Today Current Affairs: 5th May 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Notice To Jharkhand Chief Minister By Election Commission : Office Of Profit

The Election Commission issued notice to Jharkhand chief minister on a reference that he held an “office of profit” by granting a mining lease to himself in 2021.
- The chief minister is accused of violating a provision of the Representation of the People Act.
‘Office of Profit’:
- MPs and MLAs, as members of the legislature, hold the government accountable for its work.
- The essence of disqualification under the office of profit law is if legislators holds an ‘office of profit’ under the government, they might be susceptible to government influence, and may not discharge their constitutional mandate fairly.
- The intent is that there should be no conflict between the duties and interests of an elected member.
- Hence, the office of profit law simply seeks to enforce a basic feature of the Constitution-
- The principle of separation of power between the legislature and the executive.
- The law does not clearly define what constitutes an office of profit but the definition has evolved over the years with interpretations made in various court judgments.
- An office of profit has been interpreted to be a position that brings to the office-holder some financial gain, or advantage, or benefit.
- The amount of such profit is immaterial.
- In 1964, the Supreme Court ruled that the test for determining whether a person holds an office of profit is the test of appointment.
World Press Freedom Index 2022:
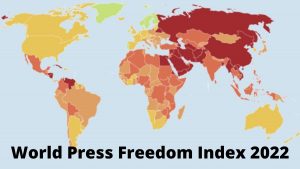
On the World Press Freedom Day (WPFD) (3rd May), the 20th edition of the World Press Freedom Index was published by Reporters Without Borders (RSF).
- India ranked 150th among the 180 countries.
- The report reveals a two-fold increase in “polarisation” amplified by information chaos, that is, media polarisation fuelling divisions within countries, as well as polarisation between countries at the international level.
Ranking of Countries:
Top and Worst Performers:
- Norway (1st) Denmark (2nd), Sweden (3rd) Estonia (4th) and Finland (5th) grabbed the top positions.
- North Korea remained at the bottom of the list of the 180 countries.
- Russia was placed at 155th position.
- Nepal has climbed up by 30 points in the global ranking at 76th position.
- The index placed Pakistan at 157th position, Sri Lanka 146th, Bangladesh 162nd and Myanmar at 176th position.
- China was ranked at 175th position.
Performance of India:
- India has fallen eight places from 142nd to 150th in the 2022 among the 180 countries.
- India’s position has been consistently falling in the index since 2016 when it was ranked 133.
- The reasons behind fall in ranking is the increased “violence against journalists” and a “politically partisan media”.
World Press Freedom Index:
- The day was proclaimed by the UN General Assembly in 1993, following the recommendation of UNESCO’s General Conference in 1991.
- The day also marks the 1991 Windhoek Declaration (adopted by UNESCO).
- It aimed towards the ‘development of a free, independent and pluralistic press’.
- Theme for 2022:Journalism under digital siege
61st Bodo Sahitya Sabha:

President Ram Nath Kovind, who is on a four-day visit to the North Eastern States, will attend the concluding session of the 61st Bodo Sahitya Sabha at Kachubari in Tamulpur district of Assam.
- It is a historic moment for the Bodo Sahitya Sabha as no President of India has ever attended any literary event of any language in the northeastern region.
- Boro, also called Bodo, is the largest ethnolinguistic group in the Assam state of India.
- They are spread across north-eastern India.
- They are concentrated mainly in the Bodoland Territorial Region of Assam, though Bodos inhabit all other districts of Assam and Meghalaya.
- Bodos are officially identified as “Boro, Borokachari” scheduled tribe under the Constitution of India.
- Bodos speak Bodo language, which is recognised as one of twenty-two Scheduled languages of India.
Lapsus$ : Cyber Crime Group

On March 22, authentication platform Okta confirmed that hackers from the cyber-crime group Lapsus$ had tried intruding into its system three months earlier.
- Lapsus$ is said to be based in South America and is led by two teenagers, a 16-year-old and a 17-year-old.
- The group is relatively new but has successfully breached major firms like Microsoft. It has also publicly taunted their victims, leaking their source code and internal documents.
- Their hacking tactics include phone-based social engineering, SIM-swapping to facilitate account takeover, accessing personal email accounts of employees at target organisations etc.
Jivhala Scheme:

It is a loan scheme for inmates serving sentences in jails launched by the Maharashtra Department of Prisons.
- The credit scheme is being offered by the Maharashtra State Cooperative Bank.
- The pilot was introduced for prisoners at Yerawada Central Jail in Pune, and will gradually be extended to nearly 60 prisons across the state.
- According to bank and prison officials, this is likely the first kind of credit scheme for prisoners in India.
- While the loan will be disbursed in the name of the inmate, it will be issued to designated family members.
- In the initial phase, a loan of Rs 50,000 will be given at a 7 percent interest rate.
- Of the interest the bank earns, one percent will be given back to the system as a contribution to the Prisoners’ Welfare Fund.
- The loan will be provided without any requirement of mortgage or guarantor.
Nomination Of Rajiv Ranjan As Ex-Officio Member Of Monetary Policy Committee:

The Central Board of Directors of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved nomination of Rajiv Ranjan as ex-officio member of Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
- The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 was amended by Finance Act (India), 2016 to constitute MPC.
- It is tasked with framing monetary policy using tools like the repo rate, reverse repo rate, bank rate, cash reserve ratio (CRR).
- It has been instituted by the Central Government of India under Section 45ZB of the RBI Act that was amended in 1934.
- The MPC is entrusted with the responsibility of deciding the different policy rates including MSF, Repo Rate, Reverse Repo Rate, and Liquidity Adjustment Facility.
- The committee will have six members. Of the six members, the government will nominate three.
- No government official will be nominated to the MPC.
- The other three members would be from the RBI with the governor being the ex-officio chairperson.
- Deputy governor of RBI in charge of the monetary policy will be a member, as also an executive director of the central bank.
- The government nominees to the MPC will be selected by a Search-cum-Selection Committee under Cabinet Secretary with RBI Governor and Economic Affairs Secretary and three experts in the field of economics or banking or finance or monetary policy as its members.
- Members of the MPC will be appointed for a period of four years and shall not be eligible for reappointment.
Vaccine Hesitancy:
While last year, before the second wave, vaccine hesitancy was ascribed to the low uptake, it is quite likely now that people are exercising their option of waiting for more kinds of the vaccine.
- The current attitude is foregrounded in the ground reality that daily infections are low despite a complete opening up of normal life.
- A vaccine is one of the essential weapons in the armamentarium in our war against the pandemic.
- Any hesitation in accepting the vaccine will have a negative consequence on our effort to control the pandemic.
- Vaccine hesitancy is defined by WHO as a “delay in acceptance or refusal of vaccines despite availability of vaccination services”.
- It was one of 10 threats to global health this year.
National Language Debate:

Remarks by a Hindi actor to the effect that Hindi is the national language of India sparked a controversy recently over the status of the language under the Constitution.
- The Constitution of India has not given any language a national status.
- Under Article 343 of the Constitution, the official language of the Union shall be Hindi in Devanagari script.
- The international form of Indian numerals will be used for official purposes.
- In the constituent assembly discussions, it was decided that English would continue to be used for a period of 15 years.
- The Constitution said that after 15 years, Parliament may by law decide on the use of English and the use of the Devanagari form of numbers for specified purposes.
- Article 351: It is the Union government’s duty to promote the spread of Hindi so that it becomes “a medium of expression for all elements of the composite culture of India” and also to assimilate elements of forms and expressions from Hindustani and languages listed in the Eighth Schedule.
- The Official Languages Act, 1963 was passed in anticipation of the expiry of the 15-year period during which the Constitution originally allowed the use of English for official purposes.
- Its operative section provided for the continuing use of English, notwithstanding the expiry of the 15-year period.
- Jawaharlal Nehru had given an assurance in 1959 that English would remain in official use and as the language of communication between the Centre and the States.
- The Official Languages Act, 1963, did not explicitly incorporate this assurance, causing apprehensions in some States as the January 1965 deadline neared.
- At that time, PM Lal Bahadur Shastri reiterated the government’s commitment to move towards making Hindi the official language for all purposes.
- It created an apprehension that Hindi would be imposed in such a way that the future employment prospects of those who do not speak Hindi will be bleak.
Restoration Of Historic Anang Tal lake : South Delhi

