Today Current Affairs: 18th April 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Tanzania’s First Woman President : Samia Suluhu Hassan

Samia Suluhu Hassan is a member of the Chama Cha Mapinduzi (CCM) party that is currently ruling the country. She is Tanzania’s first female president.
- She is the third woman head of government of a country in the East African Community.
- The other two female heads of government are Agathe Uwilingiyimana in Rwanda and Sylvie Kinigi in Burundi.
- On 19th March 2021 she took office after President John Magufuli’s death on 17th March 2021.
- In the year 2000, she decided to run for public office and was elected as a member of the Zanzibar House of Representatives and President Amani Karume appointed her as a minister.
- At that time, she was the only high-ranking female minister and her male colleagues looked down upon her.
- In 2005 she was re-elected and was re-appointed as a minister in another portfolio of the cabinet.
- In the year 2010, she sought election to the National Assembly, won by over 80 per cent of the votes and was then appointed by President Jakaya Kikwete as the Minister of State for Union Affairs.
- In the year 2014, she was elected as the constituent assembly’s Vice-Chairperson and was tasked with drafting Tanzania’s new constitution.
- In 2015, for the 2015 election, John Magufuli, the presidential nominee of CCM chose her as his running mate thus making her the first female running mate in the history of the party.
- On 5th November 2015, she became the country’s first female vice-president after Magufuli’s victory.
- In 2020, they were both re-elected for a second five-year term.
Oil Bonds:

The government issues oil bonds to compensate the oil marketing companies (OMCs) to offset the losses that are suffered by them with the aim of shielding consumers from rising crude oil prices. These bonds were issued by the government mainly from 2005 to 2010.
- Nirmala Sitharaman, Finance Minister had said that the central government is paying off dues to the OMCs for the oil bonds that were issued during the Manmohan Singh-led UPA government and this is factoring into the rising price of diesel and petrol.
- In lieu of cash, these bonds were issued to the OMCs at a time when the government of India used to fix diesel and petrol prices.
- The prices of diesel and petrol were fixed by the central government so that the price shocks of costly international crude oil do not spill over to the consumers.
- For example, if the price of crude oil was high, the oil marketing and refining companies would sell diesel and petrol at a loss to the retail outlets.
- However, the central government compensated the oil companies by issuing long-term bonds that could be redeemed by the companies at a later date, typically ranging from 15 to 20 years.
- Due to the recession in 2008 and high crude prices, the fiduciary pressure on the central government increased.
- By raising capital through the issuance of these bonds, payments could be made in installments without causing major price escalations, thus shielding the customers.
- The oil bonds are promissory notes for the government’s deferred payment of subsidies owed to oil marketing companies.
- Because the government did not subsidize these companies upfront, these payments did not appear in budget documents until the principal or interest components were repaid.
- These off-budget items are also referred to as under-recoveries of oil companies did not show up in the fiscal deficit numbers that are disclosed during the annual budget of the country.
- Only after the repayment of the interest and the principal started to take place, years after the bonds were issued, they were factored by the fiscal deficit.
Black Sea And Russia:
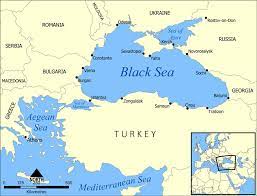
The sinking of the warship Moskva, the 600-foot, 12,500-tonne flagship of the Russian Black Sea Fleet — whether due to a Ukrainian missile strike or, as Russia claims, a fire on board — is a serious setback for Russia.
- The Black Sea, also known as the Euxine Sea, is one of the major water bodies and a famous inland sea of the world.
- This marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, located between Eastern Europe and Western Asia.
- It is surrounded by the Pontic, Caucasus, and Crimean Mountains in the south, east and north respectively.
- The Turkish straits system – the Dardanelles, Bosporus and Marmara Sea – forms a transitional zone between the Mediterranean and the Black Sea.
- The Black Sea is also connected to the Sea of Azov by the Strait of Kerch.
- The bordering countries of Black Sea are: Russia, Ukraine, Georgia, Turkey, Bulgaria and Romania.
National Data And Analytics Platform:

The NITI Aayog is planning to launch a National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP) in May to provide government data in a user-friendly format, to promote data-driven decision making and research.
- Started in 2020, the platform aims to standardise data across government sources and provide flexible analytics that make it easy for users to analyse information using multiple datasets.
- The portal will help policymakers, academics and researchers to easily analyse data without having to process it.
- The portal will have 200 datasets from more than 46 ministries at the time of the launch.
- New datasets will be added up to the village level in the future.
- Presently, many government departments have public dashboards with options to download data, some are available as image files while others are in PDF format, making it difficult to compile information.
- Experts say this will be addressed in NDAP.
Poverty In India : Status

