Today’s Current Affairs: 16th March 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Right Of Children To Free And Compulsory Education Act, 2009

The Delhi High Court recently disposed of a plea seeking direction to the Bar Council of India (BCI) to make the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act) a compulsory subject in all law schools.
- The Constitution (Eighty-sixth Amendment) Act, 2002 inserted Article 21-A in the Constitution of India to provide free and compulsory education of all children in the age group of six to fourteen years as a Fundamental Right.
- RTE Act is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted on 4 August 2009 as envisaged under Article 21-A.
- Main Features of the RTE Act:
- Free and compulsory education to all children of India in the 6 to 14 age group.
- It clarifies that ‘compulsory education’ means the obligation of the appropriate government to provide free elementary education and ensure compulsory admission, attendance, and completion of elementary education to every child in the six to fourteen age group.
- No child shall be held back, expelled, or required to pass a board examination until the completion of elementary education.
- It makes provisions for a non-admitted child to be admitted to an age-appropriate class.
- It specifies the duties and responsibilities of appropriate Governments, local authorities, and parents in providing free and compulsory education and sharing of financial and other responsibilities between the Central and State Governments.
- It lays down the norms and standards relating inter alia to Pupil Teacher Ratios (PTRs), buildings and infrastructure, school-working days, and teacher-working hours.
- It provides for the appointment of appropriately trained teachers, i.e., teachers with the requisite entry and academic qualifications.
- It prohibits physical punishment and mental harassment, screening procedures for admission of children, capitation fee, private tuition by teachers, and running of schools without recognition.
- It provides for the development of a curriculum in consonance with the values enshrined in the Constitution.
MQ 9 Reaper Drone : Crashed Into Black Sea

An MQ-9 Reaper drone belonging to the United States Air Force recently crashed into the Black Sea due to collision with a Russian Su-27 jet fighter.
- MQ 9 Reaper also known as Predator B, is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) capable of remotely controlled or autonomous flight operations.
- It is developed by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI), primarily for the United States Air Force (USAF).
- It is remotely operated by a two-person team consisting of a pilot and an aircrew member who operates sensors and guides weapons.
- The US uses the MQ-9 Reaper for both surveillance and strikes.
- It is 11 metres long with a wingspan of over 22 metres.
- Reapers can be armed with air-to-ground Hellfire missiles as well as laser-guided bombs.
- It carry as many as 16 Hellfire missiles, equivalent to the payload capacity of an Apache helicopter.
- It can fly at an altitude of 50,000 ft (15 km) and can loiter over targets for for over 27 hours.
Eurasian Otter : Spotted

Three Eurasian Otters were recently spotted in the Neeru stream of the Chenab catchment in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Eurasian Otter is a semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal.
- Scientific Name: Lutra lutra
- It has one of the widest distributions of all Palaearctic mammals.
- Its range covers parts of three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- In India, it occurs in northern, northeast, and southern India.
- It lives in a wide variety of aquatic habitats, including highland and lowland lakes, rivers, streams, marshes, swamp forests, and coastal areas.
- In the Indian sub-continent, Eurasian otters occur in cold hill and mountain streams.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Near threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule II
- CITES: Appendix I
LCA Tejas:

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully conducted a maiden flight test of the Power Take off (PTO) Shaft on Light Combat Aircraft (LCA Tejas) Limited Series Production (LSP) -3 aircraft in Bengaluru.
- LCA Tejas is the lightest, smallest and tailless multi-role supersonic fighter aircraft in its class.
- This aircraft is designed to carry a range of air-to-air, air-to-surface, precision-guided, weapons.
- It has the air-to-air refuelling capability.
- The maximum payload capacity of Tejas is 4000 kg.
- Speed: Mach 1.8.
Power Take off (PTO) shaft:
- It is indigenously designed and developed by the Combat Vehicles Research & Development Establishment (CVRDE), Chennai of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It was designed with a unique innovative patented ‘Frequency Spanning Technique’ which enables it to negotiate different operating engine speeds.
- The lightweight high-speed, lubrication-free PTO shaft transmits higher power between the aircraft engine gearbox and Aircraft Mounted Accessory Gear Box while accommodating misalignments that arise in the drive line.
13th Edition Exercise Bold Kurukshetra:

