Today Current Affairs: 11th June 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
EAGLE Act of 2021:
Democrat Representative Zoe Lofgren and Republican John Curtis introduced the Equal Access to Green cards for Legal Employment (EAGLE) Act of 2021 in the House of Representatives.
- The bipartisan act seeks to phase out the seven percent per-country limit on employment-based immigrant visas and raises the per-country limit on family-sponsored visas from seven percent to 15 percent.
- It provides for a nine-year period for the elimination of this limit.
- The seven percent limit was introduced in the mid-20th century, which has led countries with relatively small populations to be allocated the same number of visas as a relatively large-population country.
- It will “benefit the US economy by allowing American employers to focus on hiring immigrants based on their merit, not their birthplace”.
- The bill will be advantageous for Indian job-seekers who currently rely on temporary visas or await green cards to work in the US.
Fastly:

On 8 June 2021, Fastly reported problems with their CDN service which caused many major websites, such as Reddit, gov.uk, Twitch, Spotify, and Amazon, along with major news sources such as The New York Times, The Guardian, CNN, and the BBC, to become unavailable.
- Fastly is an American cloud computing services provider.
- It describes its network as an ‘edge cloud platform’, which is designed to help developers extend their core cloud infrastructure to the edge of the network, closer to users.
- The Fastly edge cloud platform includes their content delivery network (CDN), image optimization, video and streaming, cloud security, and load balancing services.
- A content delivery network is an arrangement that allows customer websites to store data such as images and videos on various mirror servers across countries so that the data is closer to users, and thus shows up faster.
- Customers rely on Fastly and its rivals to host and protect their website data from denial-of-service attacks and disruption from spikes in traffic.
The Cosmic Infrared Background Experiment-2:
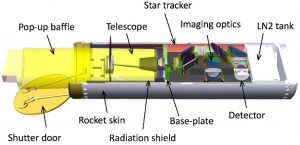
The Cosmic Infrared Background Experiment-2 (CIBER-2) was launched by NASA on June 6, 2021 from the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, USA.
- The aim of this mission is to count the number of stars that exist in the Universe.
- The experiment is measuring a mysterious glow of infrared light that fills our skies called the cosmic infrared background, which is emitted by some of the most common stars.
- While this is not the first time that such a mission has been undertaken, the CIBER-2 instrument has been improved upon to see if any stars had been undercounted in the previous counting attempts.
- The European Space Agency (ESA) infrared space observatory Herschel also counted the number of galaxies in infrared and measured their luminosity previously.
- Scientists have estimated that on average each galaxy consists of about 100 million stars, but this figure is not exact.
- The figure of 100 million could easily be an underestimation, probably by a factor of 10 or more.
- To put this into perspective, an average of 100 million stars in each galaxy (there an estimated 2 trillion of them as per NASA), would give a total figure of one hundred quintillion stars or 1 with 21 zeroes after it.
Minimum Support Prices For Kharif Crops:

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, chaired by PM Modi, has approved the increase in the Minimum Support Prices (MSPs) for all mandated Kharif crops for marketing season 2021-22.
- MSP for common paddy was hiked to ₹1,940 a quintal for the coming Kharif season, less than 4% higher than last year’s price of ₹1,868.
- The highest absolute increase in MSP over the previous year has been recommended for sesamum (Rs. 452 per quintal) followed by tur and urad (Rs. 300 per quintal each).
- In the case of groundnut and nigerseed, there has been an increase of Rs 275 per quintal and Rs 235 per quintal respectively in comparison to last year.
- The differential remuneration is aimed at encouraging crop diversification.
- The expected returns to farmers over their cost of production are estimated to be highest in the case of Bajra (85%) followed by urad (65%) and tur (62%).
- For the rest of the crops, the return to farmers over their cost of production is estimated to be at least 50%.
Atlantic Charter:

