Today’s Current Affairs: 4th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Standard Essential Patents:

There is a concern over the manner in which certain technology companies are wielding ‘standard essential patents’ (SEP) against the telecom manufacturing sector in India.
- Standard Essential Patent (SEP) is a patent granted for a technological invention which is essential for the implementation and working of a standard.
- Patents which are essential to a standard and have been adopted by a Standard Setting Organization (SSO) are known as SEPs.
- SSOs are either governmental, quasi governmental, or a private group of independently governed industry associations.
- SSOs set, develop, coordinate, interpret and maintain standards.
- Industry participants can collaborate on a single technical solution because of such standards.
- When a patent is acknowledged by the SSO and designated as a SEP, manufacturers can only produce their goods in the market after first acquiring a license under the SEP.
- From an antitrust standpoint, the lack of any competing technology grants the SEP holder a monopolistic right over the SEP.
- It is impossible to produce products that comply with standards without using technologies that are covered by one or more SEPs.
- SEPs are common in the mobile telephony and telecommunications industry, a sector which is highly standardised due mainly to the need for interoperability between mobile devices.
Shaksgam Valley : In News

India has lodged a strong protest with China for carrying out construction activities in the Shaksgam valley, in an “illegal” attempt to alter the situation on the ground.
- The Shaksgam Valley, or Trans Karakoram Tract, is part of the Hunza-Gilgit region of Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (POK) and is a disputed territory claimed by India.
- It borders Xinjiang Province of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) to the north, the Northern Areas of POK to the south and west, and the Siachen Glacier region to the east.
- It was ceded to China by Pakistan in 1963, when both countries signed a boundary agreement to settle their border differences.
- The agreement clearly stated that “the two parties have agreed that after the settlement of the Kashmir dispute between Pakistan and India, the sovereign authority concerned will reopen negotiations with the Government of the People’s Republic of China, on the boundary as described in Article Two of the present agreement, so as to sign a formal Boundary Treaty to replace the present agreement.”
- The agreement laid the foundation of Karakoram highway, which was built jointly by Chinese and Pakistani engineers in the 1970s.
Batillipes chandrayaani : New Species Of Marine Tardigrade

A new species of marine tardigrade discovered from the southeast coast of Tamil Nadu has been named Batillipes chandrayaani after the Chandrayaan-3.
- Batillipes chandrayaani has been discovered in the intertidal beach sediments at Mandapam in Tamil Nadu.
- It is similar in size to other tardigrades, it grows to a length of 0.15 millimetres and 0.04 millimetres in width.
- It has a trapezoid-shaped head and four pairs of legs with sharp-tipped sensory spines. Both sexes are similar in terms of morphology and size.
- It is also the 39th species described under the genus Batillipes
- Tardigrades are microscopic marvels commonly known as ‘water bears,’
- Marine tardigrades account for 17% of all known tardigrade species.
- They are also found in all the oceans.
Five Eyes Intelligence-Sharing Network : Accused India

4 countries on 3 continents, which are part of the Five Eyes intelligence-sharing network has been, accused India for running espionage operations.
- Five Eyes Intelligence-sharing Network is a multilateral intelligence-sharing network shared by over 20 different agencies of five English-speaking countries Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States.
- It is both surveillance-based and signals intelligence (SIGINT).
- Its genesis lies in the post-war 1946 UKUSA Agreement, intended as a cooperative arrangement for sharing signals intelligence (SIGINT).
- Intelligence documents shared between the members countries are classified as ‘Secret—AUS/CAN/NZ/UK/US Eyes Only,’ which gave the group its title ‘Five Eyes’.
- Its scope was limited to “communication intelligence matters only” related to “unrestricted” exchange of intelligence products in six areas:
- Collection of traffic; acquisition of communication documents and equipment; traffic analysis; cryptanalysis; decryption and translation; and acquisition of information regarding communication organisations, practices, procedures, and equipment.
- The arrangement was later extended to ‘second party’ countries —Canada joined in 1948, while Australia and New Zealand became part of the alliance in 1956.
Commission On Population And Development : Session

The Permanent Mission of India to the United Nations and the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, in collaboration with the United Nations Population Fund is organizing event titled “Localizing the SDGs: Women in Local Governance in India Lead the Way” during the 57th Session of the Commission on Population and Development (CPD57).
- Commission on Population and Development was established by the Economic and Social Council(ECOSOC) in 1946, which was renamed as the Commission on Population and Development by the General Assembly in 1994. It is composed of 47 member countries.
- Member countries are elected by the Economic and Social Council for a period of four years on the basis of geographic distribution.
- It was constituted as three-tiered intergovernmental mechanism that plays the primary role in the follow-up to the implementation of the programme of action at the national, regional and international levels and advise the Council thereon.
- The meetings of commission were held typically every two or three years until 1994, after which it has been held once a year
H5N1 Outbreak:

The H5N1 outbreak has highlighted critical vulnerabilities in the industrial livestock sector, underlining the imperative for a comprehensive reassessment of animal welfare within India’s environmental and legal frameworks.
- This outbreak reinforces the One Health principle, which integrates public health, ecosystem health, and biodiversity conservation.
- Regular outbreaks of Avian Influenza (bird flu) disrupt production, lead to the culling of birds, and create market panic, impacting consumption.
- ND is another highly contagious viral disease that affects poultry health and productivity.
- Inadequate biosecurity measures in farms and live bird markets facilitate the spread of diseases.
- Chickens in industrial settings are often confined in wired cages, known as ‘battery cages,’ in high densities, leading to overcrowding and stress.
- This practice leads to poor air quality, waste accumulation, and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to environmental pollution and degradation.
- Volatile prices of crucial poultry feed ingredients, such as corn and soybean meal, not only affect production costs but also exacerbate import dependence due to their significant reliance on imports.
- Rumors and misinformation surrounding poultry products during disease outbreaks can drastically reduce consumption, affecting overall market stability.
- It leads to spoilage and wastage, especially during peak production periods.
- A fragmented supply chain with multiple intermediaries raises transaction costs and lowers farmer profits, while poor transportation infrastructure hampers product movement, affecting delivery times and freshness.
Paradox Of Savings:

The paradox of savings, or the paradox of thrift, has been a topic of interest in economic discussions due to its implications on how personal savings behaviors might negatively affect broader economic growth.
- This counterintuitive economic concept has resurfaced in news and analyses, particularly in times of economic downturns, where the balance between saving and spending becomes crucial to policy debates on how best to stimulate recovery and sustain economic stability.
- The paradox of savings, also known as the paradox of thrift, suggests that while individual savings are ostensibly good, an increase in overall savings rates across an economy may lead to a decrease in total economic savings.
- This theory contrasts with the intuitive belief that higher personal savings directly contribute to increased economic savings.
6th International Conference On Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (ICDRI) 2024:

The Prime Minister of India addressed the 6th International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (ICDRI) 2024.
- ICDRI is the annual international conference of the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) in partnership with member countries, organisations and institutions
- It aim to increase the resilience of infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks, thereby ensuring sustainable development.
- CDRI was launched in 2019, at the United Nations Climate Action Summit in New York. It is India’s second major global initiative after the International Solar Alliance (ISA).
- The CDRI Secretariat is based in New Delhi, India..
- India launched this initiative and it focuses on building capacity, having pilot projects in Small Island Developing States or SIDS.
- It is a fund supported by both the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR).
- Few other CDRI programs are the resilient housing in Dominica, resilient transport networks in Papua New Guinea, and enhanced early warning systems in the Dominican Republic and Fiji.
Conflict Minerals:

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has accused Apple of using conflict minerals.
- The DRC accuses Apple of purchasing minerals that have been smuggled out of the country into neighbouring Rwanda.
- These minerals are then integrated into Apple’s global technology supply chain, where their origin is allegedly obscured.
- Conflict minerals, also known as “blood minerals,” are extracted from regions affected by armed conflict or human rights abuses.
- These minerals play a significant role in funding violence and wars.
- These minerals play a crucial role in various industries, including electronics, automotive, and renewable energy.
- The DRC is rich in untapped reserves of precious metals and minerals.
- The primary conflict minerals include: Tin , Tantalum, Tungsten, Gold.
- These minerals are extracted from ores such as cassiterite (tin), columbite-tantalite (tantalum), and wolframite (tungsten).
Ajrakh From Kutch Gets GI Tag:

Ajrakh’s GI tag was granted by the Geographical Indications Registry after a long process of documentation and verification of its origin and production techniques.
- The Ajrakh fabric is a traditional hand-block printing technique that originated in Kutch, Gujarat.
- It uses natural dyes and intricate patterns to create beautiful textiles, which are then used to make sarees, dupattas, stoles, and other garments.
- The unique feature of Ajrakh is its use of geometric patterns and rich earthy colours like indigo, madder, and mustard.
- This fabric has been an integral part of the Kutchi culture for centuries and has now gained recognition on a global level with its GI tag.
Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB):
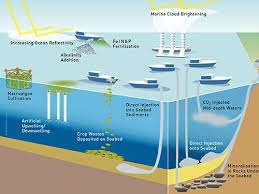
Scientists are testing a geoengineering technique called marine cloud brightening that involves using machines to inject tiny saltwater particles into marine stratocumulus clouds, aiming to increase their reflectivity and cool the Earth.
- The Brightening clouds is one of several ideas to push solar energy back into space sometimes called solar radiation modification, solar geoengineering, or climate intervention.
- Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB) is a scientific initiative that explores how altering atmospheric particles (aerosols) can impact cloud reflectivity
- By releasing tiny aerosol particles into the atmosphere, researchers aim to enhance cloud brightness, leading to increased sunlight reflection.
- Aerosols of the right size and concentration could significantly increase the reflectivity of specific types of clouds.
- This phenomenon is visible in satellite images of clouds brightened by ship emissions (known as “ship tracks”).
- It helps in better understanding of the present-day effects of pollution aerosols on clouds.
- Investigate whether aerosol particles made from sea salt could be used to intentionally reduce near-term climate warming while greenhouse gas concentrations are brought down to safer levels.




