Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:14th May 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc.
Contents:
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan: Economic Stimulus-I:
- West Bank.:
- Energy Transition Index: WEF:
- Direct Seeding of Rice’ (DSR)
- The inclusion of Taiwan in the World Health Organisation (WHO).:
- Other important current affairs:
1.Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan: Economic Stimulus-I:

Recently, the Union Finance Minister announced liquidity measures for businesses, especially Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), as part of the first tranche of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- This economic stimulus includes both liquidity financing measures and credit guarantees.
- Salaried Workers and Taxpayers:
- The deadline for income tax returns for the financial year 2019-20 has been extended, with the due date now pushed to November 30, 2020.
- The rates of Tax Deduction at Source (TDS) and Tax Collection at Source (TCS) have been cut by 25% for the FY 2020-21.
- The statutory Provident Fund (PF) payments have been reduced from 12% to 10% for both employers and employees for the next three months.
- NBFCs, Housing Finance Companies, and Microfinance Institutions:
- Many of these institutions serve the MSME sector financially and will be supported through an Rs.30,000 crore investment scheme fully guaranteed by the Centre.
- Further, an expanded partial credit guarantee scheme worth Rs.45,000 crores also has been offered, of which the first 20% of losses will be borne by the Centre.
- For instance, if the government provides a 100% credit guarantee up to an amount of Rs 1 crore to a firm, it means that a bank can lend Rs 1 crore to that firm; in case the firm fails to pay back, the government will repay all of Rs 1 crore. If this guarantee was for the first 20% of the loan, then the government would guarantee to pay back only Rs 20 lakh.
- Power Distribution Companies:
- These companies are facing an unprecedented cash flow crisis and thus will receive Rs. 90,000 crore liquidity injection.
- Real Estate and Contractors:
- Contractors (those dealing with the construction/ works and goods and services contracts) will get a six-month extension for completion of work from all Central agencies and also get partial bank guarantees to ease their cash flows.
- Registered real estate projects will get a six-month extension for registration and completion of Real Estate Projects under Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA) with Covid-19 to be treated as a “force majeure” event.
- A Force Majeure (FM) means extraordinary events or circumstances beyond human control such as an event described as an Act of God (as a natural calamity).
- Global Tenders to be Disallowed:
- Indian MSMEs and other companies have often faced unfair competition from foreign companies and would be difficult to compete in the future due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Therefore, global tenders will be disallowed in government procurement tenders up to Rs 200 crores.
Liquidity Measures for Medium, Small and Micro Enterprises (SMEs)
- New Definition of MSMEs:
- The definition of an MSMEs has been expanded to allow for higher investment limits and the introduction of turnover-based criteria.
- Earlier MSMEs were defined on the basis of the limit of investment in machinery or equipment.
- The ‘turnover’ is the more efficient way to identify an MSME as it allows a lot of firms, especially in the services sector like mid-sized hospitals, hotels, and diagnostic centers to be eligible for benefits as an MSME.
- There will be no difference between a manufacturing MSME and a services MSME.
- Infusion of Liquidity:
- Instead of directly infusing money into the economy or giving it directly to SMEs, the government will offer credit guarantees for SMEs.
- Emergency Credit Line:
- The collateral-free loans of worth Rs. 3 lakh crores will be available for MSMEs.
- It will ensure access to working capital to resume business activity and safeguard jobs for 45 lakh SMEs.
- The above measure is available for MSMEs that have an already outstanding loan of Rs. 25 crores or those with a turnover of less than Rs 100 crore.
- The loans will have a tenure of 4 years and they will have a moratorium of 12 months (that is, the payback starts only after 12 months).
- Subordinate Debt Scheme:
- The loans of amount Rs 20,000 crore will be provided to MSMEs that were already categorized as “stressed” or struggling to pay back.
- In this case, the government provides a partial guarantee.
- Equity Infusion:
- Fund of Funds with a corpus of Rs 10,000 crores will be set up which will provide equity funding for MSMEs with growth potential and viability.
2. West Bank.:
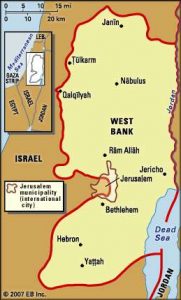
U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo recently met with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu in Jerusalem, where the two discussed Israel’s plans to annex parts of the West Bank.