President Joe Biden and British Prime Minister Boris Johnson recently inspected documents related to the Atlantic Charter, a declaration signed by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill and U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt in August 1941.
- The two leaders plan to sign what they’re calling a new Atlantic Charter, pledging to “defend the principles, values, and institutions of democracy and open societies.”
- The Atlantic Charter was a joint declaration issued during World War II (1939-45) by the United States and Great Britain that set out a vision for the postwar world.
- First announced on August 14, 1941, a group of 26 Allied nations eventually pledged their support by January 1942.
- Among its major points were a nation’s right to choose its own government, the easing of trade restrictions, and a plea for postwar disarmament.
- The document is considered one of the first key steps toward the establishment of the United Nations in 1945.
Delhi’s Master Plan 2041:
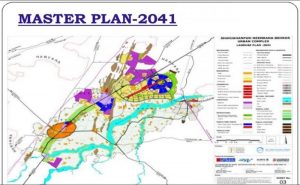
The Delhi Development Authority has gave its preliminary approval to the draft Master Plan for Delhi 2041. The draft is now in the public domain for objections and suggestions from citizens, after which it will be enforced.
- A master plan of any city is like a vision document by the planners and the land-owning agency of the city, which gives a direction to the future development.
- It includes analysis, recommendations, and proposals keeping in mind the population, economy, housing, transportation, community facilities, and land use.
Master Plan 2041 For Delhi:
- It seeks to “foster a sustainable, liveable and vibrant Delhi by 2041”.
- In the housing sector, it talks about incentivizing rented accommodation by inviting private players and government agencies to invest more, keeping in mind the large migrant population.
- ‘User pays’ principle: To address parking problems, it suggests a ‘user pays principle, which means users of all personal motor vehicles, except for non-motorized ones, have to pay for authorized parking facilities, spaces, and streets.
- It aims to minimize vehicular pollution through key strategies, including a switch to greener fuels for public transport and adoption of mixed-use of transit-oriented development (also known as TOD).
- The draft lays a clear boundary of the buffer zone near the Yamuna river– a 300-meter width shall be maintained wherever feasible along the entire edge of the river.
Beed Model: Maharashtra:

Maharashtra government has asked for state-wide implementation of the ‘Beed model’ of the crop insurance scheme Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bhima Yojana (PMFBY).
‘Beed Model’:
- Beed is a district located in the drought-prone Marathwada region.
- The district presents a challenge for any insurance company because farmers here have repeatedly lost crops either to failure of rains or too heavy rains.
- Given the high payouts, insurance companies have sustained losses.
- The solution:
- To attract the insurance companies, the state Agriculture Department decided to tweak the PMFBY guidelines for the district.
- Under the new guidelines, the insurance company provided a cover of 110% of the premium collected, with caveats.
- If the compensation exceeded the cover provided, the state government would pay the bridge amount.
- If the compensation was less than the premium collected, the insurance company would keep 20% of the amount as handling charges and reimburse the rest to the state government.
All India Survey On Higher Education (AISHE) 2019-20:

The Union Education Minister announced the release of the report of All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) 2019-20.
- This Report provides key performance indicators on the current status of Higher education in the country.
- It is the 10th in the series of AISHE annually released by the Department of Higher Education.
Total Student Enrolment:
- In the last five years from 2015-16 to 2019-20, there has been a growth of 11.4% in student enrolment.
- Total Enrolment in Higher Education stands at 3.85 crores in 2019-20 as compared to 3.74 crores in 2018-19, registering a growth of 11.36 lakh (3.04 %).
- Uttar Pradesh has the highest student enrolment in India, it has 49.1% male and 50.9% female students followed by Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra.
Gross Enrolment Ratio:
- The Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) increased by a minuscule 0.8% in 2019-20.
- GER is the number of students enrolled in a given level of education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the official school-age population corresponding to the same level of education.
- The percentage of students belonging to the eligible age group enrolled in higher education in 2019-20 is 27.1% against 26.3% in 2018-19 and 24.3% in 2014-2015.
Female Enrolment:
- There has been an overall increase of over 18% in female enrolment in higher education from 2015-16 to 2019-20.
- However, the share of girl students is lowest in institutes of national importance while female participation in professional courses is lower in comparison to academic courses.
Gender Parity Index:
- Gender Parity Index (GPI) in Higher Education in 2019-20 is 1.01 against 1.00 in 2018-19 indicating an improvement in the relative access to higher education for females of eligible age group compared to males.
- A GPI of 1 indicates parity between the sexes; a GPI that varies between 0 and 1 typically means a disparity in favor of males; whereas a GPI greater than 1 indicates a disparity in favor of females.
Teachers:
- The total Number of Teachers stands at 15,03,156 comprising 57.5% male and 42.5% female.
- Pupil-Teacher Ratio in Higher Education in 2019-20 is 26.
- Nearly 85% of the students (2.85 crores) were enrolled in the six major disciplines such as Humanities, Science, Commerce, Engineering & Technology, Medical Science and IT & Computer
President Of The 76th Session Of The United Nations (UN) General Assembly (GA) For 2021-22.:

