Today’s Current Affairs: 9th May 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Coal Gasification:
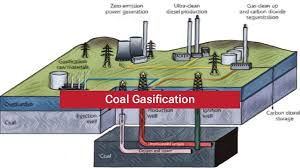
The Ministry of Coal has signed the Coal Gasification Plant Development and Production Agreement (CGPDPA) with selected applicants under Category II of the Coal Gasification Financial Incentive Scheme.
- Coal gasification is a thermo-chemical process that converts coal into syngas, a synthetic gas composed mainly of Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Methane (CH₄), and Water Vapour (H₂O).
- Coal is reacted at high temperatures (1000–1400°C) with a controlled amount of oxygen and steam, producing syngas.
- Process of Coal Gasification
- Preparation: Coal is finely crushed to increase surface area.
- Gasification reactor: The powdered coal is fed into a reactor with limited oxygen/air and steam.
- Chemical reactions: Coal breaks down into syngas components due to partial oxidation.
- Gas cleaning: Impurities like tar, sulfur, and dust are removed from raw syngas.
Lead-to-Gold Transmutation:

CERN’s ALICE detector has experimentally confirmed the conversion of lead into gold through a process of nuclear transmutation at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC).
- The concept of turning lead into gold, known as chrysopoeia, was a medieval alchemist’s dream, based on the similar density of the two metals, but modern science clarified that they are distinct chemical elements and chemical methods cannot achieve such a transformation.
- Gold nuclei (Au-203) are created when three protons and two neutrons are ejected from lead nuclei (Pb-208) during ultra-peripheral collisions in the LHC, where nuclei pass close without directly colliding.
- These near-miss collisions generate strong electromagnetic fields due to the 82 protons in each lead nucleus moving at 999993% of the speed of light, compressing the field into a short-lived photon pulse.
- The process, called electromagnetic dissociation, triggers internal nuclear oscillations, causing the emission of protons and neutrons.
- The ALICE detector utilises Zero Degree Calorimeters (ZDCs) to identify photon–nucleus interactions and detect the ejection of zero, one, two, or three protons, linked to the formation of lead, thallium, mercury, and gold, respectively.
- This is the first systematic experimental detection of gold creation at the LHC, thanks to ALICE’s high precision in recording both high-energy and rare low-particle
- The LHC is the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator, built by CERN to study fundamental particles and test predictions of the Standard Model.
Arnala : First Anti Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft

Delivery of ‘Arnala’- First Anti Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft to the Indian Navy
- ‘Arnala’ is the first of eight indigenously built Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW SWCs) delivered to the Indian Navy
- It was designed and built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, and constructed at M/s L&T Shipyard, Kattupalli, under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP).
- The warship was built according to the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS) classification rules, showcasing adherence to domestic naval architecture standards.
- The project reflects the successful collaboration between the public and private sectors in India’s defence manufacturing ecosystem, supporting strategic self-reliance.
- ‘Arnala’ is named after the historic Arnala Fort located off Vasai, Maharashtra, symbolising India’s rich maritime legacy and heritage.
- The vessel is 77 metres long and holds the distinction of being the largest Indian Naval warship powered by a Diesel Engine-Waterjet propulsion system.
- The induction of ASW SWCs like Arnala significantly enhances India’s shallow water anti-submarine warfare capacity, vital for maritime security in littoral zones.
- Over 80% of the ship’s components are sourced indigenously, marking a major step in the realization of ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ in defence manufacturing.
United Nations Forum on Forests : 20th Session

