Today Current Affairs: 27th January 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar:

29 Children have been conferred the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar this Year, selected from all regions of the country for their exceptional achievements in Innovation (7), Social Service (4), Scholastic (1), Sports (8), Art & Culture (6) and Bravery (3) categories.
- There are 15 Boys and 14 Girls among the awardees belonging to 21 States and UTs.
- The cash prize of Rs.1,00,000/- was given to the awardees of PMRBP 2022.
- The award is given by Ministry of Women and Child Development every year to recognize exceptional achievements of our children in various fields i.e., innovation, scholastic achievements, social service, arts & culture, sports and bravery.
- During the function, PM Modi gave digital certificates to the 61 winners of PMRBP 2021 and 2022 using a Block Chain-driven technology developed by IIT Kanpur under the National Blockchain Project.
- The digital certificates are stored on digital wallets installed on the mobile devices of the recipients.
- The digital certificates issued using the blockchain driven technology are unforgeable, globally verifiable, selectively disclosable and sensitive to user content.
- Block Chain Technology is being used for the first time for giving certificates to the awardees.
Ayesha Malik:

In a historic moment for Pakistan’s judiciary, Lahore High Court’s Justice Ayesha Malik was sworn in as the Supreme Court’s first female judge
- The swearing in of the first female judge of Pakistan’s highest court – which was established in 1956 – is noteworthy.
- Compare this to India, where the Supreme Court (established in 1950) currently has four female judges out of a total of 34.
- Three of them were appointed in September 2021 and one of them, Justice BV Nagarathna could possibly become India’s first female Chief Justice in 2027.
- India’s first female judge Justice Fathima Beevi was appointed in 1989.
Draft Undergraduate Curriculum Framework 22: Delhi University

The Delhi University (DU) on Friday released a draft Undergraduate Curriculum Framework 22 (UGCF-2022) keeping in line with the National Education Policy (NEP) and has invited feedback on it from stakeholders till January 30.
- The new UG curriculum will come into force from next year when the university shifts to a four-year undergraduate programme (FYUP).
- The UGCF provides the curriculum framework that will be adopted in the 2022-23 academic session when DU shifts to an FYUP. This, however, does not include the syllabi for courses, which is prepared independently.
- The UGCF is an attempt to include two of the most talked about features of the NEP – multi-disciplinarity and multiple exit points (leaving the course at the end of each year with a different degree).
- As of now, DU follows the Choice Based Credit System, according to which there are a total of 148 credits for a three-year Honours programme, and 132 credits for a Programme course – which is a course in which a combination of subjects is taught, as opposed to the focus being on one main subject in Honours courses.
Lithium Mining:

The Serbia government has revoked the licenses for lithium mining to Rio Tinto, an Anglo-Australian multinational mining organisation, following protests for nearly two months.
- Serbians have been protesting against Rio Tinto’s plans to mine lithium in the Jadar valley near Lozinca town in the country.
- Rio Tinto had discovered lithium deposits in the country in 2006 and had bought land in the Lozinca area in Serbia the mine would have produced enough lithium to operate one million electric vehicles along with boric acid and sodium sulphate.
- While Rio Tinto has said to be fulfilling all Serbia’s and European Union’s environmental standards, protestors have been pointing out that lithium mining in the $2.4-billion project would irrevocably pollute the drinking water.
- Serbian capital Belgrade is surrounded by lignite mines and coal power plants powered by these mines, which only make the pollution worse.
National Girl Child Day:

National Girl Child Day is celebrated in the country on January 24 every year with an objective to provide support and opportunities to the girls of India.
- It aims towards promoting awareness about the rights of the girl child and to increase awareness on the importance of girl education, and their health and nutrition and also to promote the girls position in the society to make their living better among the society.
- National Girl Child Day was first initiated in 2008 by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
Government of India has taken several steps over the years to improve the conditions of girls, some of them are :
- Save the Girl Child,
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao,
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
- CBSE Udaan Scheme
- Free or subsidized education for girl child,
- Reservation for women in colleges and universities
- National Scheme of Incentive to Girls for Secondary Education
Central Government Health Scheme:

Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare digitally launched the revamped CGHS (Central Government Health Scheme) website and mobile app, “MyCGHS”.
- The Website has been developed in accordance with GIGW (Guidelines for Indian Government Websites).
- These standards and guidelines make the website 3U compliant i.e., Usable, User-Centric and Universally Accessible.
- As mandated by the GIGW, the site has been made Bilingual (Hindi and English) with provision to make it multi-lingual in future.
- The Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) is the nodal healthcare provider to Central Government employees, pensioners and certain other category of beneficiaries and their dependents enrolled under the scheme.
- It caters to the healthcare needs of eligible beneficiaries covering all four pillars of democratic set up in India namely Legislature, Judiciary, Executive and Press and is unique of its kind due to the large volume of its beneficiary base and pan India presence providing healthcare through allopathic as well as indigenous systems of medicine.
Balbir:

Contract for construction of 50Ton Bollard Pull Tugs was concluded with M/s Hindustan Shipyard Ltd, Visakhapatnam in Feb 2019.
- The Fourth tug in the series, “Balbir” has been delivered to Naval Dockyard, Mumbai on 24 Jan 2022.
- These tugs have been designed and built under the classification rules of Indian Register for Shipping (IRS) with a service life of 20 years and are capable of assisting large naval ships, including Aircraft Carrier and Submarines in berthing, un-berthing, turning and manoeuvering in confined waters and in harbour.
- They also provide afloat firefighting cover/assistance to ships alongside/anchorage and have limited capability for Search and Rescue operations.
- Induction of 50Ton Bollard Pull Tugs has significantly augmented the auxiliary support services and enhanced the capability to meet high operational requirements of Fleet assets of Indian Navy.
- Tugs “Veeran” and “Balraj” have been inducted on 22 Oct 2021 and 31 Dec 2021 at Naval Dockyard, Visakhapatnam respectively and “Balram” on 30 Oct 2021 at Naval Dockyard, Mumbai.
Criminal Justice Reforms:

Experts have expressed “serious concerns over the slow pace of reforms in the criminal justice system to ensure speedy justice”.
- The delay in disposal of cases was leading to human rights violations of the under-trials and convicts.
- Despite the Supreme Court’s directions on police reforms, there had been hardly any changes on the ground.
- Court orders convicting a person are also taking years to implement.
- Special laws and fast-track courts could replace certain offences under the Indian Penal Code in order to reduce the piling up of cases at every police station.
- Digitisation of documents would help in speeding up investigations and trials.
- The construction of new offences and reworking of the existing classification of offences must be guided by the principles of criminal jurisprudence which have substantially altered in the past four decades.
- The classification of offences must be done in a manner conducive to management of crimes in the future.
- The discretion of judges in deciding the quantum and nature of sentence differently for crimes of the same nature should be based on principles of judicial precedent.
Criminal law in India:
- The Criminal law in India is contained in a number of sources – The Indian Penal Code of 1860, the Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955, Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961 and the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989.
- Criminal Justice System can impose penalties on those who violate the established laws.
- The criminal law and criminal procedure are in the concurrent list of the seventh schedule of the constitution.
- Lord Thomas Babington Macaulay is said to be the chief architect of codifications of criminal laws in India.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has constituted a national level committee for reform in criminal law.
- The committee has been constituted under Ranbir Singh and several other members.
- The committee would be gathering opinions online by consulting with experts and collating material for their report to the government.
China-Taiwan Relations:
China recently flew 39 warplanes toward Taiwan in its largest such sortie of the new year, continuing a pattern that the island has answered by scrambling its own jets in response.
- China often mounts such missions to express displeasure at something Taiwan has done or at shows of international support for the democratically ruled island, especially by the United States, Taiwan’s main arms provider.
- China has described its activities as necessary to protect the country’s sovereignty and deal with “collusion” between Taipei and Washington.
- Chinese pilots have been flying towards Taiwan on a near-daily basis in the past year and a half, since Taiwan’s government started publishing the data regularly. The largest sortie was 56 warplanes on a single day last October.
- China has ramped up military pressure, including repeated missions by Chinese warplanes near democratic Taiwan, which Beijing claims as its own and has not ruled out taking by force.
- The European Parliament’s first official delegation to Taiwan recently come in support of Taiwan and said that the diplomatically isolated island is not alone. It called for bolder actions to strengthen EU-Taiwan ties as Taipei faces rising pressure from Beijing.
- Taiwan, which does not have formal diplomatic ties with any European nations except tiny Vatican City, is keen to deepen relations with members of the European Union.
Food Fortification:
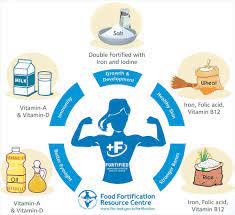
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India’s (FSSAI’s) Food Fortification Resource Centre (FFRC) has reported that over 70% of India’s population consumes less than half the daily recommended dietary allowance of micronutrients.
- These deficiencies are prevalent not only in women and children from rural areas but also affect population groups in urban India.
- In a bid to directly address anaemia and micronutrient deficiency in the country, the Centre recently approved a pilot scheme on “Fortification of Rice & its Distribution under Public Distribution System”.
- The government’s food fortification initiative is already taking shape with several states, including Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, Uttarakhand and Madhya Pradesh, starting the distribution of fortified rice under the pilot programme.
- Fortifying staple foods and condiments with key micronutrients is an effective way of addressing deficiencies.
- Timely adoption of food fortification in social and nutrition security programmes as a part of the fortification initiative will play a crucial role in addressing undernutrition in India.
- The country has high levels of malnutrition among women and children.
- According to the Food Ministry, every second woman in the country is anaemic and every third child is stunted.
- India ranks 94 out of 107 countries and is in the ‘serious hunger’ category on the Global Hunger Index (GHI).
- Malnutrition and lack of essential nutrients in poor women and poor children poses major obstacles in their development.
Food fortification :
- It is defined as the practice of adding vitamins and minerals to commonly consumed foods during processing to increase their nutritional value.
- It is a proven, safe and cost-effective strategy for improving diets and for the prevention and control of micronutrient deficiencies.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), defines fortification as “deliberately increasing the content of essential micronutrients in a food so as to improve the nutritional quality of food and to provide public health benefit with minimal risk to health”.
- According to the Food Ministry, fortification of rice is a cost-effective and complementary strategy to increase vitamin and mineral content in diets.
- According to FSSAI norms, 1 kg fortified rice will contain iron (28 mg-42.5 mg), folic acid (75-125 microgram) and Vitamin B-12 (0.75-1.25 microgram).
- In addition, rice may also be fortified with micronutrients, singly or in combination, with zinc (10 mg-15 mg), Vitamin A (500-750 microgram RE), Vitamin B1 (1 mg-1.5 mg), Vitamin B2 (1.25 mg-1.75 mg), Vitamin B3 (12.5 mg-20 mg) and Vitamin B6 (1.5 mg-2.5 mg) per kg.
- Since the nutrients are added to staple foods that are widely consumed, this is an excellent method to improve the health of a large section of the population, all at once.
- Fortification is a safe method of improving nutrition among people. The addition of micronutrients to food does not pose a health risk to people.
- It does not require any changes in food habits and patterns of people. It is a socio-culturally acceptable way to deliver nutrients to people.
- It does not alter the characteristics of the food—the taste, the feel, the look.
- It can be implemented quickly as well as show results in improvement of health in a relatively short period of time.
- This method is cost-effective especially if advantage is taken of the existing technology and delivery platforms.
Burkina Faso:

Burkina Faso’s army announced that it had ousted President Roch Kabore, suspended the constitution, dissolved the government and the national assembly, and closed the country’s borders.
- Army has toppled governments over the past 18 months in Mali and Guinea.
- The military also took over in Chad last year (2021) after President Idriss Deby died fighting rebels on the battlefield in the country’s north.
Burkina Faso:
- A former French colony, Burkina Faso has suffered chronic instability since gaining independence in 1960, including several coups.
- The country’s name, meaning “land of the honest men”, was picked by revolutionary military officer Thomas Sankara who took power in 1983. He was toppled and killed in 1987.
- Since 2015, the country has been fighting an Islamist insurgency that spilled over from neighbouring Mali. This has fuelled anger in the military and damaged the once important tourist industry.
- Landlocked Burkina Faso, one of West Africa’s poorest countries despite being a gold producer, has experienced numerous coups since independence from France in 1960.
- Islamist militants control swathes of Burkina Faso’s territory and have forced residents in some areas to abide by their harsh version of Islamic law, while the military’s struggle to quell the insurgency has drained scarce national resources.
- Kabore had faced waves of protests in recent months amid frustration over killings of civilians and soldiers by militants, some of whom have links to Islamic State and al Qaeda.
- The discontent escalated in November 2021, when 53 people, mainly members of the security forces, were killed by suspected jihadists.
Negative Ion Technology:
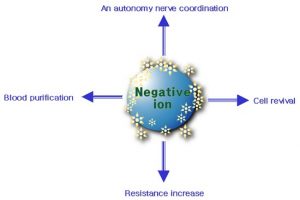
The Authority for Nuclear Safety and Radiation Protection (ANVS), Netherlands issued a statement identifying various negative ion wearable products containing more Radioactivity than legally permitted.
- Negative ion technology embeds negative ions in personal products and is currently being advertised as a means to maintain health, balance energy, and improve well-being.
- This technology is used in certain silicone wristbands, quantum or scalar-energy pendants, and kinesthesiology tape.
- Negative ions are also made when sunlight, radiation, air, or water break down oxygen.
- The minerals that produce these negative ions often include naturally occurring radioactive substances such as uranium and thorium.
- It is believed that negative ions create positive vibes and uplift the mood.
- They show the various mental and physical health benefits, such as stress reduction, better sleeping, respiration etc. whereas these ions may also act on pollutants, make them negatively charged and get them collected on surfaces.
Subhash Chandra Bose Awards For Disaster Management:

The Gujarat Institute of Disaster Management (GIDM) and Professor Vinod Sharma, the founder co-ordinator of the National Centre of Disaster Management, have been selected for the Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar for 2022 for their excellent work in disaster management.
- The GIDM was established in 2012 and since then it has been working to enhance the Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) capacity of Gujarat.
- Professor Vinod Sharma has worked tirelessly towards bringing DRR to the forefront of the national agend
- The central government has instituted the annual award —Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar—to recognise and honour the invaluable contribution and selfless service rendered by individuals and organisations in India in the field of disaster management.
- The award is announced every year on 23rd January, the birth anniversary of freedom fighter Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose.
- It carries a cash prize of Rs. 51 lakh and a certificate in the case of an institution and Rs. 5 lakh and a certificate in the case of an individual.




