Today Current Affairs: 10th March 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
PARAM Ganga: A Supercomputer

The National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) has deployed “PARAM Ganga”, a supercomputer at IIT Roorkee, with a supercomputing capacity of 1.66 Petaflops.
- The system is designed and commissioned by C-DAC under Phase 2 of the build approach of the NSM.
- The National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) is being steered jointly by Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeiTY) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and implemented by Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) and Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore.
- The four major pillars of the NSM are, namely, Infrastructure, Applications, R&D, HRD.
- C-DAC has been entrusted the responsibility to design, development, deployment and commissioning of the supercomputing systems under the build approach of Mission.
- Till now C-DAC has deployed 11 systems at IISc, IITs, IISER Pune, JNCASR, NABI-Mohali and C-DAC under NSM Phase-1 and Phase-2 with a cumulative compute power of more than 20 Petaflops.
Motor Vehicles Agreement (MVA):
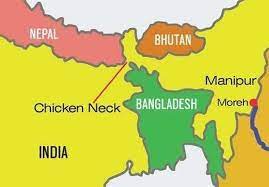
With Bhutan continuing to sit out the Motor Vehicles Agreement (MVA) of the sub-regional Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal (BBIN) grouping, a meeting of the other three countries was held to discuss the next steps in operationalising the agreement for the free flow of goods and people between them.
- The original BBIN MVA was signed by all four countries in June 2015, but after objections in Bhutan over sustainability and environmental concerns, the Bhutanese Parliament decided not to endorse the plan.
- The then Tobgay Tshering government agreed to allow the other three countries to go ahead with the project for vehicular movement (BIN-MVA) in 2017.
- Officials said that while India remained “hopeful” that Bhutan could change its position on the project, it was decided at a meeting in November 2021 to go ahead for now, given that there are no new signals from Thimphu on the project.
- Progress on the seven-year-old project has been slow, despite several trial runs being held along the Bangladesh-India-Nepal road route for passenger buses and cargo trucks. There are still some agreements holding up the final protocols.
- Meanwhile, Prime Minister Narendra Modi is expected to travel to Colombo at the end of March to attend the summit of another sub-regional grouping, BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation), which includes Bangladesh, Nepal and Bhutan as well.
What Is Ukrainian Foreign Legion?

Over 500 Indians from across the country, including some veterans, have submitted applications volunteering to join the International Legion created to fight Russian forces in Ukraine, diplomatic sources said
- The International Legion of Territorial Defense of Ukraine is also known as the Ukrainian Foreign Legion.
- It is a volunteer foreign legion military unit created by the Government of Ukraine on the request of President Volodymyr Zelenskyy to fight in the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
- It would function under the territorial defence squad.
- It is one of several Ukrainian volunteer battalions formed since 2014.
- One Indian has, so far, joined the Ukraine International Legion.
- Indian domestic law clearly states such an act is punishable under Chapter VI, Section 121-130 of the Indian Penal Code (offences against the state).
- They are punished under the section “Committing depredation on territories of power at peace with the Government of India”.
e-Bill Processing System: Key Points

The Finance Minister launched the E-bill Processing system on the occasion of 46th Civil Accounts Day (1st March).
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022 to use the technology for facilitating the financial inclusion drive in India.
- The “Civil Accounts Day” is observed every year to mark the anniversary of the inception of the Indian Civil Accounts Service (ICAS) on 1st March , 1976.
- The ICAS performs a key role in delivery of financial management services for the Government of India (GoI).
- E-bill system is part of Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) and Digital India Eco-System’ to bring in broader transparency and expedite the process of payments.
- In simple words, e-Bill Processing System is a way of transacting the bills digitally rather than the traditional use of paper.
- Currently, the suppliers of various goods and services to the Government have to submit physical, ink signed copies of their bills to the respective Ministries/Departments/offices of the Government of India.
- Customers will be able to get their bills online, via e-mail, or in the machine-readable data forms when billed electronically.
- Under the newly launched e-Bill system, vendors/suppliers can upload their bills online along with supporting documents from the convenience of their homes/offices at any time through digital signature.
- At the backend too, the electronic bill received will be processed by the authorities digitally at every stage and finally, the payments will be credited digitally to the bank account of the vendor.
- Developed by the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) Division in the office of the Controller General of Accounts in the Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance.
Equalisation Levy:

Justifying the 2 per cent equalisation levy (EL) imposed by India on the supply of services by multinational enterprises, finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman has said it is a sovereign right to tax revenues earned from operations in the country.
About the Equalisation Levy:
- India was the one of the first countries to introduce a 6 per cent equalisation levy in 2016, but the levy was restricted to online advertisement services.
- However, India introduced the digital tax in April 2020 for foreign companies selling goods and services online to customers in India and showing annual revenues more than INR 20 million.
- India has expanded the scope of the equalisation levy over the last few years, to tax non-resident digital entities.
- While the levy applied only to digital advertising services till 2019-20 at the rate of 6 percent, the government in April 2020 widened the scope to impose a 2 per cent tax on non-resident e-commerce players with a turnover of Rs 2 crore.
- The scope was further widened in the Finance Act 2021-22 to cover e-commerce supply or service when any activity takes place online.
- Since May 2021, this also includes any entity that systematically and continuously does business with more than 3 lakh users in India.
- Offshore e-commerce firms that sell through an Indian arm will not have to pay.
- This means if the goods and services sold on a foreign e-commerce platform are owned or provided by an Indian resident or Indian permanent establishment, they will not be subject to the two percent equalization levy.
The Code Of Ethics And Procedure, And Safeguards In Relation To The Digital Media:

The Information & Broadcasting (I&B) Ministry has approached the Directorate of Information and Public Relations (DIPR) of all the State and Union Territory governments to initiate an awareness drive for sensitising their officials to the code of ethics and procedure, and safeguards in relation to the digital media.
- The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, which was notified by the Central government on February 25, 2021, relates to the digital news publishers.
- It is administered by the Information & Broadcasting (I&B) Ministry Ministry.
The Rules provide for:
- A code of ethics to be followed by digital news publishers and OTT platforms.
- A three-tier grievance redress mechanism, which includes self-regulation by publishers at the first level, self-regulation by self-regulating bodies of the publishers and an oversight mechanism by the Central government.
- Procedures for them to furnish the required information.
- Significant social media firms have to appoint a chief compliance officer and have a nodal contact person who can be in touch with law enforcement agencies 24/7.
- A grievance officer: Social media platforms will also have to name a grievance officer who shall register the grievance within 24 hours and dispose of it in 15 days.
Social media companies with more than 50 lakh registered users will be considered ‘significant social media intermediaries’, as per the new norms.
- Social media giants such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and WhatsApp messenger could face a ban if they do not comply with the new Information Technology rules.
- They also run the risk of losing their status as “intermediaries” and may become liable for criminal action if they do not comply with the revised regulations.
Pal-Dadhvav Massacre:

On March 7, the Gujarat government marked 100 years of the Pal-Dadhvav killings, calling it a massacre “bigger than the Jallianwala Bagh”. Before this, the incident had been featured on the state’s Republic Day tableau.
- The Pal-Dadhvav massacre took place on March 7, 1922, in the Pal-Chitariya and Dadhvaav villages of Sabarkantha district, then part of Idar state.
- The day was Amalki Ekadashi, which falls just before Holi, a major festival for tribals. Villagers from Pal, Dadhvav, and Chitariya had gathered on the banks of river Heir as part of the ‘Eki movement’, led by one Motilal Tejawat.
- The movement was to protest against the land revenue tax (lagaan) imposed on the peasants by the British and feudal lords.
- The Mewad Bhil Corps (MBC), a paramilitary force raised by the British open-fired on the gathering.
- While the British claimed some 22 people were killed, the Bhils believe 1,200-1,500 of them died.
Swatantrata Sainik Samman Yojana:

The Centre has approved the continuation of the Swatantrata Sainik Samman Yojana (SSSY), under which freedom fighters and their eligible dependents are given pension and other financial benefits, till 2025-26.
- The Government of India introduced the ‘Ex-Andaman Political Prisoners Pension Scheme’ in 1969 to honor the freedom fighters who had been incarcerated in the Cellular Jail at Port Blair.
- In 1972, to commemorate the 25th Anniversary of Independence, a regular scheme for grant of freedom fighters’ pension was introduced.
- Since 1980, a liberalized scheme, namely the ‘Swatantrata Sainik Samman Pension Scheme, 1980’ has been implemented.
- From the financial year 2017-18 onwards, the nomenclature of the Scheme has been changed as ‘Swatantrata Sainik Samman Yojana’.
- The amount of pension has been revised from time to time and Dearness Relief is also given since 2016.
- The scheme provides for a monthly Samman Pension to freedom fighters, as a token of respect for their contribution in the national freedom struggle.
- On their demise, pension is provided to their eligible dependents viz. spouses and thereafter, unmarried and unemployed daughters and dependent parents, as per prescribed eligibility norms and procedure.
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs (Freedom Fighters Division).
- There are 23,566 beneficiaries across the country covered under this scheme.
Distribution Of Argon-40 On Moon:

Chandra’s Atmospheric Composition Explorer-2 (CHACE-2), a payload onboard Chandrayaan-2, has made the first-of-its-kind discovery on the distribution of one of the noble gases, Argon-40.
- India launched Chandrayaan-2, its second lunar exploration mission after Chandrayaan-1, from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota in July 2019.
- The gas found in the lunar exosphere is believed to have escaped from the lunar surface.
- The CHACE-2 observations reveal that the distribution in Ar-40 has significant spatial heterogeneity.
- There are localised enhancements (termed as Argon bulge) over several regions including the KREEP [potassium (K), Rare-Earth Elements, and Phosphorus (P)] on South Pole Aitken terrain (impact crater on the far side of the Moon).
- Noble gases serve as important tracers to understand the processes of surface-exosphere interaction, and Argon-40 (Ar-40) is such an important tracer atom to study the dynamics of the lunar exospheric species.
- It will also help decipher radiogenic activities in the first few tens of metres below the lunar surface.
- Ar-40 originates from the radioactive disintegration of Potassium-40 (K-40) present below the lunar surface.
- Once formed, it diffuses through the inter-granular space and makes its way up to the lunar exosphere through seepages and faults.
Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme:

The National Institute of Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development (NIESBUD has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) to develop a sustainable model for promoting entrepreneurship at the grass roots by initiating the Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP).
- Rural entrepreneurs will be able to access banking systems for receiving financial support for starting their enterprises, including support from MUDRA bank.
- Integrated ICT techniques and tools will also be provided for training and capacity building along with enterprise advisory services to augment the entrepreneurship ecosystem in India’s villages.
- The beneficiaries of the project are from the Self-Help Group (SHG) ecosystem of DAY-NRLM and the scheme not only supports existing enterprises but new enterprises as well.
- The partnership will enable the rural community by helping them set up their trades and provide complete support till they are stabilised.
- This pragmatic intervention will provide knowledge, advisory and financial support to the public and will help create village-level community cadre.
- SVEP is a sub-scheme of the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM), Ministry of Rural Development and has been implemented since 2016.
- Aim:
- Support the rural poor to come out of poverty.
- Providing self-employment opportunities with financial assistance and training in business management and soft skills.
- Create local community cadres for promotion of enterprises.
Temporary Protection Directive (TPD):

Over 1.5 million people fled Ukraine in the first 10 days of fighting, according to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, which has described the displacement as the “fastest growing refugee crisis since the Second World War”.
- Responding to the crisis, EU Member States on March 3 made the unprecedented decision to activate the European Union’s Council Directive 2001/55/EC of 20 July 2001, known as the Temporary Protection Directive (TPD).
- The war in Ukraine is the first time that the EU has invoked the TPD. It is being seen as another sign of European unity against Russia.
- The European Commission describes “temporary protection” under the TPD as an “exceptional measure to provide immediate and temporary protection to displaced persons from non-EU countries and those unable to return to their country of origin”.
- The directive applies when “there is a risk that the standard asylum system is struggling to cope with demand stemming from a mass influx risking a negative impact on the processing of claims”.




