Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 6th August 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Pakistan has released a new political map:
- The Supreme Court of India referred the petitions challenging the 103rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 2019 to a five-judge constitution bench, saying it involves ‘substantial questions of law’.:
- National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) – Sahakar Cooptube NCDC Channel and Guidance Videos on ‘Formation and Registration of A Cooperative’.:
- Bru community
- H-1B Visa Holders
- Explosion at Beirut port:
- Other important current affairs:
1. Pakistan has released a new political map:
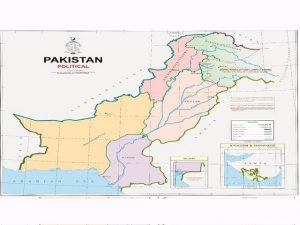
Pakistan has released a new political map that includes all of Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, Sir Creek and Junagadh.
- The map has been released on the eve of the first anniversary of the abrogation of special status to Jammu and Kashmir under Article 370.
The Map:
- The map depicts entire Jammu & Kashmir as a disputed territory and does not show any borders in the east of Kashmir.
- It has also renamed Kashmir Highway in Islamabad as Srinagar Highway.
- It claims the Siachen, regions of Sir Creek, and the erstwhile state of Junagadh in Gujarat as part of Pakistan’s territory.
- This is not the first time Pakistan has tried to portray Junagadh as part of its territory.
- The 2012 Atlas of Pakistan also portrayed Junagadh as a Pakistan’s territory.
- The map also shows the Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) as being part of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province.
India’s response:
- India has dismissed the map as an “exercise in absurdity” that made “untenable claims” to territories in India. These ridiculous assertions have neither legal validity nor international credibility.
India also said that the release of the new map confirms Pakistan’s “obsession with territorial aggrandizement” supported by cross-border terrorism.
- The map has been released a day before the first anniversary of the Indian government’s August 5 decisions rolling back the special status of J&Kand the bifurcation of the state into two UTs.
- The move also appears to be a tit-for-tat for India’s inclusion of Pakistan Occupied Kashmir as part of the union territory of Jammu & Kashmir, and of Gilgit Baltistan as part of Ladakh in the new map the government released on November 2.
2. The Supreme Court of India referred the petitions challenging the 103rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 2019 to a five-judge constitution bench, saying it involves ‘substantial questions of law’.:

According to Article 145 (3) of the Constitution, at least five judges need to hear cases that involve ‘a substantial question of law as to the interpretation’ of the Constitution, or any reference under Article 143, which deals with the power of the President of India to consult the Supreme Court.
- The Supreme Court bench consisting of at least five judges is called the Constitution bench.
103rd Constitutional Amendment Act:
- It introduced an economic reservation (10% quota) in jobs and admissions in educational institutes for Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) by amending Articles 15 and 16.
- It inserted Article 15 (6) and Article 16 (6).
- It was enacted to promote the welfare of the poor not covered by the 50% reservation policy for SCs, STs, and Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (SEBC).
- It enables both the Centre and the states to provide reservations to the EWS of society.
The amendments run contrary to the constitutional scheme, where no segment of available seats/posts can be reserved, only on the basis of economic criterion.
- The amendments also run contrary to the judgment pronounced in the Indra Sawhney V. Union of India 1992 case, that a backward class cannot be determined only and exclusively with reference to economic criterion.
- The amendments alter the 50% quota limit set up in Indra Sawhney V. Union of India 1992 case, which according to the petitioner is a part Basic Structure of the Constitution.
- Reservation in unaided institutions violates the fundamental right under Article 19(1)(g) of the Constitution.
Article 19 (1)(g) allows every citizen to practise any profession, or to carry on any occupation, trade or business.
Central Government’s Stand:
- The amendment was necessitated to benefit EWS who are not covered under existing schemes of reservation, which as per statistics, constitute a considerably large segment of the country’s population.
- The 50% limit in the Indira Sawhney ruling cannot be applied in the present petitions as the Sawhney case dealt with memoranda issued by the government while what is under challenge now is a constitutional amendment.
Substantial Question of Law Involved:
- Whether the challenged 103rd Amendment Act violates the Basic Structure of the Constitution, with reference to equality provisions of the Constitution.
