Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 22nd October 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- 77th anniversary of the formation of Azad Hind Government
- State of Global Air 2020:
- Integrated theatre commands
- Blue Dot Network (BDN):
- .Production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme:
- OSIRIS-REx mission:
- Other important current affairs:
1.77th anniversary of the formation of Azad Hind Government :

77th anniversary of the formation of Azad Hind Government on 21st October 2020.
About Azad Hind Government:
- Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose had announced the establishment of the provisional government of Azad Hind in occupied Singapore in 1943.
- Known as Arzi Hukumat-e-Azad Hind, it was supported by the Axis powers of Imperial Japan, Nazi Germany, the Italian Social Republic, and their allies.
- The provisional government was also formed in the Japanese-occupied Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The islands were reoccupied by the British in 1945.
- Bose was convinced that armed struggle was the only way to achieve independence for India.
- It drew ex-prisoners and thousands of civilian volunteers from the Indian expatriate population in Malaya (present-day Malaysia) and Burma (now Myanmar).
- The Azad Hind government had its own court, civil code and currency.
- Its provisional capital was Port Blair, while its capital-in-exile was Rangoon and Singapore.
- Bose was the head of the state, the prime minister and the minister for war and foreign affairs.
- Captain Lakshmi headed the women’s organisation.
- S A Ayer headed the publicity and propaganda wing.
- Rash Behari Bose was designated as the supreme advisor.
2. State of Global Air 2020:
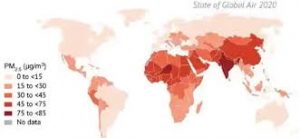
A global study, State of Global Air 2020 (SoGA 2020) has been released by the Health Effects Institute (HEI).
- It highlights that air pollution is the largest risk factor for death among all health risks and it is the first-ever comprehensive analysis of air pollution’s global impact on newborns.
- HEI is an independent, nonprofit research institute funded jointly by the USA’s Environmental Protection Agency and others.
Key Points
- India, Bangladesh, Pakistan and Nepal are among the top ten countries with the highest PM2.5 (particulate matter) exposures in 2019 and all of these countries experienced increases in outdoor PM2.5 levels between 2010 and 2019.
- India is also among the top ten countries with the highest ozone (O3) exposure in 2019. Also, among the 20 most populous countries, India recorded the highest increase (17%) in O3 concentrations in the past ten years.
- Long-term exposure to outdoor and household (indoor) air pollution contributed to over 1.67 million annual deaths from stroke, heart attack, diabetes, lung cancer, chronic lung diseases, and neonatal diseases, in India in 2019.
- High PM contributed to the deaths of more than 1,16,000 Indian infants who did not survive their first month.
- Infants in the first month of life are already at a vulnerable stage and a growing body of scientific evidence-supported studies in India indicates that particulate air pollution exposure during pregnancy is linked to low birth weight and preterm birth.
- More than half of these deaths were associated with outdoor PM2.5 and others were linked to the use of solid fuels such as charcoal, wood, and animal dung for cooking.
- Although there has been a slow and steady reduction in household reliance on poor-quality fuels, the air pollution from these fuels continues to be a key factor in the deaths of these youngest infants.
Significance of the Study:
- Addressing impacts of air pollution on adverse pregnancy outcomes and newborn health is important for low- and middle-income countries, not only because of the high prevalence of low birth weight, preterm birth, and child growth deficits but because it allows the design of strategic interventions that can be directed at these vulnerable groups.
3.Integrated theatre commands.

As part of defence reforms after the appointment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS), the government is working on the formation of integrated theatre commands.
- The Indian armed forces currently have 17 commands. There are 7 commands each of the Army and the Air Force. The Navy has 3 commands.
- Each command is headed by a 4-star rank military officer.
- There is one joint command in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- It is the first Tri-Service theatre command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India.
- It was created in 2001 to safeguard India’s strategic interests in Southeast Asia and the Strait of Malacca by increasing rapid deployment of military assets in the islands.
- The other tri-service command, the Strategic Forces Command (SFC), looks after the delivery and operational control of the country’s nuclear assets.
The appointment of the CDS and the creation of the Department of Military Affairs (DMA) are momentous steps towards the integration and advancement of defence forces.
- CDS: It is the single-point military adviser to the government as suggested by the Kargil Review Committee in 1999.
