Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 8th December 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Havana syndrome:
- France’s new security law
- Truths and Hate Speech
- United Nations Investment Promotion Award 2020
- Light Detection and Ranging Survey (LiDAR) technique
- Eco-bridge
- Other important current affairs
1.Havana syndrome:

Nearly four years ago a mysterious neurological illness, referred to as “Havana syndrome”, started to afflict American diplomats and intelligence operatives in Cuba, China, and other countries.
- Now, a report by the National Academies of Sciences (NAS) has found “directed” microwave radiation to be its “plausible” cause.
Havana syndrome’:
- In late 2016, US diplomats and other employees stationed in Havana reported feeling ill after hearing strange sounds and experiencing odd physical sensations in their hotel rooms or homes.
- The symptoms included nausea, severe headaches, fatigue, dizziness, sleep problems, and hearing loss, which have since come to be known as “Havana Syndrome”.
- Directed pulsed RF energy appears to be the most plausible mechanism in explaining these cases among those that the committee considered.
- The immediate symptoms that patients reported including sensations of pain and buzzing sound apparently emanated from a particular direction or occurred in a specific spot in a room.
2.France’s new security law:

France’s government introduced a controversial security bill in parliament that seeks to provide greater powers and protections for police officers.
Provisions:
- Enabling the police to organize ground and air mass surveillance, while at the same time restricting the filming of police officers.
- Articles 21 and 22 of the proposed “global security” law allow the police and the gendarmes (paramilitary forces) to use body cameras and drones to film citizens, and allow the recorded footage to be live streamed to the command post.
- Article 24 penalises publishing “the image of the face or any other element of identification” of a police or paramilitary official who is acting in “a police operation”, if the dissemination is done with “the intent of harming their physical or mental integrity”.
- Article 24 would make it harder to cover public events and record instances of police violence, thus making it more difficult to hold officers accountable.
- The bill’s supporters said: The government has insisted that it does not intend to target press freedoms and that the new law is aimed at protecting police officers and their families from online trolling and harassment when off duty.
3.Truths and Hate Speech: SC:

In the context of discussing the limits of free speech and what may tantamount to hate speech, the Supreme Court (SC) has recently held that “Historical truths must be depicted without in any way disclosing or encouraging hatred or enmity between different classes or communities.”
The FIRs were filed against a TV anchor for alleged remarks on the sufi saint Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti in a news show.
On ‘True Facts’:
- Elaborating on the point about truth or true facts being a defense in cases of free speech, the SC cited its ruling in K A Abbas versus Union of India case 1970, which was about censorship.
- The order said that there is no bar in showing carnage or bloodshed which have historical value, and depiction of such scenes may be permissible, if handled delicately as a part of an artistic portrayal of confrontation.
- The likelihood must be judged from a healthy and reasonable standard, thereby accepting the position that historical truth may be a relevant and important factor.
- However, historical truth must be depicted without in any way disclosing or encouraging hatred or enmity between different classes or communities.
- The court also referred to the ruling in Ebrahim Suleiman Sait versus M C Mohammed and Another case 1980.
- The order held that speaking truth was not an answer to the charge of corrupt practice under Section 123 (3A) of the Representation of the People Act 1950.
Free Speech and the Marginalised:
- There may be a possibility of divergence between truth and popular belief, and the bench held that in many ways, free speech has empowered those who were marginalised and discriminated, and thus it would be wholly incorrect and a mistake to assume that free speech is an elite concept and indulgence.
Hate Speech:
- The hate speech should have no redeeming purpose, which means that ‘the speech primarily carries no meaning other than hatred towards a particular group’.
- This is necessarily subjective and requires examination of good faith and good motives on the part of the speaker.
- Speaking on dignity in the context of hate speech, the court held that one must condemn and check any attempt at dissemination of discrimination on the basis of race, religion, caste, creed, or regional basis.
- The court pointed out that the object of criminalizing hate speech is to protect dignity and to ensure political and social equality between different identities and groups regardless of caste, creed, religion, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, linguistic preference, etc.
- Hate speech has not been defined in any law in India. However, legal provisions in certain legislations prohibit select forms of speech as an exception to freedom of speech.
4.United Nations Investment Promotion Award 2020:

The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has declared ‘Invest India’ as the winner of the United Nations Investment Promotion Award 2020.
United Nations Investment Promotion Award:
- It recognizes and celebrates the outstanding achievements of the world’s Investment Promotion Agencies (IPAs). Since 2002, UNCTAD has organised these awards annually.
- The Awards also highlight the contributions of these organizations in raising private sector investment in sustainable development and in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The response of IPAs to the Covid-19 pandemic became the basis for the evaluation of the 2020 Award.
Germany, South Korea and Singapore have been some of the past winners of the award.
Invest India:
- It is the National Investment Promotion and Facilitation Agency of India and acts as the first point of reference for investors in India.
- It is a non-profit venture set up in 2009 under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India.
- UNCTAD highlighted good practices followed by Invest India, such as the Business Immunity Platform, Exclusive Investment Forum webinar series, its social media engagement and focus Covid response teams (such as business reconstruction, stakeholder outreach and supplier outreach) created as a response to the pandemic, in its publications.
5.Light Detection and Ranging Survey (LiDAR) technique :
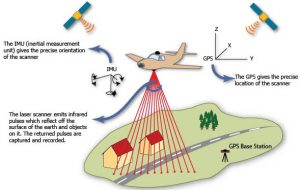
National High-Speed Rail Corporation Limited will be adopting Light Detection and Ranging Survey (LiDAR) technique using Laser enabled equipment mounted on a Helicopter for conducting ground survey for the preparation of Detailed Project Report for the proposed Delhi-Varanasi HSR corridor.
- The proposed Delhi-Varanasi HSR alignment covers mixed terrains including densely populated urban and rural areas, Highways, Roads, Ghats, Rivers, Green fields etc, which makes this activity more challenging.
- National High Speed Rail Corporation Limited (NHSRCL) has been entrusted with the work for preparing Detailed Project Report for the Delhi-Varanasi HSR Corridor by the Ministry of Railways.
- The tentative length of the corridor is about 800 km, the alignment and stations will be decided in consultation with the government.
LiDAR:
- It is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth.
- These light pulses—combined with other data recorded by the airborne system— generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
- LiDAR follows a simple principle — throw laser light at an object on the earth surface and calculate the time it takes to return to the LiDAR source. Given the speed at which the light travels (approximately 186,000 miles per second), the process of measuring the exact distance through LiDAR appears to be incredibly fast.
- A lidar instrument principally consists of a laser, a scanner, and a specialized GPS receiver.
- Airplanes and helicopters are the most commonly used platforms for acquiring lidar data over broad areas
6.Eco-bridge:

Ramnagar Forest Division in Nainital district, Uttarakhand, recently built its first eco-bridge for reptiles and smaller mammals.
- These include canopy bridges (usually for monkeys, squirrels and other arboreal species); concrete underpasses or overpass tunnels or viaducts (usually for larger animals); and amphibian tunnels or culverts. Usually these bridges are overlaid with planting from the area to give it a contiguous look with the landscape.
Eco-bridges matter:
- They enhance wildlife connectivity that can be disrupted because of highways or logging.
- Many road projects cut across animal corridors. For example, National Highway 37 through the Kaziranga-Karbi Anglong landscape in Assam, and State Highway 33 through the Nagarhole Tiger Reserve in Karnataka.
Other important current affairs:
1.Stockholm International Peace Research Institute has released a report on arms market across the world.
- The U.S. arms industry accounted for 61% of sales by the world’s “Top 25” manufacturers last year, ahead of China’s 15.7%.
- Total sales by the “Top 25” rose by 8.5% to $361 billion, or 50 times the annual budget of the UN’s peacekeeping operations.
- China and the United States are the two biggest states in terms of global arms spending.
- For the first time, a company from the West Asia made it into the “Top 25”: EDGE, of the United Arab Emirates, was formed by the consolidation of some 25 defence entities in 2019.
- Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) established in 1966 is an independent international institute dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament.
2.The Uttar Pradesh (UP) government is working to connect Tharu villages in the districts of Balrampur, Bahraich, Lakhimpur and Pilibhit bordering Nepal, with the home stay scheme of the UP Forest Department.
- The idea is to offer tourists an experience of living in the natural Tharu habitat, in traditional huts made of grass collected mainly from the forests.
- This is expected to create jobs and bring economic independence for the tribal population.
- Meaning of ‘Tharu’: The word tharu is believed to be derived from sthavir, meaning followers of Theravada Buddhism.
- Habitat: The Tharu community belongs to the Terai lowlands, amid the Shivaliks or lower Himalayas.
- Terai is a region of northern India and southern Nepal running parallel to the lower ranges of the Himalayas.
- The Tharus live in both India and Nepal. In the Indian terai, they live mostly in Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar.
- Scheduled Tribe: Tharu is a scheduled tribe in the states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- Occupation: Most of them are forest dwellers, and some practice agriculture.
- Culture:
- They speak various dialects of Tharu, a language of the Indo-Aryan subgroup, and variants of Hindi, Urdu, and Awadhi.
- Tharus worship Lord Shiva as Mahadev, and call their supreme being “Narayan”, who they believe is the provider of sunshine, rain, and harvests.
3.(NTPC) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Indian Institute of Forest Management (IIFM), Bhopal, to implement the Narmada Landscape Restoration Project (NLRP).
- NTPC Ltd. is a Central Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) under the Ministry of Power.
- It became a Maharatna company in May 2010.
- About NLRP: It is a collaborative and participatory approach that will demonstrate the interdependence of the upstream sustainably managed forest and farm practices on downstream water resources.
- The project aims to establish an incentivisation mechanism to maintain sustainable landscape practices in Narmada basin.
- Landscape management means action, from a perspective of sustainable development, to ensure the regular upkeep of a landscape, so as to guide and harmonise changes which are brought about by social, economic and environmental processes.
4.As the Odisha government is preparing to launch fortified rice in the Public Distribution System (PDS) in Malkangiri district from coming February, more than 100 activists have opposed the move saying the people have sufficient substitutes in natural food to meet the nutritional needs.
- Vitamin C and calcium are available in abundance in natural food.
- Vitamin C is water-soluble. If the rice is laced with Vitamin C, it will get washed away while the rice is cleaned before cooking.
- It is a futile exercise to add Vitamin C to uncooked rice. And the move would lead to wasteful expenditure of taxpayers’ money.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), food fortification is defined as the practice of deliberately increasing the content of essential micronutrients so as to improve the nutritional quality of the food supply and to provide a public health benefit with minimal risk to health.
5.Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways issues draft guidelines of Technical Specifications of Floating Structures for public consultation.
- The Ministry intends to promote floating jetties for various usages all along the Indian Coastline.
- The benefits of floating jetties over the conventional quay and fixed concrete structures are as follows:
- It is a cost-effective solution and much cheaper than conventional structures price.
- Setting up of floating structures is much faster as compared to conventional jetties. Usually, floating structures can be built in 6-8 months as compared to 24 months for conventional structures.
- Its environmental impact is minimal.
- Expansions are easily feasible due to modular construction techniques.
- It is easily transportable in case of reconfiguring of the port.
- It provides constant freeboard between jetties and boats.
6.After Sikkim, Lakshadweep is the first Union Territory to become 100 percent organic as all farming is carried out without the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, providing access to safer food choices and making agriculture a more environment-friendly activity.
- The ministry of agriculture has declared the island as organic.
- India’s smallest Union Territory Lakshadweep is an archipelago consisting of 36 islands with an area of 32 sq km.
- It is a uni-district Union Territory and comprises 12 atolls, three reefs, five submerged banks and ten inhabited islands.
- The islands comprise 32 sq km. The Capital is Kavaratti and it is also the principal town of the UT.
7.At the 37th General Body meeting of Central Zoo Authority chaired by Union Minister for Environment, two new zoos the Rajgir Zoo Safari in Nalanda, Bihar and Shaheed Ashfaque Ullah Khan Prani Udyaan in Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh were granted recognition.
- Rajgir Zoo Safari, Nalanda, Bihar
- The zoo is established exclusively comprising only safari enclosures which, contrary to the conventional enclosures, offer larger space for captive animals.
- The zoo is located close to the historically important Nalanda.
- Shaheed Ashfaque Ullah Khan Prani Udyaan, Gorakhpur, U.P.
- With the establishment of this zoo, the state of Uttar Pradesh has a total of 9 zoos.
- The zoo is situated in the spiritual land of Gorakhpur and has a high visitation.