The Singapore Army and Indian Army participated in Exercise Bold Kurukshetra which was held at Jodhpur Military Station, India.
- 13th edition of Exercise Bold Kurukshetra, a bilateral military exercise between India and the Singapore army.
- For the first time in the exercise series, both armies participated in a command post Exercise, which involved Battalion and Brigade level planning elements and computer wargaming.
- Hosted by the Indian Army, the exercise involved soldiers from the 42nd Battalion, Singapore Armoured Regiment and an Armoured Brigade of the Indian Army.
- It involved an understanding of mechanised warfare in emerging threats and evolving technologies, developing inter-operability through a computer simulation-based Wargame using joint operational and tactical procedures controlled through a joint command post.
- First conducted in 2005, this exercise underscores the strong and long-standing bilateral defence relationship between both countries and enhances cooperation between the two armies.
- Both defence establishments also interact regularly through high-level visits, policy dialogues, courses and other professional exchanges.
ATL Sarthi : NITI Aayog

NITI Aayog recently launched ATL Sarthi, a comprehensive self-monitoring framework to strengthen the ever-growing ecosystem of Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL).
- ATL Sarthi will enable the Atal Tinkering Labs to be efficient and effective.
- The initiative has four pillars ensuring the performance enhancement of ATLs through regular process improvements like
- MyATL Dashboard: It is a self-reporting dashboard.
- Compliance SOPs: For schools to ensure financial and non-financial compliance
- Cluster-based Approach: On-ground enablement of ATLs in collaboration with relevant local authorities.
- Performance-Enablement (PE) Matrix: It provides ownership to schools to analyze their performance
Atal Innovation Mission:
- It was set up by the Central Government in 2016.
- Objectives:
- To promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in the country.
- To provide a platform for and establish collaboration opportunities for various stakeholders.
- To act as an umbrella structure, encompassing and overseeing the entire innovation ecosystem of the country.
- Implementing Agency: NITI Aayog
India’s First Indigenous Quadruped Robot And Exoskeleton:

Hyderabad-based Svaya Robotics has developed India’s first indigenous quadruped (four-legged) robot and exoskeleton for the defense sector as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- The indigenous robots and wearable exoskeletons were developed by Hyderabad-based Svaya Robotics in collaboration with the DRDO Labs, Research and Development Establishment (R&DE), Pune, and the Defence Bioengineering and Electromedical Laboratory (DEBEL), Bengaluru, as technology demonstrators with their design inputs.
- Both are dual-use robots and have multiple use cases in both Industry and healthcare.
- Quadruped robots are four-legged robots that can walk or run on uneven and rough terrains.
- The robots can carry 25 kg in payload and walk along with the soldier.
- It is made for navigating in unstructured terrains to provide remote reconnaissance and inspection, which otherwise are not safe for humans to operate in.
- Exoskeleton is developed to suit Indian soldiers’ anthropometry and augment soldier strength for walking long distances.
- These active exoskeletons, when worn by soldiers, can carry heavy loads without expending much effort.
Ground Station Of India-Bhutan Satellite : Inaugurated

The ground station of the India-Bhutan Satellite, which has been built in Thimpu, was recently inaugurated.
- India-Bhutan Satellite is also known as the ISRO Nano Satellite 2 for Bhutan (INS-2B).
- It was launched as a payload on ISRO’s PSLV C54 rocket on November 26, 2022.
- It has been jointly developed by scientists from both countries.
- The satellite contains two payloads:
- NanoMx multispectral optical imager: It is developed by India’s Space Applications Centre (SAC). It will provide high-resolution images to Bhutan for its natural resources management.
- Automatic Packet Reporting System (APRS) repeater: It is jointly developed by Department of Information Technology and Telecom (DITT) Bhutan and ISRO’s UR Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) to serve the amateur radio community, relaying realtime information about the region.
Prussian Blue Insoluble Formulations Drug:

A critical drug, ‘prussian blue’ insoluble formulations developed on a Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) technology recently received approval from the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI).
- Prussian blue insoluble formulations is one of the critical medicines listed by the World Health Organisation for radiological and nuclear emergencies.
- It was developed under the Technology Development Fund (TDF).
- Technology Development Fund has been established to promote self-reliance in defense technology as a part of the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
- The drug has been developed based on the technology of the Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Allied Sciences (INMAS), Delhi, a laboratory of the DRDO.
- The formulations are used for the decontamination of Cesium and Thallium.
- The manufacturing and marketing licenses for the commercial use of the drug have been granted to Scott-Edil Pharmacia Limited, Himachal Pradesh, and Skanttr Lifescience, Gujarat, by DCGI.
- The drug will be available under the trade name of Pru-DecorpTM and PruDecorp-MG.
Same Sex Marriage : Centre Opposed