According to policy research working paper of World Bank, Poverty in India is 12.3 percentage points lower in 2019 as compared to 2011.
- The poverty headcount rate has declined from 22.5 percent in 2011 to 10.2 percent in 2019.
- Poverty reduction was higher in rural areas as compared to urban India.
- Rural poverty dropped by 14.7 percent while urban poverty declined by 7.9 percentage points during 2011 to 2019.
- Farmers with small landholding sizes have experienced higher income growth.
- Real incomes for farmers with the smallest landholdings have grown by 10 percent in annualized terms between the two survey rounds in 2013 and 2019 compared to a 2 percent growth for farmers with the largest landholding.
Rural Inflation:

Official data pegs rural inflation in March at 7.66%, with several States reporting even higher inflation, including West Bengal (8.85%), Uttar Pradesh and Assam (8.19%) as well as Madhya Pradesh (7.89%).
- Urban inflation has usually tended to be higher than rural inflation by an average of about 0.8 percentage points through most of 2021 — the only exceptions being August when both stood at 5.3% and May when rural inflation was 6.6% and urban inflation was 5.9%.
- In March, the gap between the two has surpassed 1.5% with urban inflation at 6.12% and rural areas clocking 7.66%.
- While food inflation was the key driver for the headline inflation rate jump in March, with the overall consumer food price index racing to 7.68% from 5.85% in February, the spike was far more pronounced in rural India where food inflation hit 8.04%.
- While high inflation affects the poor the most in general, the fact that price rise in food, the largest component of their consumption basket, is driving the current surge is particularly burdensome.
Integrated Child Development Scheme:

The Maharashtra government has developed a Migration Tracking System (MTS) application to map the movement of migrant workers to maintain the continuity of the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) like nutrition supply, immunisation and health check-up etc.
- MTS is a website based Application that tracks the movement of Vulnerable Seasonal Migrant Workers, through individual unique identity numbers.
- Migrant beneficiaries including children aged up to 18 years, lactating mothers and pregnant women registered with the anganwadi centres will be tracked for ensuring the portability of the ICDS for their families in their destination districts within or outside the state until their return to their native places.
ICDS:
- The Umbrella ICDS is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- It was launched in 1975.
Schemes Under the ICDS
- Anganwadi Services Scheme: It is a unique programme for early childhood care and development.
- The beneficiaries under the Scheme are children in the age group of 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- It provides a package of six services namely supplementary nutrition, pre-school non-formal education, nutrition & health education, immunisation, health check-up and referral services.
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana: It provides cash incentive amounting to Rs.5,000/- in three instalments directly to the Bank/Post Office Account of Pregnant Women and Lactating Mother (PW&LM) in DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer) Mode during pregnancy and lactation in response to individual fulfilling specific conditions.
- National Creche Scheme: It provides day care facilities to children of age group of 6 months to 6 years of working women.
- The facilities are provided for seven and half hours a day for 26 days in a month.
- Children are provided with supplementary nutrition, early childcare education, and health and sleeping facilities.
- Scheme for Adolescent Girls: It aims at out of school girls in the age group 11-14, to empower and improve their social status through nutrition, life skills and home skills.
- The scheme has nutritional and non nutritional components which include nutrition; iron and folic acid supplementation; health check up and referral service; nutrition and health education; mainstreaming out of school girls to join formal schooling bridge course/ skill training; life skill education, home management etc,; counselling/ guidance on accessing public services.
- Child Protection Scheme: It aims to contribute to the improvement and well-being of children in difficult circumstances, as well as, reduction of vulnerabilities to situations and actions that lead to abuse, neglect, exploitation, abandonment and separation of children from parents.
- POSHAN Abhiyaan: It targets to reduce the level of stunting, under-nutrition, anaemia and low birth weight babies by reducing mal-nutrition/undernutrition, anaemia among young children as also, focus on adolescent girls, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
What Is The Indigenisation Of Defence?

