Today’s Current Affairs: 29th Dec 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
International Financial Services Centres Authority : Global Hub Of Sustainable Finance

The Prime Minister, during his speech at the Infinity Forum 2.0, emphasised making International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) a global hub of Sustainable Finance.
- International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) has undertaken numerous regulatory initiatives for the development of financial instruments at IFSC to facilitate capital flows towards climate action in India and other developing countries.
- International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) establishment in April 2020.
- HQ: GIFT City, Gandhinagar in Gujarat.
- IFSCA is a unified authority for the development and regulation of financial products, financial services, and financial institutions in international financial services centres.
- It is a statutory authority established under the International Financial Services Centres Authority Act, 2019 (“IFSCA Act”).
- Objective is to develop and regulate the financial products, financial services, and financial institutions in the International Financial Services Centres (‘IFSC’).
P-Note Surge In Indian Markets:

In November 2023, there was an increase in participatory note investments, reaching a total of ₹1.31 lakh crore.
- Participatory Notes (P-Notes) are financial instruments used by foreign investors who wish to invest in Indian markets without directly registering with the market regulator, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- They are issued by registered foreign institutional investors (FIIs) or their sub-accounts against underlying Indian securities.
- While P-Notes offer flexibility and ease of investment, they have been a subject of regulatory scrutiny due to concerns about their potential use in money laundering, round-tripping, and lack of transparency.
Crech Scheme:

The Union Women and Child Development Ministry plans to set up 17,000 creches within Anganwadi centers across India under the ‘Palna’ scheme.
- This initiative aims to provide safe day-care facilities, enhancing the cognitive, nutritional, and health development of children.
- With an increased participation rate of women in the workforce, reaching 37% in 2022, this expansion of creches signifies a concerted effort to support women while nurturing the development of future generations.
- In July 2022, the Ministry of Women and Child Development revamped the National Creche Scheme into the Palna Scheme under ‘Mission Shakti.’
- This transformation brought about Anganwadi cum Creches and reclassified existing creches from the old scheme as Stand Alone Creches.
Global Risk Survey 2023 By PwC:

According to the Global Risk Survey 2023 by PwC, a global consultancy firm, Cyber risks are the biggest threat faced by Indian organizations.
Highlights of the Global Risk Survey 2023:
- Cyber risks are cited as the biggest threat faced by Indian organizations, with 38% of respondents feeling highly or extremely exposed to it.
- Climate change (37%) and inflation (36%) rank second and third among the top threats to Indian organizations.
- Digital and technology risks rank fourth, with 35% of Indian business leaders concerned about these risks
- Indian organizations are proactively investing in cybersecurity, with over half planning investments in cybersecurity tools (55%) and AI-related technologies (55%) in the next 1–3 years, aligning with global trends (51% and 49%, respectively).
- The survey also revealed how organizations are using emerging technologies such as Generative Artificial Intelligence for risk management, with 48% of Indian enterprises having deployed AI and machine learning for automated risk assessment and response to a large extent. This is slightly lower than the global response of 50%.
- 42% of Indian organizations grapple with heightened security vulnerabilities attributed to legacy technologies (Outdated technology systems and infrastructure), surpassing the global average of 36%.
- Moreover, 46% of Indian companies face increased maintenance costs due to legacy tech, limiting budgets for innovative risk solutions, exceeding the global figure of 39%.
- 88% of Indian organizations have actively invested in resilience building over the past year, surpassing the global average of 77%.
- Resilience Investments include a resilience team, comprising members from functions such as business continuity, cyber, crisis management and risk management to swiftly respond to risk events as they occur.
Aardvarks : Earth Pig

