Today Current Affairs: 4th September 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Turtle Survival Alliance (TSA):

Indian biologist Shailendra Singh has been awarded the Behler Turtle Conservation Award for bringing three critically endangered turtle conservation species back from the brink of extinction- Red-crowned Roofed Turtle (Batagur kachuga), Northern River Terrapin (Batagur baska), and Black Softshell Turtle (Nilssonia nigricans)
- This award is bestowed by several global bodies involved in turtle conservation such as Turtle Survival Alliance, IUCN/SSC Tortoise and Freshwater Turtle Specialist Group, Turtle Conservancy, and the Turtle Conservation Fund.
- There are 29 species of freshwater turtles and tortoises in the country.
- Tortoises have more rounded and domed shells where turtles have thinner, more water-dynamic shells. Tortoises spend most of their time on land and turtles are adapted for life spent in water.
- The Turtle Survival Alliance (TSA) was formed in 2001 as an International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) partnership for sustainable captive management of freshwater turtles and tortoises, and initially designated a Task Force of the IUCN Tortoise and Freshwater Turtle Specialist Group.
An anti-trust Case Filed Against Apple Inc:

An anti-trust case filed against Apple Inc for allegedly abusing its market position in the Indian economy.
- Apple is instituting policies that forces developers to use its proprietary in-app purchase system
- This allegation is similar to what Apple faced in the EU where regulators last year started an investigation into Apple’s imposition of an in-app fee of 30% for distribution of paid digital content and other restrictions.
- Such policies hurt the domestic companies by raising their cost of doing business
- Competition Commission of India (CCI) will review the case and could order its investigations arm to conduct a wider probe, or dismiss it altogether if it finds no merit in it
- Filings and details of cases reviewed by the Competition Commission of India (CCI) are not made public.
- Recently, South Korea’s parliament this week approved a bill that bans major app store operators like Alphabet Inc’s Google and Apple from forcing software developers to use their payment systems.
- Justification given by the companies for their current policy: The fees levied by them covers the security and marketing benefits their app stores provide for companies
- CCI is conducting an investigation into a similar payment system concerning Google
Increase In Numbers Of Migratory Birds Visiting The Pulicat Lake In India:

This positive development is largely due to increase in the storage levels in the reservoir in adjoining areas
- Pulicat lake is the second largest brackish water lake in the country; next only to Chilika lake
- Greater flamingos and pelicans are some of the famous migratory birds that visit this place
- The region in which Pulicat lake is situated receives rainfall from both South-West as well as North-East monsoon winds
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary is a famous bird sanctuary located near this lake
- The lake is also home for black-headed ibis, Asian openbill, black-crowned night heron, and little cormorant. Other migratory birds that visit the sanctuary include northern pintail, common teal, little grebe, northern shoveler, Eurasian coot, Indian spot-billed duck, grey heron, Oriental darter, black-winged stilt, garganey and gadwall
- The presence of Barringtonia and Acacia nilotica species near the Pulicat lake region provides an ideal breeding site for spot-billed pelicans.
About Pulicat Lake and Nelapattu bird sanctuary
- Nelapattu bird sanctuary is considered one of the biggest habitats for some hundreds of pelicans and other birds. Located about 20 km north of the Pulicat Lake on the Andhra Pradesh-Tamil Nadu border, the sanctuary is spread in about 459 hectares.
- Pulicat Lake is the second largest brackish water lake or lagoon in India, after Chilika Lake.
- It straddles the border of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu states with over 96% of it in Andhra Pradesh.
- The lake encompasses the Pulicat Lake Bird Sanctuary.
- Flamingo Festival is held every year to promote tourism in Pulicat and Nelapattu.
State Animal And Bird: Ladakh:

Ladakh has adopted Snow Leopard and Black-Necked Crane, as State animal and State bird, two years after it was carved out as a separate Union Territory (UT) from the erstwhile State of J&K (Jammu and Kashmir).
Snow Leopard:
- Snow leopards (Panthera uncia) act as an indicator of the health of the mountain ecosystem in which they live, due to their position as the top predator in the food web.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN: Vulnerable.
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Schedule I
- It is also listed in the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS), affording the highest conservation status to the species, both globally and in India.
Black-Necked Crane:
- The black-necked crane (Grus nigricollis), also known as Tibetan crane, is a large bird and medium-sized crane.
- Both the sexes are almost of the same size but male is slightly bigger than female.
- A conspicuous red crown adorns the head.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- CITES: Appendix I
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
State Of The World’s Trees Report

Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) launched the State of the World’s Trees Report.
- The report warns that almost a third of the world’s tree species are at risk of extinction, while hundreds are on the brink of being wiped out.
- BGCI is a membership organisation, representing botanic gardens in more than 100 countries around the world.
- It is an independent UK charity established in 1987 to link the botanic gardens of the world in a global network for plant conservation.
Species Under Threat:
- 17,500 tree species which is some 30% of the total – are at risk of extinction, while 440 species have fewer than 50 individuals left in the wild.
11% of the flora or plant life of every country was made up of threatened species. - Overall the number of threatened tree species is double the number of threatened mammals, birds, amphibians and reptiles combined.
Most At-Risk Trees:
- Among the most at-risk trees are species including magnolias and dipterocarps – which are commonly found in Southeast Asian rainforests. Oak trees, maple trees and ebonies also face threats.
Countries with Highest Risk:
- Thousands of varieties of trees in the world’s top six countries for tree-species diversity are at risk of extinction.
- The greatest single number is in Brazil, where 1,788 species are at risk. The other five countries are Indonesia, Malaysia, China, Colombia and Venezuela.
- There were also 27 countries that had no threatened species of trees.
Island Trees:
- Though megadiverse countries see the greatest numbers of varieties at risk of extinction, island tree species are more proportionally at risk.
- This is particularly concerning because many islands have species of trees that can be found nowhere else.
Major Threats:
- The top three threats facing tree species are crop production, timber logging and livestock farming, while climate change and extreme weather are emerging threats.
- At least 180 tree species are directly threatened by rising seas and severe weather, especially island species such as magnolias in the Caribbean.
Botanic Gardens Conservation International:
- It is a plant conservation charity based in Kew, London, England.
- It is a membership organisation, working with 800 botanic gardens in 118 countries, whose combined work forms the world’s largest plant conservation network.
- Headquarters location: Richmond, United Kingdom
- Founded: 2003
Report On Weather Disasters: WMO:

The World Meteorological Organization (WMO), has released a report, which stated that weather disasters killed 2 million in the last 50 years.
- WMO has published ‘Atlas of Mortality and Economic Losses from Weather, Climate and Water Extremes, from 1970 to 2019’.
- WMO is a specialized agency of the United Nations.
Findings of the Report:
- No. of Disasters: The number of disasters has increased by a factor of five over the 50-year period, driven by climate change, more extreme weather and improved reporting.
- From 1970 to 2019, weather, climate and water hazards accounted for 50% of all disasters, 45% of all reported deaths and 74% of all reported economic losses.
- More than 91% of these deaths occurred in developing countries.
- Droughts, storms, floods and extreme temperature were the leading causes.
- Decreasing Number of Deaths: Due to improved early warning systems and disaster management, the number of deaths decreased almost threefold between 1970 and 2019.
- Spiralling Costs: During the 50-year period, US$ 202 million dollars in damage occurred on average every day.
- Economic losses have increased sevenfold from the 1970s to the 2010s.
- Storms, the most prevalent cause of damage, resulted in the largest economic losses around the globe.
- Climate Change Footprints: The number of weather, climate and water extremes are increasing and will become more frequent and severe in many parts of the world as a result of climate change.
- More water vapor in the atmosphere has exacerbated extreme rainfall and flooding, and the warming oceans have affected the frequency and extent of the most intense tropical storms.
- This has augmented the vulnerability of low-lying megacities, deltas, coasts and islands in many parts of the world.
- Failure of Sendai Framework: The report also warned that the failure to reduce disaster losses as set out in the 2015 Sendai Framework is putting at risk the ability of developing countries to eradicate poverty and to achieve other important Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Sendai Framework 2015 was adopted at the Third United Nations World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction, held in 2015 in Sendai, Miyagi, Japan.
- The present Framework applies to the risk of small-scale and large-scale, frequent and infrequent, sudden and slow-onset disasters caused by natural or man-made hazards, as well as related environmental, technological and biological hazards and risks.
e-ILP Platform : For Effective Regulation Of The Inner Line Permit (ILP) System:
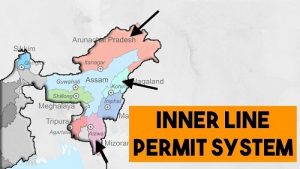
The Chief Minister of Manipur virtually launched the e-ILP platform for effective regulation of the Inner Line Permit (ILP) system in the state.
- The ILP system came into effect in Manipur on 1st January 2020.
- In Manipur, four types of permits are issued – temporary, regular, special and labour permits.
- Under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation Act, 1873, the British framed regulations restricting the entry and regulating the stay of outsiders in designated areas.
- This was to protect the Crown’s own commercial interests by preventing “British subjects” (Indians) from trading within these regions.
- In 1950, the Indian government replaced “British subjects” with “Citizen of India”.
- This was to address local concerns about protecting the interests of the indigenous people from outsiders belonging to other Indian states.
- ILP is a document that Indian citizens from other states are required to possess in order to enter states like Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Nagaland and Manipur.
- It is issued by the concerned State Government and can be issued for travel purposes solely.
- Such states are exempted from provisions of the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA).
- The CAA, which relaxes eligibility criteria for certain categories of migrants from three countries seeking Indian citizenship, exempts certain categories of areas, including those protected by the Inner Line system.
- Rules for Foreigners:
- Foreigners need a Protected Area Permit (PAP) to visit tourist places which are different from ILPs needed by domestic tourists.
- Under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order 1958, all areas falling between the ‘Inner Line’, as defined in the said order, and the International Border of the State have been declared as a Protected Area.
- A foreign national is normally not allowed to visit a Protected/Restricted Area unless it is established to the satisfaction of the Government that there are extraordinary reasons to justify such a visit.
Rural Local Bodies.