The Centre has opposed same-sex marriage in the Supreme Court, stating that marriage between a biological man and woman is a holy union, a sacrament, and a sanskar in India.
- A Bench led by Chief Justice of India refers petitions to legally recognise same-sex marriages to a Constitution Bench of five judges of the Supreme Court
- The government argued that the Court had only decriminalised sexual intercourse between same-sex persons in its 2018 judgement in Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India, and not legitimised this “conduct”.
- The court, while decriminalising homosexuality, did not accept same-sex marriage as part of the fundamental right to life and dignity under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- The government argues that marriage depends on customs, rituals, practices, cultural ethos, and societal values.
- Same-sex marriage cannot be compared to a man and woman living as a family with children born out of the union.
- The Parliament has designed and framed the marriage laws in the country to recognise only the union of a man and a woman.
- Registration of marriage of same-sex persons would result in a violation of existing personal as well as codified law provisions.
- The Special Marriage Act of 1954 provides a civil form of marriage for couples who cannot marry under their personal law.
- The government argued that any deviation from this norm can only be made through the legislature, and not the Supreme Court.
World Air Quality Report 2022:

According to the World Air Quality Report prepared by IQAir, Delhi ranked 4th out of 50 of the world’s most polluted cities in terms of PM2.5 levels in 2022.
- Out of 131 countries, India ranked 8th with a population weighted average PM2.5 level of 53.3 μg/m3 in 2022.
Key Findings of the Report:
- IQAir, a Swiss air quality technology company, prepares the annual world air quality reports based on data from monitoring stations operated by governments and other institutions and organisations across the world.
- The 2022 report is based on PM2.5 data from 7,323 cities and 131 countries.
- Chad, Iraq, Pakistan, Bahrain, Bangladesh are the 5 most polluted countries in 2022.
- Delhi had an average PM2.5 level of 92.6 μg/m3 in 2022, a little below the average of 96.4 μg/m3 in 2021.
- The report makes a distinction between New Delhi and Delhi, with New Delhi having an annual average PM2.5 level of 89.1 μg/m3.
- The WHO guideline for annual PM2.5 levels is 5 μg/m3.
- Lahore was the most polluted city in the world, followed by Hotan in China, and Bhiwadi in Rajasthan.
- New Delhi is the second most polluted capital city in the world, with N’Djamena in Chad topping the list.
- A total of 39 Indian cities (including ‘Delhi’ and ‘New Delhi’) are on the list of 50 of the world’s most polluted cities based on annual average PM2.5 levels in 2022.
Carbon Footprint Of Marine Fisheries : Lower Than Global Average

According to Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), India’s marine fisheries produced 1.32 tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce one kilogram of fish in 2016 during entire value chain (from the construction of boats to retail) lower than the global average of 2 tonnes.
- The findings were discussed at a review meeting of the fisheries component of the National Innovations in Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA), a research project launched in 2011.
- Active fishing consumes more than 90% of the fuel used in the sector, contributing 4,934 million kilograms of CO2 emissions annually.
- The country’s carbon emissions from the marine mechanized fisheries sector is 16.3%, lower than the global level.
- While the use of fossil fuels has increased the availability of fish to fisheries, the dependence of the fishing sector on fossil fuels raises concerns related to climate change.
- The carbon footprint from Indian marine fisheries is smaller because they depend largely on human force.
- Large mechanised fishing boats were introduced in India in the late 1950s, but the fleet size is growing. Their number increased to 72,559 in 2010 from 6,708 in 1961.
Survey Of Vultures:

There are 246 vultures spread across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Kerala, according to the first-ever synchronised census on the bird carried out in February 2023.
- The survey was conducted by the Kerala Forest and Wildlife department along with its counterparts in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka in the select regions of the Western Ghats.
- The survey was carried out in the Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (MTR) and the adjoining landscape consisting of Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve (STR) in Tamil Nadu, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (WWS) in Kerala, Bandipur Tiger Reserve (BTR) and Nagerhole Tiger Reserve (NTR) in Karnataka.
- A total of 98 vultures were seen in MTR, two in STR, 52 in WWS, 73 in BTR, and 23 in NTR.
- Volunteers sighted White-rumped vultures (183), Long-billed vultures (30), Red-headed vultures (28), Egyptian vultures (3), Himalayan Griffon (1), and Cinereous vultures (1).
- Vultures are witnessing a catastrophic decline from the 2000s as these species are being exposed to diclofenac drug which is mainly used as a painkiller for cattle and experts believe that increasing wild carcass availability was one of the major steps needed to help vultures thrive.
Vultures:
- It is one of the 22 species of large carrion-eating birds that live predominantly in the tropics and subtropics.
- They act an important function as nature’s garbage collectors and help to keep the environment clean of waste.
- Vultures also play a valuable role in keeping wildlife diseases in check.
- India is home to 9 species of Vulture namely the Oriental white-backed, Long-billed, Slender-billed, Himalayan, Red-headed, Egyptian, Bearded, Cinereous and the Eurasian Griffon.
Missing Antiquities In India : ASI

