Today’s Current Affairs: 11th Nov 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Link Between Air Pollution And Parkinson’s Disease:
Scientists discovered a link between air pollution and Parkinson’s disease.
- Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves.
- Symptoms start slowly.
- The risk of developing it increases with age.
- Parkinson’s disease is often accompanied by these additional problems like:-
- Thinking difficulties
- Depression and emotional changes
- Swallowing problems
- Chewing and eating problems
- Sleep problems and sleep disorders
- People also may experience rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder, which involves acting out dreams. Medicines may improve your sleep.
- Treatments:- Although there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, medicines, surgical treatment, and other therapies can often relieve some symptoms.
- Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinson’s by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
- Therapy: the main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa.
Alcalus fontinalis : New Species Of Frog

Researchers have discovered a new species of frog, Alcalus fontinalis in the northeast Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh recently.
- The identification of the new species is based on molecular, morphological, and osteological characteristics.
- Alcalus fontinalis frog was formally named Alcalus fontinalis, meaning “spring or fountain,” referencing the tiny streams or brooks where the frog was found in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It was discovered in the Namdapha Tiger Reserve, Arunachal Pradesh.
- The new species stands out from its congeners due to a unique combination of morphological features.
- These include a snout-vent length of 27–28 mm in males and 29.9–36.2 mm in females.
- It has a disc on the fingers and toes with a horizontal/transverse groove on the dorsal surface.
- It has wrinkled dorsal skin.
- It has a pair of faint dorsolateral stripes on the back.
- The new species also exhibits a DNA sequence divergence of 7.6–25.4% in the mitochondrial gene fragment 12S–tVal–16S rRNA (1533 base pairs), further distinguishing it from its congeners.
- The frog appeared to be a mix of a bush frog and a water frog.
Awaous Motla : New Freshwater Fish Species

Researchers discover new freshwater fish species ‘Awaous Motla’ in Odisha’s Mahanadi River.
- A group of scientists has discovered that an edible freshwater fish, available in the markets of western Odisha, is actually an unregistered species.
- Awaous Motla species belongs to the family ‘Awaous’ (Oxudercidae), thus named Awaous motla and ‘motla’ by fishermen.
- The fish has a vibrant yellow-coloured body and a fleshy upper lip.
- It was Can be consumed both fresh and dried.
- It was discovered from the Mahanadi River.
- It is one of the major east-flowing peninsular rivers in India.
- The river originates from the Sihawa range of hills in the Dhamtari district of Chhattisgarh state.
INDUS-X Investors Meet:

The inaugural INDUS-X Investors Meet, organized by Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) and the US Department of Defence, preceded the 2+2 Indo-US Ministerial Dialogue.
- During the event, the INDUS-X Educational Series (Gurukul) was launched.
- The Gurukul initiative aims to guide innovators and startups within the defence ecosystems of both the US and India.
- The INDUS-X initiative, launched in June 2023, serves as a defence innovation bridge, fostering strategic partnerships, joint challenges, innovation funds, academia engagement, and industry-startup connections between India and the US.
- It is a major upcoming initiative under the Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET).
2023 Production Gap Report:

The 2023 Production Gap Report, authored by SEI (Stockholm Environment Institute), Climate Analytics, E3G, IISD, and UNEP, reveals a concerning trend where governments intend to produce approximately 110% more fossil fuels by 2030 than is consistent with limiting global warming to 1.5°C.
- Production Gap quantifies the difference between the projected extraction of coal, oil, and gas (fossil fuels) by governments and the global production levels required to meet climate goals, particularly those outlined in the Paris Agreement (warming to 1.5°C or 2°C)
- Findings: Major countries, including Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, India, and the UAE, are projected to increase global coal production by 2030 and oil and gas production until at least 2050.
Artificial Rain Project To Combat Delhi Pollution:

Delhi government has been considering artificial rain through cloud seeding as a measure to combat escalating pollution levels in the city.
- IIT-Kanpur has conducted pilot projects during monsoon months, and the focus is now on winter conditions.
- A minimum requirement of 40% cloud and moisture is necessary for cloud seeding.
- The potentially favorable conditions for artificial rain are projected on November 20 and 21, 2023.
- The project involves using silver iodide and other components for cloud seeding via aircraft.
- The effectiveness of artificial rain in reducing pollution levels depends on factors like moisture and rainfall.
Cloud Seeding:
- It is the process of artificially generating rain by implanting clouds with particles such as silver iodide crystals.
- Cloud seeding uses planes to spray clouds with chemicals to condense smaller particles into larger rain droplets.
- Methods:
- Static Cloud Seeding:
- This method involves introducing ice nuclei, such as silver iodide or dry ice, into cold clouds that have supercooled liquid water droplets.
- The ice nuclei can trigger the formation of ice crystals or snowflakes, which can grow at the expense of the liquid droplets and fall as precipitation.
- Dynamic Cloud Seeding:
- Dynamic cloud seeding is a method of inducing rain by boosting vertical air currents.
- The process is considered more complex than static cloud seeding because it depends on a sequence of events working properly.
- Hygroscopic Cloud Seeding:
- This method involves spraying fine particles of hygroscopic materials, such as salts through flares or explosives into the base of warm clouds.
- The particles can act as cloud condensation nuclei and increase the number and size of the cloud droplets, which can enhance the reflectivity and stability of the clouds.
- Static Cloud Seeding:
Composite Water Management Index:

The Composite Water Management Index (CWMI) has been a pivotal tool in India, serving as a significant barometer for assessing states’ efficacy in water management.
- However, recent developments have raised queries regarding its future, casting doubts on its continuity.
- The Composite Water Management Index (CWMI) is launched by NITI Aayog to provide an annual snapshot of the water sector status and water management performance of the states and union territories (UTs) in India.
- Launched in June 2018 by Niti Aayog, the CWMI’s debut edition spotlighted India’s water challenges, rating states based on 28 parameters, utilizing data from 2015-16 and 2016-17.
- The second edition launched in August 2019 was for 2017-18.
- The report was a result of collaborative efforts between NITI Aayog and three key ministries: Water Resources, Drinking Water & Sanitation, and Rural Development.
- The Index comprises nine themes (each having an attached weight) with 28 different indicators.
New Crustacean Family : New Discovery
Research conducted at the University of Kerala has led to the unprecedented discovery of a new crustacean family off the Indian coast.
- This is the first discovery and description of a new crustacean family from India.
- This parasitic copepod was found to depend upon the Dollfus’ Stargazer (Uranoscopus guttatus), a fish dwelling in depths ranging from 300-550 m off the southwest Indian coast.
- The discovery of the new family has also led to the creation of a new genus and species, Hirodai ohstukai under it.
- These parasitic copepods are known to infest a wide range of hosts, from sponges to marine mammals.
- New isopod species which has been named Glyptothoa sagara; ‘Glypto’ as the fish parasite was found in the deep sea fish Glyptophidium macropus, and ‘sagara’ for ocean.
- Another new isopod crustacean parasite species named Elthusa aquabio was collected from an unknown fish.
- The fourth new species is a 11-12 mm “flesh-penetrating parasitic copepod,” which has been named as Cardiodectes vampire.
- It was found to infest the deep-sea fish Chlorophthalmus corniger.
Crustaceans:
- These are members of the subphylum Crustacea (phylum Arthropoda),
- They are found in a wide range of habitats – most are free-living freshwater or marine animals, but some are terrestrial.
- They are invertebrates with a hard exoskeleton (carapace), a segmented body that is bilaterally symmetrical, more than four pairs of jointed appendages (“legs”) and an open circulatory system.
- Examples: Crabs, lobsters, shrimps, and wood lice etc.
Mount St Helens : More Than 400 Earthquakes Recorded

A report by the US Geological Survey (USGS) revealed that around 400 earthquakes have been recorded under Mount St Helens since mid-July this year.
- Mount St Helens is a volcanic peak in the Cascade Range of southwestern Washington, United States of America.
- It is part of the larger Pacific Ring of Fire.
- The volcano was formed during four eruptive stages beginning about 275,000 years ago and has been the most active volcano in the Cascade Range during the Holocene.
- Its eruption on May 18, 1980, was one of the greatest volcanic explosions ever recorded in North America.
Pacific Ring of Fire:
- It also known as the Circum-Pacific Beltis a path along the Pacific Ocean characterized by active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes.
- Its length is approximately 40,000 kilometres (24,900 miles).
- It traces boundaries between several tectonic plates—including the Pacific, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Indian-Australian, Nazca, North American, and Philippine Plates.
Radiative Cooling Paint:
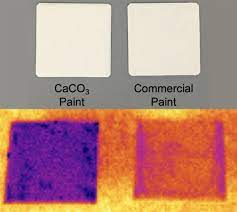
Researchers from Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) have developed a radiative cooling paint, which is specifically engineered to cool structures like buildings, pavers, and tiles in hot weather conditions.
- Radiative Cooling Paint is developed from a novel MgO-PVDF polymer nanocomposite.
- They used ultra-white and ultra-emissive magnesium oxide (MgO)-polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nano-composite prepared from materials that are earth abundant, cheap, non-toxic and non-harmful.
- The optimized MgO-PVDF with a dielectric nanoparticles resulted in large solar reflectance of 96.3% and a record high thermal emission of 98.5% due to Mg─O bond vibrations, and other stretching/bonding vibrations from the polymer.
- The researchers developed polymer nanocomposite paint by using a simple solution-processed technique.
- By measuring the temperature of the paint using a thermocouple, excellent cooling performance was demonstrated under hot sunlight.
- The nanocomposite paint exhibited water-resistant hydrophobic properties and can be easily coated on pavers, wood sticks and so on with high uniformity and good adhesion.
- The surface temperature of a treated paver decreases by approximately 10°C under intense sunlight– almost double of the reduction that conventional white paints give.
- This low-cost, solution-processed paint demonstrates significant cooling capabilities with a high solar reflectivity and infrared thermal emissivity.
4th Edition Of ISA Steel Conclave 2023:

The 4th edition of ‘ISA Steel Conclave 2023’ was held, nudging Steel Firms to ramp up their capacities so that India’s output of the critical infrastructure input doubles to 300 million tonnes a year by 2030.
- The event was marked by discussions on the theme, ‘Steel Shaping The Sustainable Future,’ underscoring the multifaceted role of the steel industry in India’s growth and development.
- India is the world’s second-largest producer of crude steel, with an output of 125.32 million tonnes (MT) of crude steel and 121.29 MT of finished steel production in FY23.
- The steel industry in India has experienced substantial growth in the past decade, with a 75% increase in production since 2008.
- The per-capita consumption of steel in India stood at 86.7 kilograms in FY23.
- The Indian steel industry has been driven by the availability of raw materials, such as iron ore, and cost-effective labor.
- As per the National Steel policy, launched in 2017, India projects crude steel capacity of 300 million tonnes (MT), production of 255 MT and a robust finished steel per capita consumption of 158 Kgs by 2030-31.




