Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:29th April 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- USCIRF Annual report-2020
- Raja Ravi Varma
- India Meteorological Department (IMD) has released a new list of names of tropical cyclones.
- Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2019
- Petersberg Climate Dialogue
- Human Challenge Trials
- BRICS Foreign Ministers Meet
- Global Report on Internal Displacement, GRID 2020
- Alzheimer disease
- Other important current affairs
1.USCIRF Annual report-2020:

The U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) has downgraded India to the lowest ranking, “countries of particular concern” (CPC) in its 2020 report.
- The report, released in Washington by the federal government commission that functions as an advisory body, placed India alongside countries, including China, North Korea, Saudi Arabia, and Pakistan. India was categorized as a “Tier 2 country” in last year’s listing.
- This is the first time since 2004 that India has been placed in this category.
- According to the report, India took a sharp downward turn in 2019, which included specific concerns about the Citizenship Amendment Act, the proposed National Register for Citizens, anti-conversion laws, and the situation in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The government of India reacted sharply to the USCIRF report on Tuesday, terming it “biased and tendentious” and rejected its observations.
2.Raja Ravi Varma:

April 29 is the birth anniversary of the famed Indian painter Raja Ravi Varma (1848-1906).
- He is remembered for giving Indians their western, classical representations of Hindu gods and goddesses.
- Through his printing press, Varma’s humanized depiction of Hindu pantheon travelled beyond the surfaces of costly canvases, and into the prayer and living rooms of working-class homes.
- He achieved this by making affordable lithographs, which were accessible even to the poor.
- Ravi Varma first started a press in Mumbai and later shifted it to a place near Lonavala.
- His 1873 painting, Nair Lady Adorning Her Hair, won Varma prestigious awards including Governor’s Gold Medal when it was presented in the Madras Presidency, and Certificate of Merit at an exhibition in Vienna.
- In 1904, the British colonial government awarded Varma with the Kaiser-i-Hind Gold Medal. In 2013, a crater on the planet Mercury was named in his honor.
3. India Meteorological Department (IMD) has released a new list of names of tropical cyclones over the north Indian Ocean including the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea.:

The new list comprises 169 names including 13 from India such as Gati, Tej, Aag, Neer, Vyom, Jhar, Jaladhi, Murasu, Probaho, Prabhanjan, Ghumi, Ambud and Vega.
- The new list starts with Nisarga (shared by Bangladesh), Gati (India), Nivar (Iran).
- Any tropical cyclone that hits the region is known by a name given in the list.
- Since the earlier list of 2004 is left with only one name – Amphan (shared by Thailand), the IMD being one of the six RSMCs in the world to provide tropical cyclone and storm surge advisories finalized the new list of 169 names.
- The naming of tropical cyclones (TCs) helps the scientific community, disaster managers, media and general masses to identify each individual cyclone; create awareness of its development; remove confusion in case of simultaneous occurrence of TCs over a region; remember a TC easily and rapidly and effectively disseminate warnings to a much wider audience.
cyclones named:
- Each Tropical Cyclone basin in the world has its own rotating list of names. For cyclones in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea, the naming system was agreed by eight member countries of a group called WMO/ESCAP and took effect in 2004.
- Cyclones are given many names in different regions of the world – They are known as typhoons in the China Sea and the Pacific Ocean; hurricanes in the West Indian islands in the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; tornados in the Guinea lands of West Africa and southern USA.; willy-willies in north-western Australia and tropical cyclones in the Indian Ocean
4.Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2019 :
NITI Aayog has questioned the methodology adopted by Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2019 to rank India as the seventh-worst terrorism affected country ahead of conflict-ridden countries such as the Democratic Republic of Congo, South Sudan, Sudan, Burkina Faso, Palestine and Lebanon.
- The Global Terrorism Index (GTI) is a report published annually by the Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP), a global think tank headquartered in Sydney, Australia.
- The index provides a comprehensive summary of the key global trends and patterns in terrorism since 2000. It produces a composite score in order to provide an ordinal ranking of countries on the impact of terrorism.
- The GTI is based on data from the Global Terrorism Database (GTD) which is collected and collated by the National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism (START) at the University of Maryland.
2019 index
- Deaths from terrorism fell for the fourth consecutive year, after peaking in 2014.
- Afghanistan has replaced Iraq as the country most affected by terrorism.
- India has moved to the seventh position from the previous year’s eighth in the annual Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2019.
- The countries ahead of it are Afghanistan, Iraq, Nigeria, Syria, Pakistan, and Somalia.
5.Petersberg Climate Dialogue:

Recently, the Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change attended the 11th Petersberg Climate Dialogue.
- The dialogue was held virtually for the first time in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Petersberg Climate Dialogue
- It has been hosted by Germany since 2010 to provide a forum for informal high-level political discussions, focusing both on international climate negotiations and the advancement of climate action.
- The virtual XI Petersberg Climate Dialogue was co-chaired by Germany and the United Kingdom (UK) and was attended by about 30 countries including India.
- The UK is the incoming Presidency of the 26th Conference of Parties (COP 26) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- COP 25 was held at Madrid, Spain in December 2019.
- This year’s dialogue was crucial because of the efforts to contain coronavirus as well as countries preparing to move into the implementation phase of the Paris Agreement 2015 in the post-2020 period.
India’s Contributions in the Dialogue:
- India expressed solidarity with the world as it combats the Covid-19 pandemic and emphasised on adopting more sustainable consumption patterns in line with the requirement of sustainable lifestyles.
- India suggested having climate technology as an open source available to all countries at affordable prices.
- India stressed on climate finance and urged to plan for 1 trillion USD in grants to the developing world immediately.
- India highlighted its Nationally Determined Contributions spanning a ten-year time frame and in compliance with the temperature goal of the Paris Agreement.
- India focused on the opportunity to accelerate renewable energy deployment and create new green jobs in the renewable energy and energy efficiency sector.
6.Human Challenge Trials:
In the race to develop a vaccine for the novel coronavirus, many people have volunteered to take part in the Human Challenge Trials (HCTs).
- It involves intentionally infecting volunteers with the novel coronavirus, in order to speed up the vaccination development.
Vaccine Development:
- In most of the regulatory regimes, vaccines take several years to develop and their development typically proceeds through three phases of clinical trials.
- Phase 1: Small groups of people receive the trial vaccine.
- Phase 2: Clinical study is expanded and the vaccine is given to people who have characteristics (such as age and physical health) similar to those for whom the new vaccine is intended.
- Phase 3: Vaccine is given to several thousand people and tested for efficacy and safety. During this phase, participants either receive the vaccine or a placebo.
- Placebo is anything which looks like real treatment but it is actually not. For example- sugar pills and saline injections
Human Challenge Trials:
- Under HCTs, participants of both the vaccine group and placebo group are deliberately exposed to the infection after their consent and thus are challenged by the disease organism.
- HCTs are not new and they are usually carried out in developing medications for diseases which are considered less lethal and have been better understood by scientists over the years like malaria.
- Few scientists have suggested replacing the conventional Phase 3 testing of vaccines by controlled HCTs of Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine which can accelerate the testing and potential rollout of efficacious vaccines.
- Such trials may reduce many months from the licensure process, making efficacious vaccines available more quickly and will also require significantly less number of people than regular Phase 3 trials.
- Ethical Concerns: HCTs for Covid-19 have been questioned by critics because it is a potentially deadly disease for even those who are less at risk, and has not been studied fully yet.
- In 2016, the World Health Organisation (WHO) emphasised on the ethical framework of the challenge studies and also highlighted the importance of informed consent.
- Human challenge studies should be conducted with abundant forethought, caution, and oversight.
- The value of the information to be gained should clearly justify the risks to human subjects.
7.BRICS Foreign Ministers Meet:

Recently, the External Affairs Minister of India attended the BRICS Foreign Ministers meet through video conferencing.
- This meeting was convened by Russia to discuss the impact of the coronavirus pandemic.
- BRICS nations have set up a “special loan instrument” of $15 billion funds for member nations to revive the economy amid Covid-19 pandemic
- BRICS nations exchanged views on possible joint measures to be taken by the member states to counter Covid-19 and overcome the financial, trade, economic and social consequences of the pandemic.
- India showcased its pharmaceutical support to around 85 countries to deal with the viral infection.
- It also highlighted the need for reforms in the multilateral bodies like the United Nations.
- The UN Security Council members are currently discussing draft resolutions on the Covid-19 pandemic.
BRICS
- BRICS is an acronym for the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies, namely Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- In 2001, the British Economist Jim O’Neill coined the term BRIC to describe the four emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, and China.
- The grouping was formalised during the first meeting of BRIC Foreign Ministers in 2006.
- South Africa was invited to join BRIC in December 2010, after which the group adopted the acronym BRICS.
8.Global Report on Internal Displacement, GRID 2020:

The Global Report on Internal Displacement, GRID 2020 released by Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre, IDMC said that over 5 million people have displaced in India in 2019. According to the report, this is the highest in the world.
- According to the report, around 33.4 million people faced displacements in the world due to conflicts and disasters. They are spread in 145 countries.
- In 2019, around 75% of the disasters were triggered by disasters. Out of these, 95% were due to weather hazards such as floods and storms.
- The disasters were dominant in the regions such as East Asia, South Asia and the Pacific.
- Of all, India, China, Bangladesh and the Philippines each recorded more than 4 million displacements in 2019.
India:
- According to the report, social and economic vulnerability, hazard intensity and high population were the major reasons for the displacement.
- The report says that 2.6 million people in India suffered displacement due to south-west monsoon.
- Around 19,000 faced displacement in the country due to conflicts.
- They were mainly high in the regions of West Bengal and Tripura.
9.Alzheimer disease:
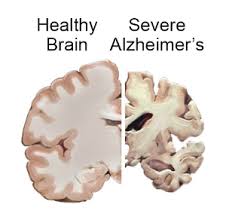
The scientists of Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) operating under the Department of Science and Technology has invented a natural product for Alzheimer disease.
Alzheimer:
- The disease is caused due to abnormal build-up of protein around the brain cells. Proteins are made up of amino acids. Therefore, the drug invented prevents the deposition of these proteins called Amyloid Beta around the brain cells.
- Alzheimer’s is a disorder that accounts for more than 70% of all types of dementia.
- It is difficult to develop effective medication for the disease as the disease attributes to multifaceted toxicity.
Ber-D
- The Ber-D invented prevents the generation of Reactive Oxygen Species.
- It rescues biomacromolecules from oxidative damages.
- It prevents the accumulation of metal-dependent and independent Amyloid Beta. Amyloid-Beta is the peptides of amino acids that build up around the brain cells.
- The Berberine used in traditional medicines has been converted into Ber-D. Ber-D is antioxidant and soluble. On the other hand, Berberine is toxic to cells and poorly soluble.
- The natural product called Isoquinoline is also used. Isoquinoline is found in India and China and has been used in traditional medicines.
Other important current affairs:
1. The government has announced around 11 % increase in annual central allocation of cooking cost under Mid-day meal scheme to 8,100 crore rupees in view of the situation arising out of COVID-19.
- With a view to enhancing enrolment, retention and attendance and simultaneously improving nutritional levels among children, the National Programme of Nutritional Support to Primary Education (NP-NSPE) was launched as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme in 1995. In 2001 MDMS became a cooked Mid Day Meal Scheme.
- The Mid-Day Meal Scheme covers children of classes I-VIII studying in government, government-aided schools, special training centres (STC) and madrasas/ maqtabs supported under Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA).
- It is the largest school feeding programme in the world.
- The Midday Meal Scheme is covered by the National Food Security Act, 2013.
2. The Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $1.5 billion loan to support India’s COVID-19 immediate response.
- They signed the loan agreement for the ADB’s COVID-19 Active Response and Expenditure Support Programme (CARES Programme).
- It will be used to implement
- (i) COVID-19 containment plan to rapidly ramp up test-track-treatment capacity, and
- (ii) social protection for the poor, vulnerable, women, and disadvantaged groups to protect more than 800 million people over the next three months.
- Established in 1966, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) is owned by 68 members—49 from the Asia and the Pacific region. It is Headquartered in Manila, Philippines.
3. According to a report published by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), the pollution in Ganga has not reduced significantly during the lockdown.
- The CPCB assessed pollution a week before lockdown and weeks after at 36 locations in Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal.
- The Dissolved Oxygen (DO) concentration improved marginally.
- There are a gradual increase in Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) levels towards downstream stretches of the river, with the maximum values in West Bengal.
- There is a marginal reduction in Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) levels which is attributed due to the stoppage of industrial activities.
- The pollution in Ganga is highest in Uttar Pradesh.
- Domestic wastewater from 97 towns situated near river Ganga, and industrial effluents, are the main sources of water pollution in the river.
- There was a notable improvement in water quality in the Yamuna.
4. The Centre has decided to utilize the forthcoming monsoon season to expand its water conservation efforts under the Jal Shakti Abhiyan.
- Such interventions would ensure water source sustainability in rural areas and would strengthen the ongoing Jal Jeevan Mission being implemented by the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- The Jal Shakti Abhiyan was launched by the Ministry of Jal Shakti in 2019.
- It is a campaign for water conservation and water security in the country through a collaborative effort of various ministries of the Government of India and state governments.
- The focus of the campaign is on water-stressed districts and blocks.
5. Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation has stated that the APEC region is to face an economic decline of 2.7% in 2020 due to the impact of COVID-19. Also, the region is to face near growth rate.
- This will be the highest decline for the region since the 2008 financial crisis.
- The unemployment rate according to the report of APEC was 3.8% in 2019 and it is to increase to 5.4% in 2020.
- The region is also expected to face an economic rebound in the year 2021. The anticipated growth of the region in 2021 is 6.3%.
6. The robotic device HCARD, Hospital Care Assistive Robotic Device was launched to help frontline health care workers. The robot will help them in maintaining physical distance from the COVID-19 infected persons.
- The HCARD was developed by CSIR laboratory located in Durgapur.
- The device is capable of working in both automatic and manual mode.
- It can be monitored and controlled using a control station or a nursing booth.
- The cost of the device is Rs 5 lakhs and it weighs 80 kilograms.
- The HCARD works on war footing mechanism to reduce the impact of COVID-19 through technological interventions.
- The device has drawers that will provide food to patients. The device will also collect samples from patients.
7.South Asia Seasonal Climate Outlook Forum.:
- The spatial forecast which shows wide variations in rainfall across India has been provided by the South Asia Seasonal Climate Outlook Forum.
- South Asian nations, supported by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), have been conducting the SASCOF since 2010.
- SASCOF is a consortium of meteorologists and hydrological experts from South Asian countries, including Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Maldives and Myanmar.
- They work collectively to issue regional forecasts and the team releases forecasts for the Southwest and Northeast monsoon seasons, every year.
- The experts usually meet ahead of preparing the forecasts, but it was called off in 2020 in the wake of Covid-19.