India actively participated in the 20th Session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20), held at the United Nations Headquarters in New York.
India at United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20):
- The Indian delegation highlighted the country’s achievements in forest conservation and sustainable forest management, reaffirming its commitment to the Voluntary National Contributions (VNCs) under the United Nations Strategic Plan for Forests (UNSPF) 2017–2030.
- India reported a steady increase in forest and tree cover, which now stands at 17% of its geographical area, as per the latest India State of Forest Report.
- Among the key national initiatives mentioned were:
- Aravalli Green Wall project for land restoration,
- A 86% increase in mangrove cover over the past decade,
- Afforestation of over 1.55 lakh hectares under the Green India Mission, and
- Planting of 4 billion seedlings under the Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam (Plant4Mother) campaign.
- A major highlight was India’s invitation to all UN Member States to join the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), a global platform initiated by India to protect the seven big cat species through collaborative research, knowledge exchange, and capacity-building.
- These studies focused on quantifying ecosystem services like carbon sequestration, water provisioning, and biodiversity conservation, using tools such as the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA) and the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA).
- The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) was established in 2000 by the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) to promote sustainable forest management and conservation
- The forum holds annual sessions at the UN Headquarters, alternating between technical discussions (odd years) and policy-level dialogues (even years).
- UNFF has universal membership, including all UN Member States and specialised forest-related agencies.
- India is a founding member of the UNFF, and continues to play a proactive role in shaping forest-related global policy.
- The 19th UNFF Session Declaration aimed to secure high-level political commitment to forest protection, with actionable steps to achieve the goals of the UN Strategic Plan for Forests (UNSPF).
Competition Commission of India (Determination of Cost of Production) Regulations, 2025:

The Competition Commission of India recently notified the Competition Commission of India (Determination of Cost of Production) Regulations, 2025, aimed at effectively assessing alleged predatory pricing and deep discounting practices in the quick commerce and e-commerce sectors.
- Competition Commission of India (Determination of Cost of Production) Regulations, 2025 was notified by the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
- It is aimed at effectively assessing alleged predatory pricing and deep discounting practices in the quick commerce and e-commerce sectors.
- Predatory pricing refers to a strategy where a dominant company deliberately lowers its prices below the cost of production to drive competitors out of the market.
- Once rival firms are weakened or eliminated, the company typically raises prices to recoup its losses and consolidate market control.
- This practice is specifically prohibited under Section 4(2)(a)(ii) of the Competition Act, 2002, when used to unfairly gain or maintain dominance.
- To strengthen oversight of such behavior, CCI (Determination of Cost of Production) Regulations, 2025, implements updated cost assessment standards.
- These revised benchmarks are designed to reflect modern economic thinking, judicial rulings, and international best practices in competition law.
- According to the latest regulations, the “cost of a good or service would be assumed to be its average variable cost”, which is the total variable cost divided by total output during a particular period.
- Here, the total variable cost refers to the total cost (including everything that goes into the production of that good or service) minus the fixed cost and fixed overheads attributable to the product.
- One of the key changes in the new regulations is the shift from sector-specific benchmarks to a case-by-case assessment model that is flexible and adaptable to various industries, including the digital economy.
- These new regulations repeal the 2009 Cost Regulations and reflect evolving global practices in competition law.
INS Sharda to Maldives for HADR:

INS Sharda arrived at Maafilaafushi Atoll, Maldives, for a joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) exercise with the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF).
- The exercise is part of India’s “MAHASAGAR (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions)” vision in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Earlier, following the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, the Indian Navy, as part of its HADR operations, launched Operation Castor to provide vital relief to the Maldives during the crisis.
- The HADR exercise aims to enhance interoperability between the Indian Navy and MNDF to respond effectively to humanitarian challenges.
- INS Sharda (P55), a Sukanya-class patrol vessel, was awarded the ‘On the Spot Unit Citation’ for rescuing 19 hostages from the hijacked Iranian vessel Omari off Somalia in 2024, showcasing operational excellence and reinforcing India’s maritime security role in the IOR.
World Thalassaemia Day:

World Thalassaemia Day is observed on May 8 every year to raise awareness and promote action around the genetic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide.
- Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder.
- Thalassemia causes the body to have less of the protein hemoglobin than usual.
- Hemoglobin is present in red blood cells and allows the red blood cells to carry oxygen.
- Not having enough hemoglobin or red blood cells can lead to a condition called anemia. That can make you feel tired and weak.
- Thalassaemia is caused by inheriting a gene mutation (change in the normal DNA) from one or both parents.
- There are different types of thalassaemia. The type someone has depends on which gene mutation they inherit.
- Symptoms: Thalassemia can cause mild or severe anemia and other complications over time (such as iron overload).
- Treatments: Blood transfusions – regular blood transfusions treat and prevent anaemia; in severe cases these are needed around once a month. Chelation therapy – treatment with medicine to remove the excess iron from the body that builds up as a result of having regular blood transfusions .The only possible cure for thalassaemia is a stem cell or bone marrow transplant, but this is not done very often because of the risks involved.
Indo-Pacific Logistics Network:

