Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 8th July 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Bubonic Plague
- Golden birdwing :
- Virtual Climate Action Ministerial:
- Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA):
- Zoonotic Diseases
- F-1 and M-1 visa holders:
- Namami Gange
- Other important current affairs
1.Bubonic Plague:

- Bayannur, a city in northern China, is on high alert after a suspected case of Bubonic plague was reported Recently. Caused mainly by Tarbagan Marmot (a species of Marmot).
- General Description:
- Marmot (genus Marmota) belongs to the squirrel family (Sciuridae) within the order Rodentia.
- These have almost 15 species and the closest living relatives of marmots are ground squirrels and prairie dogs.
- Prairie dogs are herbivorous burrowing rodents native to the grasslands of North America.
- Marmots are well suited for life in cold environments and have small fur-covered ears, short, stocky legs, and strong claws for digging.
- Marmots are diurnal (active during the day) and are almost entirely vegetarian.
- Authorities in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region announced a level III warning of plague prevention and control.
- Local authorities announced that the warning period will continue until the end of 2020 since the plague ran the risk of spreading.
Plague:
- The plague is a disease caused by the bacteria Yersinia pestis, which is found in animals, particularly rodents.
- It can be transmitted to humans through infected animals and fleas.
- In the Middle Ages (5th-15th century), this was known as the ‘Black Death’ as it was responsible for the deaths of millions of people in Europe.
- There are three types of plague:
- Bubonic plague: This infects a person’s lymphatic system (which is a part of their immune system), causing inflammation in the lymph nodes. If left untreated, the bubonic plague can also convert into either pneumonic of septicemic plague. Its symptoms include fever, chills, weakness, and headaches.
- Pneumonic plague: According to WHO, pneumonic plague is the ‘most virulent form of plague’ and can be fatal within 24 to 72 hours. It occurs when the bacteria infect the lungs. It is the only type of plague that can be transmitted from human to human. Symptoms are chest pain, fever, and cough. It is highly contagious and transmissible merely by coughing.
- Septicemic plague: This is when the bacteria enters the bloodstream and multiplies there.
- If left untreated, pneumonic and bubonic plague can lead to a septicemic plague. A person infected by septicemic plague may also notice their skin turning black.
- The plague is a life-threatening disease but if caught early, can be treated with antibiotics. However, without prompt treatment, the disease can lead to serious illnesses and even death.
- At times, antibiotics alone are not enough additionally intravenous fluids and extra oxygen are required to treat a person.
- Since it is highly contagious, those who are infected with pneumonic plague are kept in isolation.
- And people in close contact with the person infected are given a dose of antibiotics as a preventive measure.
- Other preventive measures to curb a plague outbreak are to keep the rodent population in control with pest control measures, ensuring that surrounding areas are clear of stacks of wood that rodents feed on among others.
2.Golden birdwing :

A Himalayan butterfly named golden birdwing is now India’s largest, a record the southern birdwing held for 88 years.
- With a wingspan of 194 mm, the female of the species is marginally larger than the southern birdwing (190 mm). But the male golden birdwing (Troides Aeacus) is much smaller at 106 mm.
- While the female golden birdwing was recorded from Didihat in Uttarakhand, the largest male was from the Wankhar Butterfly Museum in Shillong.
- According to the authors of the study, the only measurement used in the study of Lepidoptera is wingspan — a simple concept with various interpretations of the term.
3.Virtual Climate Action Ministerial:
Recently, the 4th edition of the virtual Ministerial on Climate Action was organized to advance discussions on the implementation of the Paris Agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- It was co-chaired by the European Union, China, and Canada.
- The participating countries exchanged their views on how they are aligning economic recovery plans amid Covid-19, with the Paris Agreement.
- India highlighted that developed country parties have not fulfilled their promise for extending financial and technological support to developing countries as envisaged under UNFCCC and its Paris Agreement.
- India hopes that in the remaining 5 months of 2020, the promised amount will be mobilized and delivered, for further strengthening climate actions in developing countries.
- The developed countries had promised to provide USD 1 trillion by 2020.
India’s Efforts in Combating Climate Change:
- India has provided 80 million LPG connections under the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) in rural areas, providing the people with clean cooking fuel and a healthy environment.
- It has distributed more than 360 million LED bulbs under the UJALA scheme, which has led to an energy saving of about 47 billion units of electricity per year and a reduction of 38 million tonnes of CO2 per year.
- India has also shifted from Bharat Stage-IV (BS-IV) to Bharat Stage-VI (BS-VI) emission norms from 1st April 2020 which was earlier to be adopted by 2024.
- It had levied a coal cess as part of one of the most explicit green initiatives.
- Under Smart Cities Mission, Climate-Smart Cities Assessment Framework 2019 has been launched which intends to provide a clear roadmap for cities and urban India towards combating climate change through the adoption of both mitigation and adaptation measures.
Achievements of India in Combating Climate Change:
- India has achieved a reduction of 21% in emission intensity of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) between 2005 and 2014, thereby on its way to achieving its voluntary target under its Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDC).
- India had pledged to cut the emission intensity of its GDP by 33-35% by 2030 below 2005 levels.
- Its renewable energy installed capacity has increased by 226% in the last 5 years and stands more than 87 gigawatts (GW).
- India has a target of installing 175 GW of renewable power capacity by 2022 under its INDC.
- The share of non-fossil sources in installed capacity of electricity generation increased from 30.5% in March 2015 to 37.7% in May 2020.
- It has further announced the aspirational target of increasing its renewable energy capacity to 450 GW.
- India has pledged to increase the share of non-fossil fuels-based electricity to 40% by 2030 under INDC.
- India’s total forest and tree cover is 8,07,276 sq. km. which is 24.56% of the total geographical area of the country.
- India has agreed to enhance its forest cover which will absorb 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 by 2030.
4.Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA):