- Their meeting took place during a day of violent clashes between Israeli troops and people in the occupied territory. One Palestinian teen was reportedly shot and killed.
West Bank:
- It is a landlocked territory near the Mediterranean coast of Western Asia, bordered by Jordan to the east and by the Green Line separating it and Israel on the south, west, and north.
- The West Bank also contains a significant section of the western Dead Sea shore.
- The West Bank was captured by Jordan after the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.
- Israel snatched it back during the Six-Day War of 1967 and has occupied it ever since. During this war, the country defeated the combined forces of Egypt, Syria, and Jordan.
- It has built some 130 formal settlements in the West Bank, and a similar number of smaller, informal settlements have mushroomed over the last 20-25 years.
- Over 4 lakh Israeli settlers many of them religious Zionists who claim a Biblical birthright over this land now live here, along with some 26 lakh Palestinians.
- The territory is still a point of contention due to a large number of Palestinians who live there and hope to see the land become a part of their future state.
- When Israel took control of the land in 1967 it allowed Jewish people to move in, but Palestinians consider the West Bank illegally occupied Palestinian land.
- The United Nations General Assembly, the UN Security Council, and the International Court of Justice have said that the West Bank settlements are violative of the Fourth Geneva Convention.
3.Energy Transition Index: WEF:

Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has released the annual rankings of the global Energy Transition Index.
The index benchmarks 115 economies on the current performance of their energy systems across economic development and growth, environmental sustainability and energy security and access indicators, and their readiness for transition to secure, sustainable, affordable, and inclusive energy systems.
Data Analysis:
- Sweden has topped the Index for the third consecutive year and is followed by Switzerland and Finland in the top three.
- France (8th) and the UK (7th) are the only G20 countries in the top ten.
- Only 11 out of 115 countries have made steady improvements in ETI scores since 2015. Argentina, China, India, and Italy are among the major countries with consistent annual improvements.
- In China (78th), problems of air pollution have resulted in policies to control emissions, electrify vehicles, and develop the world’s largest capacity for solar photovoltaic (SPV) and onshore wind power plants.
- Scores for the US, Canada, Brazil, and Australia were either stagnant or declining.
- The US ranks outside the top 25% for the first time, primarily due to the uncertain regulatory outlook for the energy transition.
Performance Analysis:
- The results for 2020 show that 75% of countries have improved their environmental sustainability.
- It is a result of multifaceted, incremental approaches, including pricing carbon, retiring coal plants ahead of schedule, and redesigning electricity markets to integrate renewable energy sources.
- Its study measuring readiness for the clean energy transition in 115 economies showed that 94 have made progress since 2015.
- The greatest overall progress is observed among emerging economies.
India’s Ranking:
- India has moved up two positions to rank 74th with improvements in all three dimensions of the energy triangle namely:
- Economic development and growth.
- Energy access and security.
- Environmental sustainability.
- For India, gains have come from a government-mandated renewable energy expansion program i.e. to add 275 GW by 2027.
- India has also made significant strides in energy efficiency through bulk procurement of LED bulbs, smart meters, and programs for the labeling of appliances.
- Similar measures are being experimented to drive down the costs of electric vehicles (EVs).
- It indicates a strong positive trajectory, driven by strong political commitment and an enabling policy environment.
4.‘Direct Seeding of Rice’ (DSR) :

Due to the labor shortage in two granary states of Punjab and Haryana, farmers are now being encouraged to adopt ‘Direct Seeding of Rice’ (DSR) in place of conventional transplanting.
- Covid-19 pandemic has led the laborers to reverse migrate to their villages, which has created a shortage of laborers.
- Normal Transplanting of Paddy vs Direct Seeding of Rice
Transplanting Paddy:
- In transplanting paddy, farmers prepare nurseries where the paddy seeds are first sown and raised into young plants.
- The nursery seedbed is 5-10% of the area to be transplanted.
- These seedlings are then uprooted and replanted 25-35 days later in the puddled field.
Direct Seeding of Rice (DSR):
- In DSR, the pre-germinated seeds are directly drilled into the field by a tractor-powered machine.
- There is no nursery preparation or transplantation involved in this method.
- Farmers have to only level their land and give one pre-sowing irrigation.
Protection against the weeds
Transplanting Method:
- In transplanting for the first three weeks or so, the plants have to be irrigated almost daily to maintain a water depth of 4-5 cm.