A recent study from Oregon State University found that a warming climate is negatively impacting the chances of long-term survival of aardvarks in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Aardvarks gets its name from a South African word meaning “earth pig.”
- They look like a pig, especially with its body and snout. But they actually share common ancestors with elephants and golden moles.
- They are nocturnal mammals, most active at night and tend to live alone. During the day, they sleep curled up in a ball in their burrows.
- This species has been assessed as having the highest score for evolutionary distinctiveness. This is because it does not have many close relatives and has been evolving independently for millions of years.
- The Aardvark is the sole surviving species of its order, Tubulidentata, and its closest relatives have been extinct since the Pleistocene era (2 million years ago).
- Aardvarks are important in their ecosystem because the holes they dig are used by a variety of other animals for shelter.
- Conservation Status :IUCN: Least Concern
Huntington’s Disease:
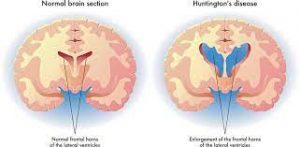
Researchers from the University of Szeged, in Hungary, have taken some important strides by studying fruit flies to understand more about Huntington’s disease.
- Huntington’s disease is a rare, inherited disease that causes the progressive breakdown (degeneration) of nerve cells in the brain.
- It has a wide impact on a person’s functional abilities and usually results in movement, thinking (cognitive) and psychiatric disorders.
- There are two types of Huntington’s disease:
- Adult onset: This is the most common form. Symptoms usually begin after age 30.
- Early onset (juvenile Huntington’s disease): Early onset affects children and teenagers. It’s very rare. When Huntington’s develops early, symptoms are somewhat different and the disease may progress faster.
- A genetic change (mutation) of the HTT gene causes Huntington’s disease. The HTT gene makes a protein called huntingtin. This protein helps your nerve cells (neurons) function.
- The normal HTT gene contains a stretch of DNA that specifies the number of times the amino acid glutamine is repeated in the HTT This number varies from 11 to 31.
- In the mutant versions of the HTT gene, this stretch is expanded to encode 35 or more repeats.
- As the number of repetitions increase, the severity of Huntington’s disease increases and its debilitation begins at an earlier age.
- Huntington’s disease usually causes movement, cognitive and psychiatric disorders with a wide spectrum of signs and symptoms.
- The patient suffers mood swings, has difficulty in reasoning, shows abnormal and uncontrollable jerky movements, and experiences difficulty in speaking, swallowing, and walking.
- Treatment: Medications are available to help manage the symptoms of Huntington’s disease. But treatments can’t prevent the physical, mental and behavioural decline associated with the condition.
Smart Lander For Investigating Moon (SLIM) Mission : Japan

Japan’s Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) spacecraft entered into orbit around the moon after months-long journey.
- Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) Mission is a spacecraft built and launched by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) on September 7, 2023, from the Tanegashima spaceport.
- It weighed only 590 kg.
- It was launched together with XRISM, a next-generation X-ray space telescope, onboard an H-2A rocket.
- It entered into an elliptical orbit around the moon over three minutes or so.
- Its apogee (farthest point) in this orbit is 4,000 km and perigee (closest point) is 600 km above the lunar surface.
- SLIM will deploy two small rovers called Lunar Excursion Vehicle (LEV) 1 and 2. LEV-1, LEV-2, and SLIM will together study the lunar surface near the landing point, collect temperature and radiation readings, and attempt to study the moon’s mantle.
XRISM Mission:
- The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) is a joint mission of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), involving contributions from the European Space Agency (ESA).
- The mission aims to observe X-rays coming from deep space and to identify their wavelengths with unprecedented precision.
- It will use state-of-the-art spectroscopy to measure changes in the brightness of celestial objects at different wavelengths.
- It detects X-rays with energies ranging from 400 to 12,000 electron volts. (For comparison, the energy of visible light is 2 to 3 electron volts.)
- This range will provide astrophysicists with new information about some of the universe’s hottest regions, largest structures, and objects with the strongest gravity.
Tansen Samaroh:

1,300 musicians played Vande Mataram on tabla to enter the Guinness World Record for the “largest table ensemble” during the ongoing 99th International Tansen Samaroh in Gwalior.
- Tansen Samaroh is a tribute to Indian musical legend, Shri Ramtanu Misra, famously known as Tansen.
- It is held every year in December in Gwalior to celebrate Tansen.
- Artists and music lovers from all over the world gather here to pay tribute to the Great Indian Musical Maestro Tansen.
Tansen :
- He was a vocalist, instrumentalist and music composer.
- He is credited as the founder of the Hindustani classical music.
- He was one of the Navratnas (Nine gems) in Emperor Akbar’s court.
- Akbar considered him as a Navaratnas (nine jewels), and gave him the title Mian, an honorific, meaning learned man.
- Tansen is remembered for his epic Dhrupad compositions, creating several new ragas, as well as for writing two classic books on music Sri Ganesh Stotra and Sangita Sara.
Wang’s Garden Lizard : New Reptile Species