The Ministry of Culture has ordered the restoration of Historic Anang Tal lake in South Delhi.
- National Monuments Authority (NMA) and Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) have asked officials to expedite conservation work so the site could be declared a National Monument.
- The lake is situated in Mehrauli, Delhi and is claimed to be created by Tomar King, Anangpal II, in 1,060 AD.
- He is known to have established and populated Delhi in the 11th century.
- The millennium old Anang Tal signifies the beginning of Delhi.
- Anang Tal has a strong Rajasthan connection as Maharaja Anangpal is known as nana (maternal grandfather) of Prithviraj Chauhan whose fort Rai Pithora is on the list of the ASI.
- Anangpal II, popularly known as Anangpal Tomar, belonged to the Tomar dynasty.
- He was the founder of Dhillika Puri, which eventually became Delhi.
- Evidence about the early history of Delhi is inscribed on the iron pillar of Masjid Quwaatul Islam, adjacent to Qutub Minar.
- Multiple inscriptions and coins suggest Anangpal Tomar was the ruler of present-day Delhi and Haryana in between the 8th-12th centuries.
- He had built the city from ruins and under his supervision, Anang Tal Baoli and Lal Kot were constructed.
- Anangpal Tomar II was succeeded by his grandson Prithviraj Chauhan.
- Delhi Sultanate was established in 1192 after Prithviraj Chauhan’s defeat in the Battle of Tarain (present-day Haryana) by the Ghurid forces.
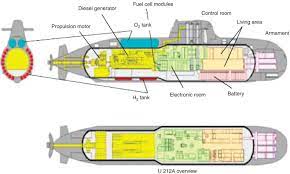
AIP (Air-Independent Propulsion) Technology:
France’s Naval Group declined the bid for the P-75I Project, citing it does not use AIP (Air-Independent Propulsion) Technology yet.
- Around 10 countries have developed or are close to building AIP technology, and almost 20 nations have AIP submarines.
P-75I project:
- In June 1999, the Cabinet Committee on Security approved a 30-year plan for the Navy to indigenously build and induct 24 submarines by 2030.
- In the first phase, two lines of production were to be established — the first, P-75; the second, P-75I. Each line was to produce six submarines.
- While the six P-75 submarines are diesel-electric, they can be fitted with AIP technology later in their lives.
- This P-75I project envisages indigenous construction of submarines equipped with the state-of-the-art Air Independent Propulsion system at an estimated cost of Rs. 43,000 crore.
AIP :
- AIP is a technology for conventional non-nuclear submarines.
- Submarines are essentially of two types: conventional and nuclear.
- The conventional submarines use diesel-electric engines, which require them to surface almost daily to get atmospheric oxygen for fuel combustion.
- If fitted with an AIP system, the submarine will need to take in oxygen only once a week.
- The indigenously developed AIP, which is one of the key missions of the Naval Materials Research Laboratory (NMRL – DRDO), is considered one of the ambitious projects of the DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation) for the Navy.
What Is Sedition Law?

The Government has sought more time to submit its written response to petitions challenging the constitutional validity of Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code dealing with the offense of sedition.
- In the year 2021, the CJI (Chief Justice of India) had questioned why a colonial law used against Mahatma Gandhi and Bal Gangadhar Tilak continued to survive in the law book after 75 years of Independence.
- The Chief Justice had said sedition or Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code was prone to misuse by the government.
- Sedition laws were enacted in 17th century England when lawmakers believed that only good opinions of the government should survive, as bad opinions were detrimental to the government and monarchy.
- The law was originally drafted in 1837 by Thomas Macaulay, the British historian-politician, but was inexplicably omitted when the Indian Penal Code (IPC) was enacted in 1860.
- Section 124A was inserted in 1870 by an amendment introduced by Sir James Stephen when it felt the need for a specific section to deal with the offence.
- Today the Sedition is a crime under Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code (IPC).
- Section 124A IPC:It defines sedition as an offence committed when “any person by words, either spoken or written, or by signs, or by visible representation, or otherwise, brings or attempts to bring into hatred or contempt, or excites or attempts to excite disaffection towards the government established by law in India”.
- Disaffection includes disloyalty and all feelings of enmity.
- However, comments without exciting or attempting to excite hatred, contempt or disaffection, will not constitute an offence under this section.
- Punishment for the Offence of Sedition: It is a non-bailable offence. Punishment under Section 124A ranges from imprisonment up to three years to a life term, to which a fine may be added.
- A person charged under this law is barred from a government job.
- They have to live without their passport and must produce themselves in the court at all times as and when required.
Operation Satark:

RPF launches Focused effort under “Operation Satark” from 5th April to 30th April, 2022.
- Railway Protection Force (RPF) is a security force under the ownership of Indian Railways, Ministry of Railways, Government of India.
- It was formed in 1872 under the Railway Protection Force Act, 1957.
- It is the lead security agency in the field of railway security having a pan India reach.
- It is entrusted with the security of railway property, passenger area and passengers.
- Railway Protection Force has recently started “Operation Satark” with an objective of taking action against illicit liquor/FICN/illegal tobacco products/unaccounted gold and any other items being transported through railway network for the purpose of tax evasion and smuggling.
National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID) : Bengaluru

Union Minister for Home and Cooperation Amit Shah inaugurated the National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID) campus in Bengaluru.
- The NATGRID CEO informed that the services of NATGRID solution will be available to 11 central agencies and police of all States and Union Territories.
- It will link user agencies with data holders, giving them access to real-time information needed for intelligence services and investigations.
- C-DAC Pune has been roped in as Technology Partner and IIT, Bhilai as Plan Management Consultant for the development of NATGRID solution.
- The National Intelligence Grid or NATGRID is the integrated intelligence master database structure for counter-terrorism purpose connecting databases of various core security agencies under Government of India collecting comprehensive patterns procured from 21 different organizations that can be readily accessed by security agencies round the clock.
- NATGRID came into existence after the 2008 Mumbai attacks.