- Water prevents the growth of weeds by denying them oxygen in the submerged stage, whereas the soft ‘aerenchyma tissues’ in paddy plants allow air to penetrate through their roots. Water, thus, acts as a herbicide for paddy.
DSR Method:
- In DSR as flooding of fields is not done during sowing, chemical herbicides are used to kill weeds.
The advantage with Direct Seeding of Rice- Water savings.
- Fewer numbers of laborers required.
- Saves labor cost.
- Reduce methane emissions due to a shorter flooding period and decreased soil disturbance compared to transplanting rice seedlings.
5. The inclusion of Taiwan in the World Health Organisation (WHO).:

US lawmakers have written to over 60 nations to garner their support towards the inclusion of Taiwan in the World Health Organisation (WHO).
- These include Germany, Thailand, Canada, Britain, Saudi Arabia, and Australia.
- To this date, Taiwan is not a part of the WHO owing to objections from China which calls the nation a part of its own.
- However, that has not deterred Taiwan from seeking to join a ministerial meeting of WHO’s the decision-making body, the World Health Assembly (WHA).
- The meeting is set to be held in the coming days of this month.
- China has claimed Taiwan through its “one China” policy since the Chinese civil war forced the defeated Kuomintang, or Nationalist, to flee to the island in 1949 and has vowed to bring it under Beijing’s rule, by force if necessary.
- China is Taiwan’s top trading partner, with trade totaling $226 billion in 2018. Taiwan runs a large trade surplus with China.
- While Taiwan is self-governed and de facto independent, it has never formally declared independence from the mainland.
- Under the “one country, two systems” formula, Taiwan would have the right to run its own affairs; a similar arrangement is used in Hong Kong.
- Taiwan is a member of the World Trade Organization, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, and Asian Development Bank under various names.
Other important current affairs:
1. Recently, the Army has proposed 3 years of voluntary Tour of Duty (ToD) for civilians on a trial basis.
- The Army plans to take civilians on a three- year ‘Tour of Duty’ (ToD) or ‘Three-year Short Service’ on a trial basis to serve in the force as both officers and Other Ranks (ORs).
- The proposal suggests several measures to incentivize this scheme like a tax-free income for three years and a token lump sum at the end of three years of about Rs.5-6 lakh for officers and Rs.2-3 lakh for ORs.
- However, there will be no severance packages, resettlement courses, professional encashment training leave, ex-Servicemen status, ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS) for the ToD officers and other ranks.
- The proposal is a shift from the concept of permanent service/job in the Armed Forces, towards internship/temporary experience for three years.
- If approved it will be a voluntary engagement and there will be no dilution in selection criteria.
- The Army hopes that this would attract individuals from the best colleges, including the Indian Institute of Technology.
2. The Department of Science and Technology has helped in developing various assistive tools, devices and technological solutions to mitigate the impact of Covid-19 among Divyangjan and Elderly through a program on Technology Interventions for Disabled and Elderly (TIDE).
- Technology Interventions for Disabled and Elderly (TIDE):
- It is the Department of Science and Technology’s (DST) focused initiative on Science and Technology (S&T) interventions for the benefit of the elderly and also the differently-abled Divyangjan persons in the country.
- In addition to improving the quality-of-life of the target population with appropriate and/or innovative scientific-technological interventions, TIDE also aims at giving them autonomy, and independence through holistic development by creating requisite enabling environments for their empowerment.
- Proposals on Research and Development for technological solutions with a multidisciplinary approach to improving the quality of life of the Elderly population and Divyangjan and in making them self sufficient are considered for financial assistance under this program.
3. Recently, the Ministry of Tourism organized a webinar- ‘Exploring River Nila’ as a part of the Dekho Apna Desh Webinar series.
- River Nila is also known as Bharathapuzha and Ponnani.
- Origin: Amaravathipuzha originating from Thrimoorthy Hills of Anamalais in Tamil Nadu joins with Kalpathipuzha at Parali in Palakkad District and forms Nila.
- Drainage Area: Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- It flows westward through Palakkad Gap (most prominent discontinuity in the western ghats) and drains into the Arabian Sea.
- Main Tributaries: Kannadipuzha (Chitturpuzha), Kalpathipuzha (Korapuzha), Gayathripuzha and Thuthapuzha
- Malampuzha Dam is the largest among the reservoirs built across Bharathapuzha.