According to an RTI, only 486 antiquities have been reported as missing (since Independence) from the 3,696 monuments protected and maintained by the ASI.
- According to ASI, 292 antiquities have been brought back to India from abroad since 2014 and 13 between 1976 and 2013.
- The ASI’s list of missing antiquities covers 17 states and two Union Territories.
- It includes 139 from Madhya Pradesh, 95 from Rajasthan and 86 from Uttar Pradesh.
- The Antiquities and Art Treasures Act of 1972, which came into effect on April 1, 1976, defines an “antiquity” as any object or work of art that has been in existence for at least 100 years.
- This includes coins, sculptures, paintings, epigraphs, detached articles, and other items that reflect science, art, literature, religion, customs, morals, or politics from a bygone era.
- For “manuscript, record or other document which is of scientific, historical, literary or aesthetic value”, this duration is “not less than 75 years.”
Learning Science Via Standards : Bureau Of Indian Standards

The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), has launched ‘Learning Science via Standards’, a unique initiative for students.
- Learning Science via Standards focuses on a series of lesson plans aimed to use scientific concepts, principles and laws to help students understand their practical applications in manufacturing, functioning and testing of quality characteristics of different products as stated in the relevant Indian Standards.
- The series is in a continuum with an earlier BIS initiative under which ‘Standards Clubs’ are being established in educational institutions across India.
- Benefits:
- Bridges the gap between theory and real-life usage of science education.
- Contributes towards the capacity building to successfully engage in a variety of economic sectors in the country.
Lightning Be Declared a Natural Disaster:

Recently few States have demanded that “lightning” be declared as a “natural disaster” because deaths caused by it surpass any other disaster in India.
- Presently Cyclone, drought, earthquake, fire, flood, tsunami, hailstorm, landslide, avalanche, cloudburst, pest attack, frost, and cold waves are covered under the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) which is 75% funded by the Centre.
- According to a newly published yearly report on lightning from the Lightning Resilient India Campaign (LRIC), India may have seen up to 18.5 million lightning strikes between April 2020 and March 2021.
- Each year, lightning claims the lives of more than 2,500 Indians.
- Madhya Pradesh had the highest number of lightning-related deaths (162), followed by Maharashtra (121), Gujarat (72), Bihar (70), Rajasthan (49), and Chhattisgarh (40).
- India has experienced 90,632 deaths due to lightning strikes between 1972 and 2019.
- The Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2021 report confirms that 40.4% of deaths due to natural disasters took place due to lightning.
- 77% of farmers are killed due to lightning as they work in agricultural fields during the Kharif cropping season in the monsoon period.
Lightening :
- It is the natural process of “an electrical discharge of very little duration and high voltage between a cloud and the ground or within a cloud,” accompanied by a bright flash, a loud sound, and occasionally thunderstorms.
McMahon Line:
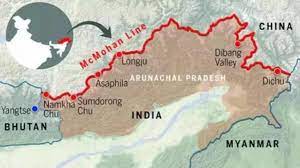
A recent bipartisan Senate resolution in the United States recognizes the McMahon Line as the international boundary between China and Arunachal Pradesh.
- McMahon Line is a geographical border between Northeast India and Tibet.
- It is the boundary between China and India, although its legal status is disputed by the Chinese
- It was negotiated between Tibet and Great Britain at the end of the Shimla Conference in 1914.
- It is named after Henry McMahon, who was the foreign secretary of British India and the chief negotiator of the convention at Simla.
- The length of this boundary is 890 kilometers.
- It runs from the eastern border of Bhutanalong the crest of the Himalayas until it reaches the great bend in the Brahmaputra River, where that river emerges from its Tibetan course into the Assam Valley.
- Though India considers the McMahon Line as the legal national border, China rejects it, contending that Tibet was not a sovereign state and therefore did not have the power to conclude treaties.




