Today Current Affairs: 1st February 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
India- Oman’s Top Defence:
India is laying out the red carpet for Oman’s top defence official Mohammed Nasser Al Zaabi, who will be in India from January 30 to February 4 on an official visit.
- Zaabi will be in Delhi to co-chair the Joint Military Cooperation Committee (JMMC) with Defence Secretary Ajay Kumar.
- The JMCC is the highest forum of engagement between India and Oman in the field of defence that evaluates and provides guidance to the overall framework of defence exchanges between the two sides.
- The JMCC is expected to meet annually, but could not be organised since 2018 when the meeting of the 9th JMCC was held in Oman.
- Oman is India’s closest defence partner in the Gulf region and an important anchor for India’s defence and strategic interests.
- Defence cooperation has emerged as a key pillar for the robust India-Oman strategic partnership. Defence exchanges are guided by a Framework MOU which was recently renewed in 2021.
- Oman is the only country in the Gulf region with which all three services of the Indian armed forces conduct regular bilateral exercises and staff talks, enabling close cooperation and trust at the professional level.
- Oman also provides critical operational support to Indian naval deployments in the Arabian sea for anti-piracy missions.
- Bilateral training cooperation between the two sides is also robust with Omani forces regularly subscribing to training courses in India both at professional as well as higher command level.
- Indian armed forces also subscribe to the Staff and Command courses conducted at NDC, Oman.
- Oman also actively participates in the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
SilverLine : Kerala

Despite the protests taking place across Kerala against SilverLine, the CPI(M)-led government remains firm on implementing the project.
- SilverLine is a semi high-speed railway project connecting the state’s northern and southern ends at a cost of over Rs 63,000 crore.
- The proposed 529.45-km line will link Thiruvananthapuram in the south to Kasaragod in the north, covering 11 districts through 11 stations.
- When the project is completed, one can travel from Kasaragod to Thiruvananthapuram in less than four hours at 200 km/hr. On the existing Indian Railways network, it now takes 12 hours.
- The deadline for the project, being executed by the Kerala Rail Development Corporation Limited (KRDCL), is 2025.
- KRDCL, or K-Rail, is a joint venture between the Kerala government and the Union Ministry of Railways created to execute big railway projects.
Bomb Cyclone:

The US East Coast is bracing itself for a “bomb cyclone” (Nor’easter) that is on course to to barrel in from the mid-Atlantic.
- Bombogenesis is the technical term. ‘Bomb cyclone’ is a shortened version of it, better for social media.”
- It is a mid-latitude cyclone that intensifies rapidly.
- It has low pressure at its center, weather fronts and an array of associated weather, from blizzards to severe thunderstorms to heavy precipitation.
- Generally, a bomb cyclone happens when atmospheric pressure in the middle of the storm drops at least 24 millibars over 24 hours, quickly increasing in intensity. The lower the pressure, the stronger the storm.
- It essentially amounts to a rapidly developing storm system, distinct from a tropical hurricane because it occurs over midlatitudes where fronts of warm and cold air meet and collide, rather than relying on the balmy ocean waters of late summer as a catalyst.
- Bomb cyclones have cold air and fronts: Cold air rapidly weakens hurricanes, while it is an essential ingredient for bomb cyclones.
- Bomb cyclones form during winter: Hurricanes form from late spring to early fall, while bomb cyclones form from late fall to early spring.
- Bomb cyclones form at higher latitudes: Hurricanes form in tropical waters, while bomb cyclones form over the northwestern Atlantic, northwestern Pacific and sometimes the Mediterranean Sea.
Budget:

The Budget Session of Parliament has begun and is scheduled to conclude on April 8.
- First, President Ram Nath Kovind will address both Houses in the Central Hall.
- The Economic Survey 2021-22 will be laid by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitaraman in Lok Sabha on January 31.
- The Budget will be presented by her on February 1 at 11 am.
- There will be no Zero Hour and Question Hour in both Houses of Parliament during the first two days of the Budget Session.
- During the First Part of the Session after the presentation of the Budget (February 2-11), 40 hours of normal time will be available for various Businesses such as Question, Private Members’ Business, Discussion on Motion of Thanks, General Discussion on Union Budget, etc.
- Article 85 requires that there should not be a gap of more than six months between two sessions of Parliament.
- The Constitution does not specify when or for how many days Parliament should meet.
- The procedure for presentation of the Budget in and its passing by Lok Sabha is as laid down in articles 112—117 of the Constitution of India, Rules 204—221 and 331-E of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha and Direction 19-B of Directions by the Speaker.
- The Budget is presented to Lok Sabha on such day as the President may direct.
- Immediately after the presentation of the Budget, the following three statements under the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003 are also laid on the Table of Lok Sabha:
- (i) The Medium-Term Fiscal Policy Statement;
- (ii) The Fiscal Policy Strategy Statement; and
- (iii) The Macro Economic Framework Statement.
Bad Bank:

A key proposal announced in this year’s (2021) Budget, a bad bank to deal with stressed assets in the loss-laden banking system, has received all regulatory approvals.
- Setting up of NARCL, the proposed bad bank for taking over stressed assets of lenders, was announced in the Budget for 2021-22.
- The plan is to create a bad bank to house bad loans of ₹500 crore and above, in a structure that will contain an asset reconstruction company (ARC) and an asset management company (AMC) to manage and recover dud assets.
- The new entity is being created in collaboration with both public and private sector banks.
- Majority-owned by state-owned banks, the NARCL will be assisted by the India Debt Resolution Company Ltd (IDRCL), in turn majority-owned by private banks, in resolution process in the form of a Principal-Agent basis.
- The proposed bad bank will have a public sector character since the idea is mooted by the government and majority ownership is likely to rest with state-owned banks.
- At present, ARCs typically seek a steep discount on loans. With the proposed bad bank being set up, the valuation issue is unlikely to come up since this is a government initiative.
- The government-backed ARC will have deep pockets to buy out big accounts and thus free up banks from carrying these accounts on their books.
Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC):
- It is a specialized financial institution that buys the Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) from banks and financial institutions so that they can clean up their balance sheets. This helps banks to concentrate on normal banking activities.
- The asset reconstruction companies or ARCs are registered under the RBI.
Forex Reserves:

According to recent data from Reserve bank of india (RBI), India’s Foreign Exchange (Forex) reserves posted a decline of USD 678 million during the week ended 21st January 2022 to reach USD 634.287 billion.
- The slip in the reserves was on account of a drop in the Foreign Currency Assets (FCA), a vital component of the overall reserves. FCA declined by USD 1.155 billion to USD 569.582 billion in the reporting week.
- Gold reserves saw an increase of USD 567 million to USD 40.337 billion in the reported week.
- The Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) fell USD 68 million to USD 19.152 billion.
Foreign Exchange Reserves:
- Foreign exchange reserves are assets held on reserve by a central bank in foreign currencies, which can include bonds, treasury bills and other government securities.
- It needs to be noted that most foreign exchange reserves are held in US dollars.
- India’s Forex Reserve include:
- Foreign Currency Assets
- Gold reserves
- Special Drawing Rights
- Reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Objectives of Holding Forex Reserves:
- Supporting and maintaining confidence in the policies for monetary and exchange rate management.
- Provides the capacity to intervene in support of the national or union currency.
- Limits external vulnerability by maintaining foreign currency liquidity to absorb shocks during times of crisis or when access to borrowing is curtailed.
- Significance of Rising Forex Reserves:
- The rising forex reserves give comfort to the government and the RBI in managing India’s external and internal financial issues.
- It serves as a cushion in the event of a Balance of Payment (BoP) crisis on the economic front.
- The rising reserves have also helped the rupee to strengthen against the dollar.
- Reserves will provide a level of confidence to markets and investors that a country can meet its external obligations.
Nord Stream Pipeline:
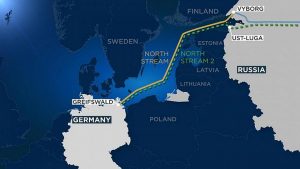
The US has said it will stop the Nord Stream if Russia attacks Ukraine.
- However, European countries, led by Germany, seemed reluctant initially to impose sanctions on the Nord Stream due to its importance though it has now said sanctions are not off the table.
- Nord Stream, the longest subsea pipeline, is an export gas pipeline which runs under the Baltic Sea carrying gas from Russia to Europe.
- Nord Stream consists of two pipelines, which have two lines each.
- Nord Stream 1 was completed in 2011 and runs from Vyborg in Leningrad (Russia) to Lubmin near Greifswald, Germany.
- Nord Stream 2 which runs from Ust-Luga in Leningrad to Lubmin was completed in September 2021 and has the capacity to handle 55 billion cubic meters of gas per year once it becomes operational.
- The twin pipelines together can transport a combined total of 110 billion cubic metres (bcm) of gas a year to Europe for at least 50 years.
- The Nord Stream crosses the Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) of several countries including Russia, Finland, Sweden, Denmark and Germany, and the territorial waters of Russia, Denmark, and Germany.
- In Germany, the pipeline connects to the OPAL (Baltic Sea Pipeline) and NEL (North European Pipeline) which further connects to the European grid.
Second ASEAN Digital Ministers Meeting:
2nd ASEAN Digital Ministers’ (ADGMIN) Meeting with India virtually, where two sides finalized India-ASEAN Digital work plan 2022 for future collaboration in the field.
- ADGMIN is an annual meeting of telecom ministers of 10 ASEAN (Association of South-East Asian Nations) countries and dialogue partner countries—Australia, Canada, China, EU, India, Japan, Republic of Korea, New Zealand, Russia, UK and US.
- ASEAN nations include Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- India and ASEAN nations have jointly approved a work plan under which they will develop a system to combat use of stolen and counterfeit mobile handsets.
- Other areas of cooperation include wifi access network interface for nationwide public internet.
- Emphasis will also be given on the capacity building and knowledge sharing in emerging areas in the field of information and communication technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, advanced satellite communication, cyber forensics.