The Navy is ramping up indigenisation efforts especially in weapons and aviation related items in line with the Government’s push to cut down on defence imports and boost domestic manufacturing.
- Indigenisation efforts has gained further urgency due to ingoing Russian war in Ukraine and the large scale dependency of Indian military on Russian arms and equipment.
- Earlier, the Ministry of Defence (MoD) has released the third positive indigenisation list of 101 items, comprising major equipment/platforms.
- The Navy has now forward deployed user inputs through Naval Project Management Teams at cluster Headquarters of DRDO and two such clusters are already operational.
- These have interfaced with the DRDO labs and their Development cum Production Partners (DcPP) to provide user inputs at every stage to 15 futuristic Technology and 100 plus DRDO projects underway for development of Indian Navy’s combat capability.
- The Navy has more than 20 Make I & Make II cases being progressed, under various domestic development routes of the procurement procedure.
- The ‘Make’ category of capital acquisition is the cornerstone of the Make in India initiative that seeks to build indigenous capabilities through the involvement of both public and private sector.
- ‘Make-I’ refers to government-funded projects while ‘Make-II’ covers industry-funded programmes.
- Make-I is involved in development of big-ticket platforms such as light tanks and communication equipment with Indian security protocols.
- Make-II category involves prototype development of military hardware or its upgrade for import substitution for which no government funding is provided.
Indigenisation of Defence:
- Indigenisation is the capability of developing and producing any defence equipment within the country for the dual purpose of achieving self reliance and reducing the burden of imports.
- Self-reliance in defence manufacturing is one of the key objectives of Department of Defence Production.
- Defence Research Development Organisation (DRDO), Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs) and private organisations are playing a critical role in indigenisation of defence industries.
- India is among the world’s largest arms importers, and the armed forces are expected to spend about USD 130 billion on defence purchases over the next five years.
e-DAR Portal:
The Ministry of Roads, Transport and Highways (MoRTH) developed the portal named ‘e-DAR’ (e-Detailed Accident Report).
- The portal provides instant information on road accidents and helps accelerate accident compensation claims, bringing relief to victims’ families.
- Road safety continues to be a major developmental issue, a public health concern and a leading cause of death and injury across the world.
- It kills more than 1.35 million globally as reported in the Global Status report on Road Safety 2018 with 90% of these casualties taking place in the developing countries and 11% alone being accounted for by India.
- As per the Report on Road accidents in India 2019, the accident related deaths in India in 2019 were 1,51,113 in number.
- Digitalised Detailed Accident Reports (DAR) will be uploaded to the portal for easy access.
- The web portal will be linked to the Integrated Road Accident Database (iRAD).
- From iRAD, applications to more than 90% of the datasets would be pushed directly to the e-DAR.
- Stakeholders like the police, road authorities, hospitals, etc., are required to enter very minimal information for the e-DAR forms.
- Thus, e-DAR would be an extension and e-version of iRAD.
- DAR portal would conduct multiple checks against fake claims by conducting a sweeping search of vehicles involved in the accident, the date of the accident, and the First Information Report number.
- The portal would be linked to other government portals like Vaahan or and would get access to information on driving licence details and registration of vehicles.
- Hotspots for accidents would also be identified so as to obtain solutions to avoid accidents at these hotspots.
Bernardinelli-Bernstein Comet:

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Hubble Space Telescope has confirmed that the huge Bernardinelli-Bernstein comet is indeed the largest icy comet nucleus ever seen by astronomers.
- The nucleus is called the C/2014 UN271 which has an estimated diameter of almost 129 kilometres.
- The nucleus is around 50 times larger than that of most known comets, and its mass is estimated to be around 500 trillion tonnes.
- Bernardinelli-Berstein Comet was discovered by astronomers Pedro Bernardinelli and Gary Bernstein in archival images from the Dark Energy Survey at an astronomical observatory in Chile.
- It was discovered in November 2010 and has been intensively studied since.
- The comet has been travelling towards the sun for over a million years and it is believed to have originated in the Oort Cloud.
- Oort Cloud is a distant region of the solar system that is predicted to be the source of most comets.
- The Oort Cloud is still only a theoretical concept as the comets that constitute it are too faint and distant to be directly observed.
- It was first hypothesised by Dutch astronomer Jan Oort in 1950.
- The Bernardinelli-Berstein comet follows a 3-million-year-long elliptical orbit and has an estimated temperature of minus 348 degrees Fahrenheit.
- It is warm enough to sublimate carbon monoxide (CO) from the surface to produce the dusty coma.
Hubble Space Telescope:
- It was launched by NASA in 1990 and is named in honour of Edwin Hubble, a revered American astronomer of the early 20th century.
- The telescope is a space-based observatory and has made significant observations related to interstellar objects, including moons around Pluto and a comet crashing into Jupiter.
- The telescope has now been in operation for over thirty years.
- In December 2021, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a revolutionary instrument built to peer the farthest yet into the cosmos, was launched.
- It is also considered a successor of the Hubble Telescope and will extend and complement its discoveries.
South Asia Economic Focus: World Bank