The Maldives’ Foreign Minister Abdulla Shahid was elected the President of the 76th session of the United Nations (UN) General Assembly (GA) for 2021-22.
- The win was welcomed by India as Indian diplomats had been helping the Maldives and India expects close cooperation with Maldives at the UN.
- However, the Maldives has made no decision on opening an Indian consulate in its southern Addu Atoll even as the Indian Cabinet cleared a proposal for it.
President of UNGA:
- This is a post held on an annual basis, rotated amongst various regional groupings. The 76th session (2021-22) is the turn of the Asia-Pacific group.
- This is the first time Maldives will be occupying the office of the President of UNGA.The
- Maldives also sees it as a win for the 52-member Small Island Developing States (SIDS), which are battling climate change vulnerability and other developmental challenges.
- Addu Atoll, also known as Seenu Atoll, is the southernmost atoll of the Maldives.
- Apart from its strategic location in the Indian Ocean, Addu is the second-largest city in the archipelago, home to over 30,000 people.
India’s Stand:
- India approved the opening of a new consulate in the Maldivian city of Addu, in reflection of the importance, India attaches to its ties with the strategically located island nation.
- India’s decision to expand its diplomatic presence in the Maldives comes amid China’s consistent efforts to increase its influence in the island nation.
- Also, Indian rationale for the consulate was to help Addu residents with speedy visa services.
Roadmap For Ethanol Blending In India By 2025:

The central government has released an expert committee report on the Roadmap for Ethanol Blending in India by 2025.
- The roadmap proposes a gradual rollout of ethanol-blended fuel to achieve E10 fuel supply by April 2022 and a phased rollout of E20 from April 2023 to April 2025.
- The Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas (MoP&NG) had instituted an Expert Group to study the issues such as pricing of ethanol, matching the pace of the automobile industry to manufacture vehicles with new engines with the supply of ethanol, pricing of such vehicles, the fuel efficiency of different engines, etc.
Ethanol Blending:
- It is one of the principal biofuels, which is naturally produced by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration.
- The Government of India has advanced the target for 20% ethanol blending in petrol (also called E20) to 2025 from 2030.
- Currently, 8.5% of ethanol is blended with petrol in India.
What Are Fast Radio Bursts?:

Researchers from the Pune-based Tata Institute for Fundamental Research (TIFR) and the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA), have assembled the largest collection of Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) catalogue.
- The data is from Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME).
- In 2020, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) spotted FRB for the first time in the Milky Way.
Fast Radio Bursts:
- FRB are bright bursts of radio waves (radio waves can be produced by astronomical objects with changing magnetic fields) whose durations lie in the millisecond-scale, because of which it is difficult to detect them and determine their position in the sky.
- It was first discovered in 2007.
- A defining property of these bursts is their dispersion (scattering or separation), the bursts produce a spectrum of radio waves, and as the waves travel through matter, they spread out or disperse with bursts at higher radio frequencies arriving at telescopes earlier than those at lower frequencies.
- Dispersion can result in signal degradation in many applications, especially over large distances.
- This dispersion allows researchers to learn about two important things:
- They can measure this dispersion to learn about the stuff that radio bursts pass through as they travel toward Earth
- They can indirectly determine how far apart things are.
The new catalogue significantly expands the current library of known FRBs, and is already yielding clues as to their properties.
- For instance, the newly discovered bursts appear to fall into two distinct classes: those that repeat, and those that don’t.
- The repeaters looked different, with each burst lasting slightly longer and emitting more focused radio frequencies than bursts from single, non-repeating FRBs.
- These differences strongly suggest that emission from repeaters and non-repeaters is generated either by different physical mechanisms or in different astrophysical environments
- The bursts were evenly distributed in space, seeming to arise from any and all parts of the sky.
- Bright FRBs occur at a rate of about 800 per day across the entire sky – the most precise estimate of FRBs overall rate to date.
Odisha Announced A Cash Award Of Rs. 1,000 To Conserve Gharials In Mahanadi River Basin.:

