Today’s Current Affairs: 13th January 2026 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
National Environmental Standard Laboratory:

The CSIR-National Physical Laboratory established the National Environmental Standard Laboratory (NESL).
- It was established to test and recalibrate instruments used for air pollution monitoring systems and environmental sensors under Indian environmental conditions.
- It provides ensured credible data for the National Clean Air Programme.
- Location: CSIR–National Physical Laboratory, New Delhi
- Features of National Environmental Standard Laboratory:
- NESL allowed manufacturers, industries, and municipal agencies to validate performance within the country,
- It provides Industrial emission audits, and smart-city monitoring networks, and provided reference gases, protocols.
- It is expected to help MSMEs, start-ups, and indigenous manufacturers to demonstrate product quality at lower cost, meet tightening regulatory guidelines on quality and transparency.
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) is a cutting edge R&D organisation dealing in diverse fields of science and technology.
- It undertakes research, design & development of scientific & industrial instruments, components and systems.
- It facilitates service, maintenance, testing & calibration of instruments.
- It promotes Human Resource Development in the area of instrumentation.
- It offers technical assistance to industry and provides ecosystem support.
- Headquarter: New Delhi.
Bannerghatta National Park:

The Central Empowered Committee recommended that the Ecologically Sensitive Zone (ESZ) around Bengaluru’s Bannerghatta National Park (BNP) should be restored to its original 2016 extent.
- It is in the hills of the Anekal range, near Bangalore, Karnataka.
- It was declared a National Park in 1974.
- In 2006, India’s first butterfly enclosure was inaugurated at the park.
- The Suvarnamukhi stream, the main source of water for the animals in the park, runs through the centre of the park.
- There are three types of vegetation that can be found: Dry Deciduous Scrub Forests, Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests and Southern Tropical Moist Mixed Forests.
- Include Narcissus latifolia, Schleichera oleosa, Sandalwood, Neem, Tamarind, Bamboo, Eucalyptus, etc.
- Prime habitat for several species, including the endangered Asian Elephant, Indian gaur, Tiger, Sambar deer, Spotted deer,Leopard, Wild dog, Wild pig, Sloth bear, Common mongoose, Pangolin, Slender loris, Black-naped hare, etc.
- Ecologically Sensitive Zone are created as “shock absorbers” for the protected areas, to minimize the negative impact on the “fragile ecosystems”.
- These zones are notified by the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Mustard Crop:

Mustard Crop increasingly susceptible to infestation by Orobanche aegyptiaca.
- It is a predominantly self-pollinating crop.
- Common Name: Sarason (Hindi), Rai (Punjabi), Katuku (Tamil), Kaduk (Malayalam), Avalu (Telugu).
Crop Season:Rabi season - Mustard seeds and its oil is used for culinary purpose. Young leaves are used for vegetable purpose. Its oil cake is used for feeding cattle.
- Sandy loam soil is the most ideal textural classification for the cultivation of mustard crop.
- Mustard thrives well in dry and chilled environmental conditions.
- It requires temperatures ranging between 10°C to 25°
- An annual rainfall between 625 to 1000 mm is suitable for cultivation of mustard crop.
- It is highly sensitive to frost damage.
- Major Mustard Production States: Rajasthan (largest producing state), Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Haryana, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh.
- Orobanche aegyptiaca is a parasitic weed that attaches to mustard roots and siphons off water and nutrients, leading to poor plant growth and reduced seed yields.
- This leads to wilting, yellowing, stunted plant growth and ultimately sharp declines in seed yields.
- This parasite remains hidden below the soil initially, damage is already extensive by the time it becomes visible.
Indian Customs Electronic Gateway: In News

The Special Secretary Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC) inaugurated Indian Customs Electronic Gateway–Land Port Management System (ICEGATE–LPMS) at the Integrated Check Post (ICP), at Agartala, Tripura.
- It is known as ICEGATE which was established in 2007.
- It is the national portal of Indian Customs of Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
- It provides e-filing services to the Trade, Cargo Carriers and other Trading Partners electronically.
- It serves as a centralized hub for all electronic interactions between Indian customs and the trading community.
- It is the main infrastructure for connecting trade users with the Indian government’s customs department, and acts as a hub for exchanging information between external trading partners involved in international trading.
- It is internally linked with multiple partner agencies including RBI, Banks, DGFT, DGCIS, Ministry of Steel, Directorate of Valuation and other various Partner Government Agencies involved in EXIM
- It collectively contributes to streamlining customs procedures, enhancing trade facilitation and promoting transparency and efficiency in cross – border trade activities in India by providing multiple features for its users.
- Integration of ICEGATE -Land Port Management System focuses on critical customs data elements, including Bill of Entry, Shipping Bill, Out of Charge (OOC), and Let Export Order (LEO).
- It enables real-time, bidirectional exchange of data between ICEGATE and the Land Port Management System, creating a seamless digital ecosystem at land ports.
- It also helps in early risk assessment, identification of anomalies, and selective application of controls.
- This approach improves compliance outcomes while minimising disruption to compliant trade.
Yemen:
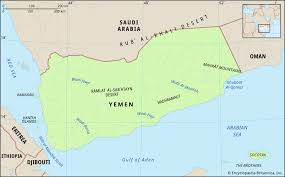
The Southern Transitional Council (STC) in Yemen announced a new Constitution for the “State of South Arabia”.
- It is situated at the south-western corner of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia.
- It shares Saudi Arabia (North) and Oman (East).
- Coastline & Strategic Importance: Red Sea (West), Gulf of Aden, Arabian Sea, and Guardafui Channel (South).
- Yemen is strategically located at the entrance of the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait. The strait links the Indian Ocean to the Red Sea via the Gulf of Aden.
- Capital City: Sanaa
- Geographical Features of Yemen
- It lies in the border zone between two main weather patterns: the regular northerly winds (from the Mediterranean basin) and the southwest monsoon winds.
- Desert: Rub’ Al Khali Desert.
Bhadrakali Inscription:

The Bhadrakali inscription is a key 12th-century record that confirms the history and development of Somnath Temple and patronage given by the Solanki dynasty.
- It is situated in Prabhas Patan, Gujarat specifically on the wall of the Bhadrakali Temple.
- It was carved in 1169 CE and currently protected by the State Department of Archaeology.
- It is a eulogistic inscription of Param Pashupata Acharya Shriman Bhavabrihaspati, the (spiritual preceptor of Maharajadhiraj Kumarapala of Anhilwad Patan).
- It mentions the construction of Somnath Temple in all four yugas.
- The historic Bhadrakali inscription reflects the devotion of the Solanki rulers and scholars like Bhavabrihaspati.
- Protection: State Department of Archaeology, Gujarat.
National Federation of Cooperative Sugar Factories Limited:

The National Cooperative Sugar Federation sought government intervention amid falling sugar prices.
- It was established in 1960 to build a strong and vibrant co-operative sugar sector in India.
- It is deemed to be under the Multi State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002.
- It participates in sugar policy formulation at national and state level and helps set agenda for the development and growth of the sector in India.
- It advocates, promotes and safeguards the collective interests of its members in accordance with the cooperative principles.
- It also offers Techno-commercial services to establish, expand and modernize sugar factories, within India and Overseas.
- It functions under the overall guidance of an elected Board of Directors, comprising of representatives of Cooperative Sugar Factories and State Sugar Federations across India.
Man Portable Anti-tank Guided Missile Weapon System:

The Defence Research and Development Organisation & Indian Army conducted successful trials of indigenous Man Portable Anti-tank Guided Missile Weapon System.
- It is indigenously designed and developed by Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The system consisted of the MPATGM, Launcher, Target Acquisition System, and the Fire Control Unit.
- It is the third-generation “fire and forget” missile
- It incorporates cutting-edge indigenous technologies, including:
- An Imaging Infrared (IIR) homing seeker, all-electric control actuation system, advanced fire control system, tandem warhead, propulsion system and a high-performance sighting system.
- The IIR seeker provides robust day-and-night operational capability.
- The tandem warhead is designed to defeat modern main battle tanks equipped with advanced armour protection.
- The missile can be launched from a tripod-mounted system as well as from a military vehicle-based launcher, enhancing its operational flexibility.
- Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) are the development-cum-production partners (DcPP) for the MPATGM.
World Hindi Day:
The Third Technical Hindi Symposium “Abhyuday-3” was organised with the collaboration of CSIR-National Institute of Science Communication and Policy Research, Indian Institute of Technology Indore, and Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur to promote Technical Hindi and inclusive science outreach.Abhyuday-3 reflected India’s push to expand science and technology outreach through Indian languages, especially Hindi, aligning with World Hindi Day’s goal of strengthening Hindi’s global and functional use.10th January is observed annually as World Hindi Day. It was on this day in 1975 that the first World Hindi Conference was held in Nagpur under the auspices of Rashtra Bhasha Prachar Samiti, Wardha (organization founded by Mahatma Gandhi).The official observance of World Hindi Day began in 2006, following its announcement by then Prime Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh, distinct from National Hindi Diwas celebrated on 14th September.It commemorates the adoption of Hindi in the Devanagari script as an official language of India by the Constituent Assembly in 1949.
Nipah Virus:
Two suspected Nipah virus infections among healthcare workers in West Bengal have triggered an urgent state and central public health response, highlighting India’s preparedness against high-risk zoonotic diseases.Nipah virus (NiV) is a highly infectious zoonotic virus, first identified in 1998–99 in Kampung Sungai Nipah, Malaysia. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is transmitted from animals to humans, with fruit bats (Pteropodidae) as the natural reservoir and pigs as intermediate hosts. The virus belongs to the Henipavirus genus of the Paramyxoviridae family. It has the potential for human-to-human transmission, making it a serious public health threat that requires rapid surveillance and containment. Nipah infection usually begins with influenza-like symptoms such as fever, muscle pain, sore throat, and respiratory distress. In severe cases, it can progress to acute encephalitis, leading to convulsions, disorientation, coma, and even death.Importantly, asymptomatic infections are also reported, complicating containment efforts. NiV is classified as a Biosafety Level-4 (BSL-4) pathogen, requiring testing in high-security laboratories.Diagnosis is confirmed using real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), ELISA, serum neutralisation tests, histopathology, and virus isolation techniques.There is no approved vaccine for Nipah virus in humans or animals.Treatment relies on intensive supportive care and isolation. India, particularly Kerala, has improved outcomes by using monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs such as Remdesivir, reducing mortality from 91% in 2018 to around 33% by 2023–25. India has witnessed Nipah outbreaks in West Bengal (2007) and Kerala (2018, 2023, and 2025), making early detection, contact tracing, and rapid medical response critical for public health preparedness.
Aadhaar Mascot Udai:
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has introduced ‘Udai’, a resident-friendly Aadhaar mascot, as a communication tool to make Aadhaar services more accessible and relatable to the public.It aims to simplify updates, authentication, offline verification, selective sharing of information, and responsible usage.Aadhaar is a 12-digit biometric identification number issued by the UIDAI, serving as a proof of identity and address for residents across India. It is not proof of citizenship or date of birth, and cannot be used to establish nationality.Aadhaar is issued by UIDAI, a statutory authority under the Aadhaar Act, 2016. Any individual, including foreign nationals, who has resided in India for 182 days or more in the 12 months before the enrolment application date is eligible, subject to submission of one of the 18 notified identity and address documents.