A new reptile species was recently discovered in China and has been called Wang’s Garden Lizard.
- Wang’s Garden Lizard is a new species of iguana.
- Scientific Name: Calotes wangi
- It is found in subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests and tropical monsoon forests in southern China and northern Vietnam, mostly in mountainous areas, hills and plains on forest edges, arable land, shrub lands, and even urban green belts.
- It is not threatened at present. However, in some areas, their habitat was being fragmented.
- It is less than 9 cm long, and one of its distinguishing features is its orange tongue.
- It is active at the edge of the forest, and when it is in danger, it rushes into bushes or climbs tree trunks to hide.
- It lies on sloping shrub branches at night, sleeping close to the branches.
Eurasian Otter : Discovered

A team of researchers recently discovered a Eurasian otter in the Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary in Idukki, a first in Kerala.
- Eurasian Otter is a semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal native to Eurasia.
- Scientific Name: Lutra lutra
- It has one of the widest distributions of all Palearctic mammals, from Ireland to China and down to Southeast Asia.
- It lives throughout Europe, North Africa, and Asia.
- It inhabits streams, rivers, lakes, freshwater and peat swamp forests, ocean shores, rice fields, fjords, caves, and other terrestrial habitats close by waterways.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Near threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule II
- CITES: Appendix I
Executive Chairperson Of The National Legal Services Authority:

The President recently nominated Justice Sanjiv Khanna, the second senior-most judge of the Supreme Court, as the Executive Chairperson of the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA).
- NALSA has been constituted under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, to provide free legal services to the weaker sections of society and to organise Lok Adalats for amicable settlement of disputes.
- The prime objective of NALSA is the speedy disposal of cases and reducing the burden on the judiciary.
- The Chief Justice of India is the patron-in-chief of NALSA, while the second senior most judge of the Supreme Court of India is the Executive Chairman.
- It is housed at the Supreme Court of India, New Delhi.
- In every State, a State Legal Services Authority and in every High Court, a High Court Legal Services Committee has been constituted.
- District Legal Services Authorities and Taluk Legal Services Committees have been constituted in the Districts and most of the Taluks to give effect to the policies and directions of the NALSA, and to provide free legal services to the people, and conduct Lok Adalats in the State.
- NALSA, through the State Legal Services Authorities, also conducts legal literacy programmes.
- The free legal services include:
- Payment of court fees, process fees, and all other charges payable or incurred in connection with any legal proceedings;
- Providing the service of lawyers in legal proceedings;
- Obtaining and supply of certified copies of orders and other documents in legal proceedings.
- Preparation of appeal, paper book, including printing and translation of documents in legal proceedings.
Foreign Exchange Management Act : RBI Released a Draft

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently released a draft ‘Licensing Framework for Authorised Persons (APs)’ under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999.
- FEMA came in 1999 as a successor to the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, or FERA, of 1973, with changing economic conditions in a post-liberalisation India.
- The main objective of FEMA is to facilitate external trade and payments and promote the orderly development and maintenance of the foreign exchange market in India.
- FEMA deals with provisions relating to procedures, formalities, dealings, etc. of foreign exchange transactions in India.
- The FEMA regulates various aspects of foreign exchange transactions, including the acquisition and holding of foreign exchange, the payment and settlement of foreign exchange transactions, the export and import of currency, and other related activities.
- The act also empowers the RBI to make rules and regulations to carry out the provisions of the act.
- Violations of the provisions of FEMA can result in penalties and fines.
- FEMA’s head office is known as the Enforcement Directorate and is situated in Delhi.
- It is applicable to the whole of India and equally applicable to the agencies and offices located outside India (which are owned or managed by an Indian Citizen).
- Section 2(c) of the FEMA states that ‘authorised person’ means an authorised dealer, money changer, off-shore banking unit, or any other person authorised under section 10 (1) to deal in foreign exchange and foreign securities.
- These are authorised by the RBI to deal in foreign exchange or in foreign securities.