- CDS oversees and coordinates the working of the three Services.
- As the head of DMA, CDS is vested with the authority in prioritising inter-service procurement decisions.
Integrated Theatre Command:
- An integrated theatre command envisages a unified command of the three Services, under a single commander, for geographical theatres (areas) that are of strategic and security concern.
- The commander of such a force will be able to bear all resources at his disposal — from the Army, the Indian Air Force, and the Navy — with seamless efficacy.
- The integrated theatre commander will not be answerable to individual Services.
- Integration and jointness of the three forces will avoid duplication of resources. The resources available under each service will be available to other services too.
- The services will get to know one another better, strengthening cohesion in the defence establishment.
- The Shekatkar committee has recommended the creation of 3 integrated theatre commands — northern for the China border, western for the Pakistan border, and southern for the maritime role.
4.Blue Dot Network (BDN).:
A group of the US Senators, in a letter, has asked India to join the Blue Dot Network (BDN).
- The letter also backed India’s decision to invite Australia to the annual Malabar naval exercise.
Blue Dot Network:
- The BDN was formally announced on 4th November 2019 at the Indo-Pacific Business Forum in Bangkok, Thailand.
- It is led by the USA along with Japan and Australia.
- It is a multi-stakeholder initiative to bring together governments, the private sector and civil society to promote high-quality, trusted standards for global infrastructure development.
- It is expected to serve as a globally recognized evaluation and certification system for roads, ports and bridges with a focus on the Indo-Pacific region.
- Infrastructure projects would be graded on debt, environmental standards, labour standards etc.
- This system would apply to projects in any citizen-centric country where citizens would like to evaluate such projects.
- It is planned as a direct counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- However, unlike the BRI, the BDN would not offer public funds or loans for the project.
Blue Dot certification:
- BDN will serve as a globally recognized seal of approval for major infrastructure projects, letting people know that projects are sustainable and not exploitative.
5.Production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme:

The government is considering an extension of the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme to 7-8 more sectors to promote domestic manufacturing.
About the PLI scheme:
- To make India a manufacturing hub, the government recently announced the PLI scheme for mobile phones, pharma products, and medical equipment sectors.
- Notified on April 1 as a part of the National Policy on Electronics.
- It proposes a financial incentive to boost domestic manufacturing and attract large investments in the electronics value chain.
Key features of the scheme:
- The scheme shall extend an incentive of 4% to 6% on incremental sales (over base year) of goods manufactured in India and covered under target segments, to eligible companies, for a period of five (5) years with financial year (FY) 2019-20 considered as the base year for calculation of incentives.
- The Scheme will be implemented through a Nodal Agency which shall act as a Project Management Agency (PMA) and be responsible for providing secretarial, managerial and implementation support and carrying out other responsibilities as assigned by MeitY from time to time.
Eligibility:
- According to the scheme, companies that make mobile phones which sell for Rs 15,000 or more will get an incentive of up to 6 per cent on incremental sales of all such mobile phones made in India.
- In the same category, companies which are owned by Indian nationals and make such mobile phones, the incentive has been kept at Rs 200 crore for the next four years.
6.OSIRIS-REx mission:

On October 20th, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft briefly touched asteroid Bennu, from where it is meant to collect samples of dust and pebbles and deliver them back to Earth in 2023.
OSIRIS-REx mission:
- OSIRIS-Rex stands for Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer.
- This is NASA’s first mission meant to return a sample from the ancient asteroid.
- Launched in 2016, it reached its target in 2018.
- The departure window for the mission will open up in 2021, after which it will take over two years to reach back to Earth.
Asteroid Bennu:
- The asteroid was discovered by a team from the NASA-funded Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research team in 1999.
- Scientists believe that it was formed in the first 10 million years of the solar system’s formation, implying that it is roughly 4.5 billion years old.
- Because of Bennu’s age, it is likely to contain material that contains molecules that were present when life first formed on Earth, where life forms are based on carbon atom chains.
- Because of its high carbon content, the asteroid reflects about four per cent of the light that hits it, which is very low when compared with a planet like Venus, which reflects about 65 per cent of the light that hits it.
- Earth reflects about 30 per cent.
- It classified as a Near-Earth Object (NEO), might strike the Earth in the next century, between the years 2175 and 2199.