- The case of the Union of India that though ordinarily, 50% is the rule same will not prevent the amendment of the Constitution itself in view of the existing special circumstances to uplift the members of the society belonging to economically weaker sections.
3. National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) – Sahakar Cooptube NCDC Channel and Guidance Videos on ‘Formation and Registration of A Cooperative’.:

The Union Minister of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare launched the two initiatives of the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) – Sahakar Cooptube NCDC Channel and Guidance Videos on ‘Formation and Registration of A Cooperative’.
Sahakar Cooptube NCDC Channel:
- The Channel aims to facilitate the involvement of the youth in the cooperative movement.
- Cooperatives lend strength to farmers to minimize risks in agriculture and allied sectors and act as a shield against exploitation.
- The channel will give a boost to Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan under which the government has announced a series of transformative measures and sector-specific financial packages to help agriculture.
- The initiatives are steps towards One Nation One Market with the objective of India to become a food factory of the world.
- These have been produced by the NCDC on ‘Formation and Registration of A Cooperative’ for eighteen different states in Hindi and regional languages.
- These would help strengthen and deepen the major initiatives of the government to promote and form 10,000 Farmer-Producer Organisations (FPOs).
- One such initiative is the formation of FPOs under the “One-Product One-District” approach.
National Cooperative Development Corporation
- Formation: NCDC was established by an Act of Parliament in 1963 as a statutory Corporation under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare.
- Office: NCDC functions through its Head Office at New Delhi and multiple Regional Offices.
- The objectives of NCDC are planning and promoting programs for agricultural produce, foodstuffs, industrial goods, livestock and certain other notified commodities and services on cooperative principles.
- The NCDC has the unique distinction of being the sole statutory organization functioning as an apex financial and developmental institution exclusively devoted to the cooperative sector.
4.Bru community :

Three organizations representing the Bru community displaced from Mizoram have rejected the sites proposed by the Joint Movement Committee (JMC), an umbrella group of non-Brus in Tripura, for their resettlement.
- The JMC had on July 21 submitted a memorandum to the Tripura government specifying six places in Kanchanpur and Panisagar subdivisions of North Tripura district for the resettlement of the Brus who fled ethnic violence in Mizoram since 1997.
- The JMC also proposed settling 500 families at most in these places.
- However, the organizations representing the Bru Community have opposed the involvement of non-Brus in JMC.
- Resettle some 6,500 families in clusters of at least 500 families at each of the sites of their choice —seven in North Tripura district and five in the adjoining Dhalai district.
- The sites proposed by the JMC, they said, are unconnected by road and electricity and too far from hospitals, schools and other facilities.
- The Brus, also referred to as the Reangs, are spread across the northeastern states of Tripura, Assam, Manipur, and Mizoram.
- In Tripura, they are recognized as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group. In Mizoram, they have been targeted by groups that do not consider them indigenous to the state.
The centre, in January 2020, signed a historic pact for permanent solution of Bru refugees’ issue.
- The agreement was between Union Government, Governments of Tripura and Mizoram and Bru-Reang representatives to end the 23-year old Bru-Reang refugee crisis.
Highlights of the agreement:
- Under the agreement, the center has announced a package of Rs. 600 crore under this agreement.
- As per the agreement the Bru tribes would be given land to reside in Tripura.
- A fixed deposit of Rs. 4 lakh will be given to each family as an amount of government aid. They will be able to withdraw this amount after two years.
- Each of the displaced families will be given 40×30 sq ft residential plots.
- Apart from them, each family will be given Rs. 5,000 cash per month for two years.
- The agreement highlights that each displaced family will also be given free ration for two years and aid of Rs. 1.5 lakh to build their houses.
5.H-1B Visa Holders:

Recently, the President of the USA has signed an executive order barring federal agencies from hiring H-1B visa holders and other foreign workers in place of USA citizens or green cardholders.
H-1B Visas:
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa that allows USA companies to employ foreign workers in specialty occupations that require theoretical or technical expertise.
- The technology companies depend on it to hire tens of thousands of employees each year from countries like India and China to keep costs in check.