The World Bank in its report South Asia Economic Focus (Bi- Annual) cut its economic growth forecast for India and the whole South Asian region.
- South Asia Economic Focus describes recent economic developments, analyses the economic impact on South Asia of the war in Ukraine, presents growth forecasts, provides risk scenarios, and concludes that reshaping economies goes hand in hand with reshaping norms.
- Lowered India’s growth to 8% from previous estimate of 8.7% for the current fiscal year 2022-23.
- Cut by a full percentage (1%) points the growth outlook for South Asia, excluding Afghanistan, to 6.6%.
- Raised its growth forecast for Pakistan, the region’s second-largest economy, for the current year ending in June, to 4.3% from 3.4% and kept next year’s growth outlook unchanged at 4%.
Tribute To Veer Kunwar Singh:

The Government will pay tribute to freedom fighter Veer Kunwar Singh (1777-1858) on his birth anniversary (23rd April).
- He belonged to a family of the Ujjainiya clan of the Parmar Rajputs of Jagdispur, currently a part of Bhojpur district, Bihar.
- He was the chief organiser of the fight against the British in Bihar.
- He is popularly known as Veer Kunwar Singh.
- Singh led the Indian Rebellion of 1857 in Bihar. He was nearly eighty and in failing health when he was called upon to take up arms.
- He was assisted by both his brother, Babu Amar Singh and his commander-in-chief, Hare Krishna Singh. Some argue that the latter was the real reason behind Kunwar Singh’s initial military success.
- He gave a good fight and harried British forces for nearly a year and remained invincible until the end. He was an expert in the art of guerilla warfare.
- He passed away on 26th April 1858.
- To honour his contribution to India’s freedom movement, the Republic of India issued a commemorative stamp on 23th April 1966.
- The Government of Bihar established the Veer Kunwar Singh University, Arrah in 1992.
- In 2017, the Veer Kunwar Singh Setu, also known as the Arrah–Chhapra Bridge, was inaugurated to connect north and south Bihar.
- In 2018, to celebrate the 160th anniversary of Kunwar Singh’s death, the government of Bihar relocated a statue of him to Hardinge Park.
- The park was also officially renamed as ‘Veer Kunwar Singh Azadi Park’.
The Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Bill, 2021:

The Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Bill, 2021 after being introduced in Lok Sabha was later referred to the Standing Committee on Science and Technology, Environment, Forests and Climate Change.
- The panel has recently recommended the Central Government not to encourage sale and purchase of captive elephants.
- Section 43 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 states that no person having in his possession captive animal, animal article, trophy or uncured trophy in respect of which he has a certificate of ownership shall transfer by way of sale or offer for sale or by any other mode of consideration of commercial nature, such animal or article or trophy or uncured trophy.
- The amended Bill introduces an exemption clause for elephants.
- Other issues wrt Bill highlighted by the standing committee:
- The Standing Committee pointed out that a number of species is missing in all the three Schedules.
- The committee also finds species that should be in Schedule I but have been placed in Schedule II.
- There are species missing altogether both in Schedules I and II as well as in Schedule III.
- The Bill also fails to address “human-animal conflict”, the committee noted.
Highlights of the Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Bill, 2021:
- The proposed amendment is likely the most expansive so far in scope: it covers more areas of legislation, from trade in wild species to permitting filmmaking in protected areas and controlling the spread of invasive species.
- The Bill increases penalties for wildlife crimes. For example, offences that attracted a fine of Rs 25,000 now attract Rs 1 lakh.
- There’s a new and separate chapter on regulating species involved in international trade according to the CITES treaty.
- The Bill prohibits possessing, trading and breeding species without prior permissions from CITES authorities.
- The Bill also recognises threats that invasive alien species pose.
- The Bill doesn’t include regional invasive species – some of which may be native to the country but invasive in some parts.
- The amendment Bill has no separate Schedule for species the Act classifies as ‘vermin’, so the Centre can directly notify such species and open them up to be hunted – including some of the species currently in Schedule II.
- The Bill also proposes changes to the Schedules.
- Foremost, it reduces the number of Schedules from six to four, to “rationalise” the lists. But the two main substitute Schedules that will specify the protected species are incomplete.
- The Bill will render the existing ‘State Boards for Wildlife’ defunct by replacing it them with set up a ‘Standing Committee’ of the State Board of Wildlife – headed by the respective state forest minister and 10 members nominated by the minister.
- The State Boards of Wildlife currently manage the conservation and protection of wildlife at the state level. The state chief minister sits atop the board and is supported by 20+ members, including of the state legislature, NGOs, conservationists and representatives of the state forest departments and tribal welfare.
- Under the proposed amendments, the commercial sale and purchase of elephants will no longer be prohibited under the Act. This clause is prone to abuse and can severely impact elephant populations by legitimising live trade of elephants.