Other important current affairs:
1.The Election Commission of India (ECI) has constituted a committee to examine the issues concerning the expenditure limit for a candidate.
- It has been tasked with assessing the change in the number of electors across states/UTs and the change in the Cost Inflation Index (CII) and their bearing on expenditure pattern of candidates in recent elections.
- Political parties in the feedback to the Commission had asked for an increase in the expenditure of Bihar assembly elections to meet the increased digital campaign expenses amid the Covid-19 pandemic.
- The Ministry of Law and Justice notified an amendment in Rule 90 of Conduct of Elections Rules, 1961, which enhanced the existing expenditure limit by 10%, applicable with immediate effect.
- The expenditure limit was last revised in 2014 while the same was done for Andhra Pradesh and Telangana in 2018, following their bifurcation in 2014.
- After that, the limit has not been increased despite an increase in the electorate from 834 million in 2014 to 921 million in 2020 and an increase in the Cost Inflation Index from 220 in 2014 to 301 in 2020.
2.Major Opposition parties have demanded the repeal of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), 1967 after the arrest of Stan Swamy, an 83-year-old tribal rights activist, under the UAPA in the Bhima Koregaon case.
- According to the Ministry of Home Affairs data, placed before the Parliament, there has been a steady increase in the number of those arrested under the UAPA.
- In 2016, 999 people were arrested, in 2017, 1,054 were arrested, while in 2018 1,031 were arrested.
- However, the conviction rate in UAPA cases was found to be less than 25%.
- Also, in almost 43% of cases, the charge sheet has taken more than a year or two to be filed.
- UAPA was passed in 1967. It aims at effective prevention of unlawful activities associations in India.
- Unlawful activity refers to any action taken by an individual or association intended to disrupt the territorial integrity and sovereignty of India.
- The Act assigns absolute power to the central government, by way of which if the Centre deems an activity as unlawful then it may, by way of an Official Gazette, declare it so.
- It has death penalty and life imprisonment as highest punishments.
- Under UAPA, both Indian and foreign nationals can be charged. It will be applicable to the offenders in the same manner, even if crime is committed on a foreign land, outside India.
- Under the UAPA, the investigating agency can file a charge sheet in maximum 180 days after the arrests and the duration can be extended further after intimating the court.
- The 2004 amendment, added “terrorist act” to the list of offences to ban organisations for terrorist activities, under which 34 outfits were banned.
- Till 2004, “unlawful” activities referred to actions related to secession and cession of territory.
- In August 2019, Parliament cleared the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Bill, 2019 to designate individuals as terrorists if the individual commits or participates in acts of terrorism, prepares for terrorism, promotes terrorism or is otherwise involved in terrorism.
- The Act empowers the Director-General of National Investigation Agency (NIA) to grant approval of seizure or attachment of property when the case is investigated by the said agency.
- The Act also empowers the officers of the NIA, of the rank of Inspector or above, to investigate cases of terrorism in addition to those conducted by the DSP or ACP or above rank officer in the state.
3.The Ministry of Jal Shakti launched a mobile application for geo-tagging of the components of projects under Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
- Developed By: The mobile application has been developed with the help of Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications & Geo-informatics (BISAG-N).
- BISAG-N is an autonomous scientific society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860. It comes under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Objective: To track the pace of work and the actual status of the projects.
- The mobile application can be used to capture the image of the project component along with other details such as location, type of canal/ structure, completion status, etc.
- The captured information can be submitted by the user for geo-tagging on the geographic information system (GIS) portal developed for this purpose.
- Geo-tagging is the process of adding geographical identification data to various media such as websites, SMS messages, QR Codes.
- This data usually consists of latitude and longitude coordinates. It can also include altitude, bearing, distance, accuracy data, and place names, and perhaps a time stamp.
- GIS is a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing geography-related data.
- Operation: The mobile application can be operated in both online & offline mode depending on the network availability in the region.
4.The State Election Commission (SEC) has filed a writ petition in the High Court seeking a direction to the government to provide budget and release funds as and when a request is made by it for conducting elections.
- The SEC also prayed for assistance from the government in holding the civic polls.
- The Constitution of India vests in the State Election Commission, consisting of a State Election Commissioner, the superintendence, direction and control of the preparation of electoral rolls for, and the conduct of all elections to the Panchayats and the Municipalities (Articles 243K, 243ZA).