- Such jobs in developed countries pay minimum wages, which are not lucrative enough for employable individuals of these countries.
- The executive order has asked the federal agencies to stop replacing USA workers and green card holders with H-1B visa holders or other foreign workers.
- A green card holder (permanent resident) is someone who has been granted authorization to live and work in the USA on a permanent basis.
- The order has also directed all agencies under the federal government to review the contracts they gave out in the two previous financial years and the performance of such contracts or subcontracts.
- The heads of departments will undertake an audit and check whether the jobs could have been performed by the USA workers and whether opportunities for domestic workers were impacted by such hiring.
- The Department of Labour will also finalize guidelines to prevent H-1B employers from moving H-1B workers to other employers’ job sites to displace American workers.
- The order seems to be an extension of an earlier order in which the entry of non-immigrant visa workers had been banned until the end of 2020.
Background: - The USA government under Trump’s leadership is moving towards a more conservative work visa regime under the America First policy.
- It has alleged Indian and Chinese IT companies of sending workers at very low cost, which hurt the prospects of skilled workers in the USA.
- The immediate trigger was an announcement by the federally-owned Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) that it would outsource 20% of its technology jobs to foreign countries.
- This action could result in loss of jobs for up to 200 highly-skilled American tech workers in Tennessee and could also lead to possible leaking of sensitive user data and theft of intellectual property, detrimental to national security.
- The USA government has held that outsourcing of jobs should be avoided as far as possible because it is especially detrimental in the middle of a pandemic, which has already cost millions of Americans their jobs.
Impact on Indian Workers in the USA: - The H-1B visa is the most sought-after among Indian IT professionals.
- Apart from workers hired by federal agencies, the order will also impact workers of Indian companies that are on contract with federal agencies.
- Bigger federal agencies such as state-run banks give the contract for supply and maintenance of their databases and other services to bigger Indian companies such as Infosys, TCS or Wipro.
- The order comes at a time when there is a huge shortage of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) skills in the USA that workers on short-term non-immigrant visas like H-1B and L-1 help bridge.
- Such a measure could slow down the recovery phase of the USA as countries start unlocking.
6. Explosion at Beirut port:

The catastrophic explosion at Beirut port on August 4 was caused by over 2,700 tonnes of ammonium nitrate kept in storage for over six years.
- In its pure form, ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) is a white, crystalline chemical which is soluble in water.
- It is the main ingredient in the manufacture of commercial explosives used in mining and construction.
- It is a common chemical ingredient of agricultural fertilizers.
- It is also the main component of the explosive composition known as ANFO — ammonium nitrate fuel oil.
- Pure ammonium nitrate is not an explosive on its own. It is classified as an oxidizer (Grade 5.1) under the United Nations classification of dangerous goods.
- If mixed with ingredients like fuel or some other contaminants, or because of some other external factors, it can be very explosive.
- The explosion of large storage can happen primarily in two ways:
- By some type of detonation or initiation because the storage comes in contact with the explosive mixture.
- Due to a fire that starts in the ammonium nitrate store because of the heat generated due to the oxidation process at large scale.
- In India, its usage is regulated as per The Ammonium Nitrate Rules, 2012, under The Explosives Act, 1884.
- The rules also make storage of ammonium nitrate in large quantities in populated areas illegal in India.
- For the manufacture of ammonium nitrate, an Industrial license is required under the Industrial Development and Regulation Act, 1951.
- A license under the Ammonium Nitrate Rules, 2012 is also required for any activity related to ammonium nitrate.
- An ammonium nitrate explosion produces massive amounts of nitrogen oxides. Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) is a red, bad-smelling gas.
- It can irritate the respiratory system. Elevated levels of these pollutants are particularly concerning for people with respiratory conditions.
Other important current affairs:
1. Union Housing Minister released Affordable Rental Housing Complexes (ARHC) Knowledge Pack. This includes MoUs to be signed with States and UTs to provide ease of living to urban migrants in the country.
- The Union Cabinet had approved ARHC as a sub-scheme under Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) earlier this month to provide housing facilities to migrant workers and urban poor.