Quad partners recently convened at the Asia-Pacific Center for Security Studies in Honolulu, Hawaii, for a Tabletop Exercise, a simulation to launch the Quad Indo-Pacific Logistics Network IPLN.
- The Quad Indo-Pacific Logistics Network pilot project was launched during the fourth Quad Leaders’ Summit in September 2024.
- IPLN is an initiative that enables Quad partners to leverage shared logistics capabilities in the Indo-Pacific to support civilian response to natural disasters more rapidly and efficiently across the region.
- This effort will complement existing efforts with Indo-Pacific partners.
- Together with the Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness, the IPLN reflects the Quad’s commitment to ensuring a free and open Indo-Pacific and highlights the value of strengthening practical cooperation to address regional challenges.
- The Quad, officially the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, is a group of four countries: the United States, Australia, India, and Japan.
Balochistan : In News
On May 9, 2025, Mir Yar Baloch declared Balochistan’s independence from Pakistan, urging India to recognize it and host an embassy in New Delhi, the UN to deploy peacekeepers, and the Pakistani Army to withdraw. Balochistan is Southwestern province of Pakistan, largest by area (~44% of Pakistan’s territory), bordering Iran and Afghanistan, and facing the Arabian Sea.
UK’s Proposed Carbon Border Tax:
India has stated it will retaliate if the UK imposes a carbon tax (CBAM) on Indian exports starting January 2027, calling it a violation of the CBDR (Common But Differentiated Responsibilities) principle under international climate agreements. CBAM is a form of carbon tax on imports imposed by developed countries (like the EU or UK) based on the carbon intensity of production in the exporting country. Aims to prevent carbon leakage by equalizing carbon prices between domestic and imported goods.
The UK’s version of CBAM is expected to start from January 1, 2027. Sectors like steel, aluminium, cement, and energy-intensive goods are likely to be affected first.
Mission Sankalp:
Mission Sankalp, a massive anti-Naxal operation along the Chhattisgarh–Telangana border, entered its third week, with confirmed Maoist casualties and strategic gains.Launched by: Security forces under the joint command of Chhattisgarh Police, Telangana Police, CRPF, and CoBRA. Area of Operation: Karregutta hills, Bijapur district (Chhattisgarh) – Mulugu district (Telangana) border. Objective: Flush out top Maoist leaders, especially Battalion 1 of the People’s Liberation Guerrilla Army (armed wing of CPI-Maoist). Dismantle fortified Maoist hideouts and destroy logistics bases and bunkers.
India and Chile signed the Terms of Reference:
India and Chile signed the Terms of Reference (ToR) to begin negotiations for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).Chile is ocated in South America, Chile is a long, narrow country bordered by: Peru and Bolivia to the North, Argentina to the East, Pacific Ocean to the West. The Argentina–Chile border is the longest in South America and the third-longest globally. Andes Mountains: The World’s longest continental mountain range. Member of the “Lithium Triangle” (with Argentina and Bolivia), holding over 75% of global lithium reserves under salt flats. Other resources include molybdenum, iron ore, timber, hydropower, and precious metals.
World Red Cross and Red Crescent Day:
World Red Cross and Red Crescent Day is observed annually on 8th May to honour the humanitarian efforts of millions of volunteers worldwide.Theme 2025: “Keeping Humanity Alive” reflects a commitment to humanitarian service amid rising inequalities, health crises, and conflicts.The day was established in 1948 to commemorate the birth of Henry Dunant, born on 8th May 1828, who was the founder of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and the first Nobel Peace Prize laureate, sharing the award with Frédéric Passy.