The US has urged all its allies and partners to forgo transactions with Russia that risk triggering sanctions under the Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA).
- This indicates that despite a change in the ground realities following the deadly clash between India and China along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) last month, the U.S’s message to countries, including India, on sanctions for the purchase of Russian arms has not changed.
CAATSA:
- Enacted in 2017, it is a US federal law that imposed sanctions on Iran, North Korea, and Russia.
- Includes sanctions against countries that engage in significant transactions with Russia’s defence and intelligence sectors.
- The Act empowers the US President to impose at least five of the 12 listed sanctions on persons engaged in a “significant transaction” with Russian defense and intelligence sectors.
Sanctions imposed:
- prohibition on loans to the sanctioned person.
- prohibition of Export-Import bank assistance for exports to sanctioned persons.
- prohibition on procurement by the United States Government to procure goods or services from the sanctioned person.
- denial of visas to persons closely associated with the sanctioned person.
Implications on India:
- Although the sanctions are not directly imposed on India, it affects India nevertheless. The major reason for this is the nature of the relationship India has with Iran and Russia. India happens to have strong trade ties with both these nation-states.
- No, as per the provisions of the bill, the US imposes sanctions on all its adversaries, as well as all countries and firms dealing with these adversaries.
5.Zoonotic Diseases:
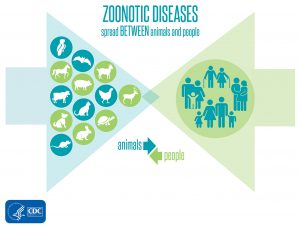
According to a report published by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), about 60% of known infectious diseases in humans and 75% of all emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic.
- The report was released on 6th July 2020, observed as ‘World Zoonoses Day’.
- It focuses on the context and nature of potential future zoonotic disease outbreaks, during the Covid-19 pandemic by identifying the anthropogenic (changes in the environment due to human activity) factors.
Zoonoses or Zoonotic Disease:
- It is a disease that passes into the human population from an animal source directly or through an intermediary species.
- Zoonotic infections can be bacterial, viral, or parasitic in nature, with animals playing a vital role in maintaining such infections.
- Examples of zoonoses include HIV-AIDS, Ebola, Malaria, and the current Covid-19 disease.
United Nations Environment Programme
- The UNEP is a leading global environmental authority established on 5th June 1972.
- Functions: It sets the global environmental agenda, promotes sustainable development within the United Nations system, and serves as an authoritative advocate for global environment protection.
- Major Reports: Emission Gap Report, Global Environment Outlook, Frontiers, Invest into Healthy Planet.
- Major Campaigns: Beat Pollution, UN75, World Environment Day, Wild for Life.
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya
6. F-1 and M-1 visa holders:

Recently, the USA has announced that F-1 and M-1 visa holders who are planning to take online-only models will not be allowed to stay in the USA.
- Many universities in the USA are planning to shift all their classes online for the fall semester due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Fall semester starts in late August and ends in late December or early January whereas the Spring semester begins in January and ends in early May.
- F-1 visas are issued to study in the USA for full-time students whereas M-1 visas are issued to students engaging in vocational or non-academic studies.
- The announcement comes weeks after the USA President suspended H1-B highly skilled worker visas through the end of the year. Most of these visas go to Indian citizens each year.
Announcements Made:
- The students outside the USA planning to take all courses online in the fall semester would not be permitted entry into the country.
- The USA would not issue visas to students who are going to take all their classes online due to the pandemic.
- It also stated that the active students under F-1 and M-1 visas in such programs must depart the country or take other measures, such as transferring to a school with in-person instruction to remain in lawful status.
- The USA regulations do not allow students in F-1 status to be in online classes but normally F-1 students are allowed to take one class or three credit hours online.
There were more than one million international students in the United States for the 2018-19 academic year.
- That accounted for 5.5% of the total USA’s higher education population.
- Also, international students contributed $44.7 billion to the USA’s economy in 2018.
- India is the second-largest source of foreign students in the USA after China.
- The largest number of international students come from China, followed by India, South Korea, Saudi Arabia, and Canada.
7.Namami Gange:

The World Bank and the Government of India have signed a loan agreement to enhance support for the Namami Gange program that seeks to rejuvenate the Ganga river.
- World Bank provides $400 million to enhance support for rejuvenating the Ganga.
Namami Gange Programme:
- It is an umbrella program that integrates previous and currently ongoing initiatives by enhancing efficiency, extracting synergies, and supplementing them with more comprehensive & better-coordinated interventions.
- Implemented by the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), and its state counterparts—State Programme Management Groups.
National Ganga Council (NGC):
- Created in October 2016 under the River Ganga (Rejuvenation, Protection, and Management) Authorities Order, 2016, dissolving the National Ganga River Basin Authority.
- Headed by the Prime Minister.
- It replaced the National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA).
- NGC would have onboard the chief ministers of five Ganga basin states—Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh (UP), Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal—besides several Union ministers and it was supposed to meet once every year.
Main Pillars of the Namami Gange Programme are:
- Sewerage Treatment Infrastructure
- River-Surface Cleaning
- Afforestation
- Industrial Effluent Monitoring
- River-Front Development
- Bio-Diversity
- Public Awareness
- Ganga Gram
Other important current affairs:
1. Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has prepared a concept note for implementing the scheme of cashless treatment of motor accident victims, as contemplated under the MV Act 2019. The Ministry has asked the States and Union Territories to share their views on it.
- It has been envisaged in the scheme to provide compulsory insurance cover to all road users in the country.
- The scheme also includes the creation of a Motor Vehicle Accident Fund.
- The fund would be utilized for the treatment of road accident victims and for payment of compensation to the injured or to the family of a person losing life in a hit and run case.
- This includes the treatment of victims during the crucial Golden hour.
- The National Health Authority, being the nodal agency for PM-JAY has been entrusted to implement the scheme.
2. In the United States, two renowned Indian-Americans who have contributed towards the efforts in mitigating the COVID-19 health crisis are among the 38 immigrants honoured by a prestigious American foundation.
- Pulitzer Prize-winning author and oncologist Siddhartha Mukherjee and Professor of Economics at Harvard University Raj Chetty have been named by the Carnegie Corporation of New York as ‘2020 Great Immigrants’ honorees.
- Siddhartha Mukherjee is a noted biologist, oncologist and the author of several acclaimed books, including the Pulitzer Prize-winning ‘The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of Cancer’. Since 2009, he has served on the faculty of Columbia University. In 2014, Dr. Mukherjee was awarded the Padma Shri, one of India’s highest civilian honors.
- Professor Raj Chetty, who was born in New Delhi, has been one of the youngest professors to be granted tenure in Harvard’s history.
3. Union Minister for Animal Husbandry launched the first edition of the Fisheries and Aquaculture Newsletter “MATSYA SAMPADA.”
- The Newsletter “MATSYA SAMPADA” aims to reach out to the stakeholders especially fishers and fish farmers through various means of communication, and to inform and educate them about the latest developments in the fisheries and aquaculture sector.
- It would be published on a quarterly basis starting from the first quarter of the year 2020-21.
- The Government of India in May, 2020 launched a new Flagship Scheme i.e. the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) for the sustainable and responsible development of fisheries sector at an investment of Rs. 20050 crore.
4. A new study has found that even the sickest Covid-19 patients produce T cells that help fight the virus.
- A T cell is a type of lymphocyte, which develops in the Thymus gland.
- T cells are a key component of the immune system and their roles include killing infected host cells, activating other immune cells, and regulating the immune response.
5. The National Medicinal Plants Board (NMPB) under the Ministry of AYUSH and the National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR) under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU).
- The purpose of this MoU is to conserve the Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Genetic Resources (MAPGRs) in the National Gene Bank (NGB).
- Establishment: The National Gene Bank was notified in 1996-97.
- Hosted By: National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR), New Delhi.
- Purpose: To conserve the Plant Genetic Resources (PGR) for future generations in the form of seeds, genomic resources, pollen, etc.
- The NGB has four kinds of facilities, namely, Seed Genebank (- 18°C), Cryogenebank (-170°C to -196°C), In vitro Genebank (25°C), and Field Genebank, to cater to long-term as well as medium-term conservation.
- It stores different crop groups such as cereals, millets, medicinal and aromatic plants, and narcotics, etc.