- The Affordable Housing Complex scheme will be implemented through two models in the country.
- Under the first model, existing Government funded vacant houses will be converted into ARHCs through Public-Private partnerships or by public agencies for a period of 25 years.
- Under the second model ARHCs will be constructed, operated and maintained by Public or Private Entities on their own available vacant land for a period of 25 years.
- Successful implementation of ARHC Scheme will not only benefit urban migrants and poor but will also accelerate entrepreneurship and investment in the rental housing market giving a boost to the economy.
2. The Delhi High Court has asked Delhi Police and Zee News to respond to a plea by Trinamool Congress MP Mahua Moitra challenging the summons and framing of charges against her in a defamation case filed by the news channel and its editor.
- The case relates to Ms. Moitra’s June 25, 2019 speech in Parliament on the ‘Seven Signs of Fascism’ and a TV show run by the news channel and other subsequent developments.
- Zee News has filed the defamation complaint against Ms. Moitra for allegedly making statements against the channel to the media.
- Defamation is the communication of a false statement that harms the reputation of an individual person, business, product, group, government, religion, or nation.
- In India, defamation can both be a civil wrong and a criminal offense.
- The difference between the two lies in the objects they seek to achieve.
3. The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has set stringent conditions for commercial groundwater use.
- The order came on a plea seeking direction to check the depleting groundwater level in the country.
NGT has also struck down the Central Ground Water Authority’s (CGWA) 2020 guidelines, saying they were against the law. - The 2018 version of the guidelines had been struck down by the NGT last year.
- Industries must expect a complete overhaul in the manner in which the permits are issued for the extraction of groundwater for commercial activities.
- They must ensure that all the conditions are complied with.
- The tribunal has specifically banned the general permission for the withdrawal of groundwater, especially to the commercial entities without an environmental impact assessment.
- Permits must be for the specified quantity of water and must be monitored with digital flow meters and audited every year by the third parties.
- Strict actions, including prosecution and blacklisting, must be taken against those who will fail the audit.
- All overexploited, critical, and semi-critical (OCS) assessment units must undergo water mapping.
- Authorities are given three months to make water management plans for all the overexploited, semi-critical, and critical areas.
5.MyGov (mygov.in) is the Government of India’s citizen engagement and crowdsourcing platform.
- Launched in 2014.
- It aims to promote active citizen participation in governance and policymaking.
Since its launch on 26th July 2014, MyGov has adopted multiple engagement methodologies like discussions, tasks, innovation challenges, polls, surveys, blogs etc. - Goa joins the MyGov Citizen Engagement Platform; 12 states had already launched their MyGov Platforms.
6. Pokkali variety of rice:
- The pokkali variety of rice is known for its saltwater resistance and flourishes in the rice paddies of coastal Kerala districts.
- The uniqueness of the rice has brought it the Geographical Indication (GI) tag and is the subject of continuing research.
- The organically-grown Pokkali is famed for its peculiar taste and its high protein content
7. Government of India launched ‘Vidyarthi Vigyan Manthan, 2020-21.
- Vidyarthi Vigyan Manthan (VVM) is an initiative of Vijnana Bharati (VIBHA), in collaboration with Vigyan Prasar, an autonomous organization under the Department of Science and Technology, and NCERT, an institution under the Ministry of Education.
- VVM is a national program for popularizing science among school students of standard VI to XI, conceptualized to identify the bright minds with a scientific attitude among the student community.
8. Northern Railway today ran its first-ever Vyapar Mala Express train.
- This train destined for Jirania in Tripura has 46 wagons.
- This is an express service where the piece-meal stock will reach its destination in a shorter time.
- The train departed from Delhi Kishanganj for Jirania and it will cover a distance of 2,673 km from Punjab to Tripura.
- Wheat was loaded in 34 wagons at Guniana station of Firozpur Division by Food Corporation of India and in the remaining Rice and Pulses have been loaded.
- Railways has earned more than 94 lakh rupees from this Vyapar Mala Express train.
- It will help small traders in moving their cargo through Railways, in a short time, cost-effective, convenient, and environment-friendly mode of transportation.