The Ministry of Finance has released an amount of Rs. 13,385.70 crore to 25 States for providing grants to the Rural Local Bodies.
- This Grant-in-aid is the 1st installment of Tied grants of the year 2021-22.
- The grants have been released as per the recommendations of the 15th Finance Commission.
Finance Commission (FC) Grants:
- The Union Budget provides funds to local bodies, state disaster relief funds and compensates any revenue loss to states after devolution of taxes on the recommendation of FC.
- The 73rd Constitutional Amendment, 1992 requires both the Centre and states to help Panchayati Raj institutions to evolve as a unit of self-governance by assigning them funds, functions and functionaries.
- The 15th FC has recommended over 1 lakh 42 thousand crore rupees tied to Panchayats for water & sanitation during the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Out of the total Grant-in-aid allocated for Panchayati Raj institutions, 60% is ‘Tied Grant’.
- Tied grants are meant to ensure availability of additional funds to the Rural local bodies over and above the funds allocated by the Centre for improving the sanitation and maintenance of Open-Defecation Free (ODF) status and supply of drinking water, rain water harvesting and water recycling under the Centrally Sponsored Schemes.
- Remaining 40% is ‘Untied Grant’ and is to be utilized at the discretion of the Panchayati Raj institutions for location specific needs, except for payment of salaries.
- Allocation of Resources: The States are required to transfer the grants to the Rural local bodies within 10 working days of their receipt from the Union Government.
- Any delay beyond 10 working days requires the State Governments to release the grants with interest.
South Asian Institute For Advanced Research And Development (SAIARD):

National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) signed an MoU with South Asian Institute for Advanced Research and Development (SAIARD) for ‘Capacity Building on Integrated River Basin Management with a focus on Geospatial Technology in Riverine Ecosystem’.
- It aims to create an academic platform to engage young students as well as develop a research and capacity building hub to support regional development in the eastern region.
- With the signing of this MoU, SIAIRD will also henceforth be considered as the regional capacity building center for NMCG in the eastern region.
- South Asian Institute for Advanced Research and Development (SAIARD) is a premier academic cum research institution, formed in Kolkata under the Trustee Registration Act of Govt. of India with a motto to spread the arena of research throughout the world particularly focusing on the major issues of the South Asian region.
125th Birth Anniversary Of Srila Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada Ji.

Prime Minister Narendra Modi released a special commemorative coin on the occasion of the 125th Birth Anniversary of Srila Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada Ji.
- Abhay Charanaravinda Bhaktivedanta Swami (1896 – 1977) or Srila Prabhupada, born Abhay Charan De, was an Indian spiritual teacher and the founder-acharya of the International Society for Krishna Consciousness (ISKCON), commonly known as the “Hare Krishna movement”.
- Members of the ISKCON movement view Bhaktivedanta Swami as a representative and messenger of Krishna Chaitanya.
- His mission was to propagate throughout the world Gaudiya Vaishnavism, a school of Vaishnavite Hinduism that had been taught to him by his guru, Bhaktisiddhanta Sarasvati.
- His translation of and commentary on the Bhagavad Gita, titled Bhagavad-gītā As It Is, is considered by ISKCON adherents and many Vedic scholars as the finest, bonafide translation of Vaishnava literary works.