- The State Election Commissioner is appointed by the Governor.
- As per article 243(C3) the Governor, when so requested by the State Election Commission, make available to the State Election Commission such staff as may be necessary for the discharge of the functions conferred on the SEC.
- The ECI and SECs have a similar mandate; do they also have similar powers?
- The provisions of Article 243K of the Constitution, which provides for setting up of SECs, are almost identical to those of Article 324 related to the EC. In other words, the SECs enjoy the same status as the EC.
- In Kishan Singh Tomar vs Municipal Corporation of the City of Ahmedabad case, the Supreme Court directed that state governments should abide by orders of the SECs during the conduct of the panchayat and municipal elections, just like they follow the instructions of the EC during Assembly and Parliament polls.
5.India’s first seaplane service in Gujarat is set to begin from 31 October, the anniversary of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.
- It will connect Sabarmati Riverfront in Ahmedabad to the Statue of Unity in Kevadia.
The service will be operated by Spicejet Airlines. - Given the large and small water bodies that dot the country, India provides an ideal opportunity for seaplane operations.
- Unlike a conventional aircraft, a seaplane can land both on a waterbody and on land, thereby opening up more opportunities for business and tourism.
- Such projects provide faster and hassle-free travel option for the long, treacherous and hilly regions of the country.
- Environmental concerns: The water aerodrome is not a listed project/activity in the Schedule to the Environmental Impact Assessment Notification, 2006 and its amendments.
- However, the Expert Appraisal Committee was of the opinion that the activities proposed under the water aerodrome project may have a similar type of impact as that of an airport.
6.National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- It is being implemented and steered jointly by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY).
- Implemented by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Pune and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru.
- The Mission envisages empowering national academic and R&D institutions spread over the country by installing a vast supercomputing grid comprising of more than 70 high-performance computing facilities.
- These supercomputers will also be networked on the National Supercomputing grid over the National Knowledge Network (NKN).
- The NKN is another program of the government which connects academic institutions and R&D labs over a high-speed network.
- The Mission includes development of highly professional High Performance Computing (HPC) aware human resource for meeting challenges of development of these applications.
- India has developed an indigenous server (Rudra), which can meet the High-Performance Computing (HPC) requirements of all governments and PSUs. This is the first time that a server system was made in India, along with the full software stack developed by C-DAC.
7. Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has approved a new low-cost Covid-19 diagnostic method named COVIRAP, developed by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Kharagpur.
- COVIRAP has an automated pre-programmable temperature control unit, a special detection unit on genomic analysis, and a customised smartphone app for results.
- The machine has an isothermal nucleic acid amplification method, which did away with the need for a thermocycler.
- Isothermal amplification of nucleic acids is a process that rapidly and efficiently accumulates nucleic acid sequences at constant temperature. The Isothermal Amplification Techniques have been developed as alternatives to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
- Thermocyclers are instruments used to amplify DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) samples by the polymerase chain reaction.
- Once the sample is processed in the machine after being mixed with solutions developed by the IIT team, treated paper strips (similar to the pregnancy strips) are dipped into it, and the emergence of coloured lines will depict the presence of the virus.
8.The Ministry of Civil Aviation has celebrated the UDAN day on the 4th anniversary of the UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik) Scheme.
- The Government of India has acknowledged the contribution of the scheme and has identified 21st October as UDAN Day, the day on which the scheme document was first released.
- Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik (UDAN) was launched as a regional connectivity scheme (RCS) under the Ministry of Civil Aviation in 2016.
- Aim:
- To develop the regional aviation market.
- To provide affordable, economically viable and profitable air travel on regional routes to the common man even in small towns.
- It envisages providing connectivity to un-served and under-served airports of the country through the revival of existing airstrips and airports.
- Under-served airports are those which do not have more than one flight a day, while unserved airports are those where there are no operations.
- The scheme is implemented by the Airports Authority of India (AAI) and is operational for a period of 10 years.
- Achievements Highlighted:
- Created a virtuous circle wherein the UDAN routes feed the national network and the national routes further create new opportunities for the people across the country who then generate demand for more regional routes.
- Played a major role in adding new airports and routes to the aviation landscape of the country.




