charge stage. It held that in addition to the nature and quality of the evidence before it, the court would also factor in certain real-life considerations.
- These include whether the offense alleged involved threat, intimidation, violence, or brutality. Also, the court, hearing the bail would consider whether the offense was repeated against the victim.
Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012
- It was enacted to protect the children from offences of sexual assault, sexual harassment and pornography with due regard for safeguarding the interest and well-being of children.
- It defines a child as any person below eighteen years of age and regards the best interests and welfare of the child as a matter of paramount importance at every stage, to ensure the healthy physical, emotional, intellectual and social development of the child.
- It defines different forms of sexual abuse, including penetrative and non-penetrative assault, as well as sexual harassment and pornography.
- It deems a sexual assault to be “aggravated” under certain circumstances, such as when the abused child is mentally ill or when the abuse is committed by a person in a position of trust or authority like a family member, police officer, teacher, or doctor.
- It also casts the police in the role of child protectors during the investigative process.
- The Act stipulates that a case of child sexual abuse must be disposed of within one year from the date the offence is reported.
- It was amended in August 2019 to provide more stringent punishment, including the death penalty, for sexual crimes against children.
Other important current affairs:
1.World Teachers’ Day is being celebrated on October 5, 2020.
- World Teachers’ Day is celebrated every year on October 5 globally to recognize and celebrate the works of educators including teachers, researchers, and professors worldwide.
- International Teachers Day is celebrated by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO) in partnership with United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), International Labour Organisation (ILO) and Education International.
- The theme for World Teachers’ Day 2020 is “Teachers: Leading in Crisis, Reimagining the Future”.
- On October 5, 1966, a recommendation on the status of teachers was adopted and to mark that event, UNESCO has been celebrating World Teachers’ Day since 1994 on this day.
- The recommendation had set standards including teachers’ rights and responsibilities, initial preparation and further education, recruitment, employment, and teaching-learning conditions.
2.Scientists from Agharkar Research Institute, Pune, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science & Technology, discovered two new species of pipeworts from the Western Ghats of Maharashtra & Karnataka.
- Two new species of a plant group known for their varied medicinal properties have been discovered in the Western Ghats – one of the thirty-five hot-spots of biological diversity in the world.
- The plant group is known as pipeworts (Eriocaulon), which completes their life cycle within a small period during monsoon, exhibits great diversity in the Western Ghats, having around 111 species in India.
- The one reported from the Sindhudurg district of Maharashtra was named Eriocaulon parvicephalum (due to its minute inflorescence size).
- The other reported from Kumta, Karnataka was named Eriocaulon karaavalense (named after Karaavali = Coastal Karnataka region).
3.A successful trial of the nuclear-capable Shaurya missile was conducted by India.
- Shaurya is a land-based parallel of the submarine-launched K-15 missile.
- These ballistic weapons belong to the K missile family — codenamed after late Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam — which is launched from the Arihant class of nuclear submarines.
- K family of missiles:
- The K family of missiles is primarily Submarine Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs), which have been indigenously developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The development of these naval platforms launched missiles began in the late 1990s as a step towards completing India’s nuclear triad — the capability of launching nuclear weapons from land, sea, and air-based assets.
- Because these missiles are to be launched from submarines, they are lighter, smaller and stealthier than their land-based counterparts, the Agni series of missiles which are medium and intercontinental range nuclear-capable ballistic missiles.
- While K family are primarily submarine-fired missiles to be fired from India’s Arihant class nuclear-powered platforms, the land and air variants of some of its members have also been developed by the DRDO.
4.The French territory of New Caledonia voted against independence from France in a referendum held recently.
- The referendum was a part of a decolonization plan agreed in 1998, known as the Noumea Accord.
- New Caledonia is an archipelago and special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean.
- The indigenous Kanaks represent around 39% of the population, while European settlers (known as Caldoches) make up about 27%.
- Most of the remainder are from other Pacific islands, which are of mixed heritage, called Caledonians.
5.To catalyze cutting-edge PV manufacturing in India, NITI Aayog, Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, and Invest India, is organizing a global symposium virtually, ‘India PV EDGE 2020’, on October 6, 2020.
- India has become the third-largest solar capacity country in the world and set an ambitious target of 450 GW of renewable capacity by 2030, comprising 300 GW of solar capacity.
- The major factor behind the rise of solar deployment is giga-scale solar manufacturing and the continuous adoption of innovations to reduce prices.
- Cutting-edge giga-scale solar manufacturing stands on three pillars:
- disruptive PV chemistries,
- manufacturing by custom-engineered advanced production equipment, and
- utilization of innovative BOM components like special glasses and coatings.
- India’s NDC document of the Paris Agreement in 2015 called for extraordinary leadership to combat climate change. India PV EDGE 2020 is one small step towards that ambition.
6.India participated at the Science & Technology Ministerial Roundtable, organized in the 17th annual Science and Technology in Society (STS) Forum.
- Hosted by: Japan
- Science and Technology Ministers’ Roundtable is held along with the STS forum every year.
- Major highlights:
- Deliberated on the role of international R&D collaboration,
- Social sciences & humanities,
- Open science.
- Participation: S&T heads from about 50 countries around the world participated and explored the opportunities arising from international collaborations at the Roundtable to address the challenges posed by COVID 19.
- India highlighted initiatives by India regarding the sharing of scientific data- National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy and an open government data portal.
7.The Chief Minister of Delhi will be among the five urban leaders from around the world to speak at the ‘Daring Cities 2020’ conference on 7th October.
- Daring Cities is a virtual, action-oriented forum to recognize and empower urban leaders – including mayors and other decision-makers, technical staff, researchers, private sector representatives, and community organizers – to disrupt business-as-usual and shift towards business-as-possible.
- It showcases and catalyzes exemplary local climate action to tackle the climate emergency, including ambitious resilience-building and climate mitigation efforts.
- It was created by ICLEI and the Federal City of Bonn (Germany).
- It builds upon the experience and network established during the Resilient Cities Congresses convened annually from 2010 to 2019 by ICLEI and the Federal City of Bonn.
- ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability is a global network of more than 1,750 local and regional governments committed to sustainable urban development.
- Many municipal corporations and councils from India such as Pune Municipal Corporation, Nainital Municipal Council, North Delhi Municipal Corporation, etc. are members.
- Daring Cities 2020:
- It will be a three-week event (7th-28th October 2020) comprising high level and visionary speakers, a series of informative workshops and personal networking opportunities in a variety of virtual formats to accommodate different topics, time zones, internet bandwidth limits, and languages.
- The event will help to set the course to COP26, Daring Cities 2021 and beyond.
- The 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP 26) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) will be held in 2021 in Glasgow, UK.