Gharials, sometimes called gavials, are a type of Asian crocodilian distinguished by their long, thin snouts. Crocodilians are a group of reptiles that includes crocodiles, alligators, caimans, and more.
- India has three species of Crocodilians namely:
- Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus): IUCN Red List- Critically Endangered
- Mugger crocodile (Crocodylus palustris): IUCN- Vulnerable.
- Saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus): IUCN- Least Concern.
- All the three are listed on Appendix I of CITES and Schedule I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Exception: Saltwater Crocodile populations of Australia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea are included in Appendix II of CITES.
- Habitat of Gharials:
- Natural Habitat: Freshwaters of the northern part of India.
- Primary Habitat: Chambal river (a tributary of Yamuna).
- Secondary Habitat: Ghagra, Gandak River, Girwa river (Uttar Pradesh), the Ramganga river (Uttarakhand) and the Sone river (Bihar).
- Significance: The population of Gharials are a good indicator of clean river water.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Breeding Centres of Kukrail Gharial Rehabilitation Centre in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, National Chambal Sanctuary (Gharial Eco Park, Madhya Pradesh).
- Threats:
- Increased river pollution, dam construction, massive-scale fishing operations and floods.
Illegal sand mining and poaching.
- Increased river pollution, dam construction, massive-scale fishing operations and floods.
Heritage Tree:

The Maharashtra Cabinet has passed an action plan to protect and preserve trees older than 50 years in urban areas by terming them heritage trees.
- Few important criteria for considering a tree as a “heritage tree” are: size, shape, rarity, aesthetical/historical values, association with historic person, place, or even myths.
- A certain species need not be native to an area for this tag.
- The provisions included in the plan are the concept of heritage trees and a plan of action for conservation, methods to define the age of the tree, rules to be followed before hacking trees, etc.
Compensatory Plantation:
- It will include planting the number of trees equivalent to the age of trees to be cut.
- The saplings need to be six to eight feet in height while planting and they will undergo geo-tagging with seven years of caring period.
- The option of monetary compensation has also been given, instead of the compensatory plantation.
- State-level Tree Authority: The authority will be formed to protect and preserve heritage trees.
- Tree Census: It will ensure that the tree census is conducted after every five years.
- Land Use: Ensuring that 33% of government land is used for tree plantation.
Global Liveability Index: EIU:

Auckland (New Zealand) has topped the Economist Intelligence Unit’s (EIU) Global Liveability Index of 140 cities around the world.
- Austria’s Vienna, number one in both 2018 and 2019, has completely dropped out of the top 10 after being heavily affected by Covid-19, and now ranks 12.
- Auckland rose to the top of the ranking owing to its successful approach in containing the Covid-19 pandemic, which allowed its society to remain open and the city to score strongly on a number of metrics including education, culture, and environment.
- Damascus remains the world’s least liveable city, as the effects of the civil war in Syria continue to take their toll.
- Most of the previous ten least liveable cities remain in the bottom ten this year, including Dhaka (Bangladesh) and Karachi (Pakistan) in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region.
- However, there is a strong contingent of cities in the APAC region at the top of the rankings, with Osaka, Adelaide, Tokyo and Wellington rounding out the top five.
- Apart from cities in New Zealand, Australia and Japan, other cities in the Asia-Pacific region such as Taipei (Taiwan) (33rd) and Singapore (34th) have also performed well.
Top 3 Liveable Cities:
- Auckland (New Zealand), Osaka (Japan), Adelaide (Australia).
Bottom 3 Liveable Cities:
- Damascus (Syria), Lagos (Nigeria), Port Moresby (Papua New Guinea).
About Global Liveability Index:
- The index takes into account more than 30 qualitative and quantitative factors spanning five broad categories: stability (25%), healthcare (20%), culture and environment (25%), education (10%), and infrastructure (20%).
- Due to the pandemic, the EIU added new indicators such as stress on healthcare resources as well as restrictions around local sporting events, theatres, music concerts, restaurants, and schools.
El Salvador First In The World To Adopt Bitcoin, As Legal Tender:

El Salvador, a small coastal country in Central America has become the first in the world to adopt Bitcoin, as legal tender.
- Legal tender is the legally recognized money within a given political jurisdiction.
Bitcoin:
- Introduced in 2009, it is a type of cryptocurrency that enables instant payments to anyone.
- Cryptocurrency is a specific type of virtual currency, which is decentralized and protected by cryptographic encryption techniques.
- Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple are a few notable examples of cryptocurrencies.
- Bitcoin is based on an open-source protocol and is not issued by any central authority.
- Originally, Bitcoin was intended to provide an alternative to fiat money and become a universally accepted medium of exchange directly between two involved parties.
- Fiat money is a government-issued currency that is not backed by a commodity such as gold.




