Today’s Current Affairs: 6th Sep 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
World’s First Portable Disaster Hospital:

India has built the world’s first portable disaster hospital, called the “Aarogya Maitri Cube”.
- The hospital can be airlifted and assembled into 72 cubes that contain essential medical equipment and supplies.
- The cubes can support 200 survivors for 48 hours during natural disasters or crises.
- It has been developed indigenously under the Project BHISHM(Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog Hita and Maitri).
- The hospital includes Operation theatres, mini-ICUs, Ventilators, Blood test equipment, an X-ray machine, a Cooking station, Food, Water, a Shelter, Power generator.
- The “Aarogya Maitri Cube” is part of “Aarogya Maitri” project.
- The project aims to provide essential medical supplies to any developing country affected by natural disasters or humanitarian crises.
Adopt a Heritage 2.0:

The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has launched a revamped version of the ‘Adopt a Heritage’ program, along with an Indian Heritage app and an e-permission portal.
- This updated program encourages corporate stakeholders to utilize their Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) funds to enhance facilities at historically important monuments.
- It also provides a comprehensive guide through the Indian Heritage app, offering information on ASI’s monuments, including historical structures, pictures, public facilities, and geo-tagged locations.
- The ‘Adopt a Heritage 2.0’ program includes various changes, such as a streamlined management structure for partner agencies, clear guidelines for semi-commercial activities, and a detailed scope of work and amenities required for monuments.
- The updated program offers more flexibility, allowing companies to adopt entire monuments and develop their tourism infrastructure or provide specific amenities like drinking water facilities or cleaning services for one or more sites.
Gujarat Declaration : WHO

World Health Organization (WHO) has released the outcome document of the first WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit 2023 in the form of the “Gujarat Declaration”.
- India hosted the first WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre in Gujarat.
- The declaration reaffirmed global commitments towards indigenous knowledge, biodiversity and traditional, complementary and integrative medicine.
- The Gujarat Declaration aims to advance evidence-based traditional medicine interventions for universal health coverage and health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- It calls for standardized documentation and data collection on traditional medicine.
- The summit explored the role of digital health technologies, including AI, in traditional medicine.
Kinzhal Missile:

The first Su-34 multipurpose bomber aircraft crew to have fired a Kinzhal missile on Ukraine was recently presented with state awards.
Kinzhal Missile:
- The Kh-47M2, nicknamed “Kinzhal” (Dagger), is a nuclear-capable, Russian air-launched hypersonic ballistic missile.
- It was one of six “next generation” weapons unveiled by Russian President Vladimir Putin during a speech in March 2018.
- The Kinzhal can reach speeds of up to Mach 10 (12,350 km/hr).
- It can carry both conventional and nuclear warheads with a payload of up to 480 kg and a thermonuclear option with a 10-50 kt warhead.
- It has a reported range of 1,500-2,000 km.
- The Kinzhal has a length of 8 m, a body diameter of 1 m, and a launch weight of approximately 4,300 kg.
- It is designed to be launched from MiG-31 fighter jets at altitudes of about 18 km (59,000 ft).
- This missile manoeuvres during all stages of its flight to overcome hostile air defence systems.
Zealandia : Discovered
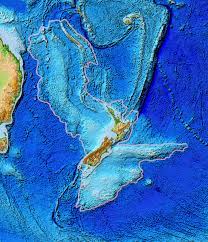
Geoscientists recently discovered a continent known as Zealandia that had been hiding in plain sight for almost 375 years.
- Zealandia is a long, narrow microcontinent that is mostly submerged in the South Pacific Ocean.
- It is located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, primarily to the east of Australia and to the south of New Caledonia. It encompasses the region that includes New Zealand and New Caledonia.
- Zealandia or Te Riu-a-Māui in the Māori language was formally one of the constituent continents of the ancient supercontinent called Gondwana, which also included Western Antarctica and Eastern Australia over 500 million years ago.
- It began to “pull away” from Gondwana roughly 105 million years ago.
- As Zealandia started pulling away, it began to sink beneath the waves, with over 94 per cent remaining underwater for millennia.
- It is approximately 1.89 million square miles (4.9 million square km) in size, about half the size of Australia.
- The vast majority of this new continent lies beneath 6,560 feet (2km) of water.
- The part of Zealandia that is above water forms the foundation of New Zealand’s north and south islands as well as the island of New Caledonia.
- Zealandia is situated along the boundary of several tectonic plates, including the Australian Plate, Pacific Plate, and Indo-Australian Plate.
- The existence of Zealandia was first recorded in 1642 by Dutch businessman and sailor Abel Tasman, who was on a mission to find the “great Southern Continent,” or Terra Australis.
PM-DAKSH Yojana:

During 2020-21 to 2022-23, a total of 107,156 beneficiaries have been trained under the PM-DAKSH Yojana.
- The Pradhan Mantri Dakshata Aur Kushalata Sampanna Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) Yojana is a Central Sector Scheme.
- It was launched during 2020-21.
- The main objective of the Scheme is to enhance the competency level of the target groups to make them employable both in self-employment and wage-employment for their socio-economic development.
- It is a National Action Plan for skilling marginalised persons covering SCs, OBCs, EBCs, DNTs, Sanitation workers and waste pickers.
- Target Group:
- Artisans- who may be able to improve their revenue generation capacities within their practising vocations;
- Women- who may be able to enter into self-employment and financially empower themselves without neglecting their domestic activities and
- Youth- who may acquire long-term training and specialisation in employable vocations and gain a better standing in the job market.
- The age criterion of the scheme is between 18-45 years, and the income criteria are no income limit for SCs, SafaiKaramcharis, including waste pickers and DNT.
- The annual family income should be below Rs.3 lakh for OBCs, and the EBCs (Economically Backward Classes) annual family income should be below Rs.1 lakh.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment (MoSJ&E).
GRIHA Norms:

The Indian Army’s new Thal Sena Bhawan (TSB) is coming up with GRIHA-IV (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment) norms.
- GRIHA norms is an acronym for Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment. GRIHA is a Sanskrit word meaning – ‘Abode’.
- It is a rating tool that helps people assess the performance of their building against certain nationally acceptable benchmarks.
- It evaluates the environmental performance of a building holistically over its entire life cycle, thereby providing a definitive standard for what constitutes a ‘green building’.
- The rating system, based on accepted energy and environmental principles, will seek to strike a balance between the established practices and emerging concepts, both national and international.
- It is developed by TERI (The Energy and Resources Institute).
- This tool has been adopted by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
- It assesses a building out of 34 criteria and awards points on a scale of 100.
- In order to qualify for GRIHA certification, a project must achieve at least 50 points.
- Certain criteria / sub-criteria are mandatory and have to be complied with for the project to be at all eligible for rating.
Tharosaurus indicus : Dinosaur Fossils

In a paper published recently, scientists from IIT Roorkee have characterised dinosaur fossils from the Middle Jurassic period found in the Thar desert near the Jaisalmer Basin by the Geological Survey of India
- Tharosaurus indicus belongs to the family Dicraeosauridaeand from the superfamily Diplodocoidea.
- These fossils are the first dicraeosaurid sauropods to have been found in India.
- It is 167 million years old and the oldest known diplodocoid fossils in the world.
- The scientists named the dinosaur Tharosaurus indicus, with Tharo deriving from the Thar desert, saurus from the Greek ‘sauros’, or lizard, and indicus from its Indian origin.
- This family was unique: its members were smaller and had shorter necks and tails compared to the other long-necked sauropods.
- Sauropods first appeared on the earth during the Jurassic period, about 200 million years ago.
- They were one of the most dominant clades of dinosaurs, surviving until the late Cretaceous period 65 million years ago when the dinosaurs went extinct.
- According to the scientists, fossils of dicraeosaurid dinosaurs have been found previously in North and South Americas, Africa and China, but such fossils were not known from India.




