Today Current Affairs: 9th October 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Nobel Prize For Literature:

Abdulrazak Gurnah, 72, who was born in Zanzibar and now lives in the UK, became the fifth African writer to win the Nobel Prize for Literature, after Nigerian writer Wole Soyinka (1986), Egyptian Naguib Mahfouz (1988), and South African writers Nadine Gordimer (1991) and John M Coetzee (2003).
- He is the author of 10 novels and several short stories and essays, including Memory of Departure (1987), Pilgrims Way (1988), Paradise (1994), By the Sea (2001), Desertion (2005), Gravel Heart (2017) and, most recently, Afterlives (2020).
- His writing explores the immigrant experience and how exile and loss shape identities and cultures.
- Most of his books feature African Arab protagonists trying to come to terms with dislocation and estrangement, looking in on societies and cultures on which their holds are tenuous.
- Zanzibar is an autonomous region of Tanzania. It is composed of the Zanzibar Archipelago in the Indian Ocean.
Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA)

In the first such signal to New Delhi, visiting US Deputy Secretary of State Wendy Sherman has indicated that Washington might reconsider slapping sanctions on the Indian government when New Delhi takes delivery of five Russian-built S-400 Triumf anti-aircraft missile systems in a US$5.5 billion deal later this year.
- There has been unease in Washington ever since 2016 when India announced the deal with Russia, which remains New Delhi’s biggest defence partner.
- Now, the S-400 deal could attract sanctions under US’ CAATSA law. The US has already sanctioned China and Turkey over similar purchases.
- The S-400 Triumf is a mobile, surface-to-air missile system (SAM) designed by Russia.
- It is the most dangerous operationally deployed modern long-range SAM (MLR SAM) in the world, considered much ahead of the US-developed Terminal High Altitude Area Defense system (THAAD).
- Countering America’s Adversaries through Sanctions Act (CAATSA)‘s core objective is to counter Iran, Russia and North Korea through punitive measures.
- Enacted in 2017.
- Includes sanctions against countries that engage in significant transactions with Russia’s defence and intelligence sectors.
PM MITRA Scheme:

The government has approved the setting up of seven PM MITRA textiles parks, following the “Union Budget for 2021-22″ commitments, with a total outlay of Rs. 4,445 crores in a period of 5 years.
About “PM-MITRA” Scheme:
- The scheme aims to realize the vision of building an Aatmanirbhar Bharat by positioning India strongly on the Global textiles map.
- It is inspired by the 5F vision of Hon’ble Prime Minister –Farm to Fibre to Factory to Fashion to Foreign.
- The scheme aims to create a world-class industrial infrastructure that would attract cutting-edge technology and boost FDI and local investment in the sector.
- Sites for the scheme will be selected by a Challenge Method, based on objective criteria for Greenfield / Brownfield sites.
- PM MITRA park will be developed by a Special Purpose Vehicle which will be owned by the Central and State Government and in a Public Private Partnership (PPP) Mode.
- Each MITRA Park will have an incubation centre, common processing house and a common effluent treatment plant and other textile related facilities such as design centres and testing centres.
- The Master Developer will not only develop the Industrial Park but also maintain it during the concession period.
- Under the scheme, the centre will provide development capital support for the development of common infrastructure of Rs 500 crore for each greenfield MITRA park and upto Rs 200 crore for each brownfield park.
- Greenfield describes a completely new project that has to be executed from scratch, while a brownfield project is one that has been worked on by others.
- An additional Rs 300 crore will be provided as Competitiveness Incentive Support for the early establishment of textiles manufacturing units in each of these parks.
- Investors who set up “anchor plants” that employ at least 100 people will be eligible for incentives of upto Rs 10 crore every year for upto three years.
What Is Buddhist Circuit?
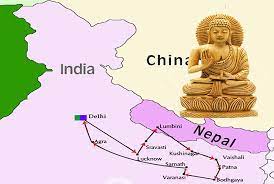
Centre has planned major infrastructure push for Buddhist Circuit. The Union Tourism Ministry has aggressively started tourism promotion with participation of the industry stakeholders, especially after the dramatic improvement of Covid situation in the country and achievement of vaccination targets.
- The Buddhist Circuit project was announced by the central government in 2016. Since then, Rs 343 crore has been sanctioned for the project under various schemes.
- The Buddhist circuit is a route that follows in the footsteps of the Buddha from Lumbini in Nepal where he was born, through Bihar in India where he attained enlightenment, to Sarnath and Kushinagar in Uttar Pradesh in India, where he gave his first teachings and died.
- Under the Ministry of Tourism’s flagship Swadesh Darshan scheme, multiple projects have been undertaken in Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh.
- In Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, the plan is to further develop the sites of Bodh Gaya, Nalanda, Rajgir, Viashali, Sarnath, Shravasti, Kushinagar, Kaushambi, Sankisa and Kapilavastu.
- These sites currently receive approximately six per cent of nationwide foreign tourist arrivals, with Sarnath and Bodh Gaya leading the pack.
- Initially, it was envisaged only to seven major Buddhist pilgrimage sites in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, later it was expanded to 21 more states to make it India’s first trans- national tourist circuit.
- It has identified stupas and viharas in these 21 states, around which small intra-state Buddhist zones will be developed.
- The states now that will be covered include Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Kerala, West Bengal, Goa, Gujarat and Jammu & Kashmir.
- The Buddhist circuit has four international and two domestic airports, while two more in the pipeline.
- There are also plans of developing helicopter services and improving international connectivity under the UDAN scheme.
High Ambition Coalition For Nature And People:

At a ceremony held between the French and Indian governments on 7th October in New Delhi, India officially joined the High Ambition Coalition for Nature and People, a group of more than 70 countries encouraging the adoption of the global goal to protect 30×30.
- HAC members currently include a mix of countries in the global north and south; European, Latin American, Africa and Asia countries are among the members. India is the first of the BRICS bloc of major emerging economies (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) to join the HAC.
- India’s announcement comes in the lead up to a high-level biodiversity meeting, hosted by China. The virtual meeting to take place October 11-15 will tackle key aspects of the biodiversity treaty to be finalized in 2022.
- The global 30×30 goal – to protect at least 30% of the planet by 2030 – is currently a centrepiece of the treaty, known as the post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework.
Cyber Security In Power Sector:

Ministry of Power has released guidelines for the Cyber Security in Power Sector.
- Central Electricity Authority (CEA) under the provision of Section 3(10) on Cyber Security in the “Central Electricity Authority (Technical Standards for Connectivity to the Grid) (Amendment) Regulations, 2019” has framed Guideline on Cyber Security in Power Sector to be adhered by all Power Sector utilities to create cyber secure eco system.
- This is the first time that a comprehensive guideline has been formulated on cyber security in power sector.
- It lays down a cyber assurance framework, strengthens the regulatory framework, puts in place mechanisms for security threat early warning, vulnerability management and response to security threats, and secures remote operations and services.
- The norms are applicable to all responsible entities as well as system integrators, equipment manufacturers, suppliers/ vendors, service providers, and IT hardware and software OEMs (original equipment manufacturers) engaged in the Indian power supply system.
- The guidelines mandate ICT-based procurement from identified ‘trusted sources’ and ‘trusted products’ or else the product has to be tested for malware/ hardware trojan before deployment for use in the power supply system network.
Javan Gibbon:

Indonesia is taking steps to protect the habitat of Javan Gibbon (Hylobates moloch), which is endangered by climate change and human encroachment.
- The species is also hunted for both meat and pet trade.
- The silvery gibbon, also known as the Javan gibbon, is a primate. They are found in groups only, usually in a pair of two.
- It is endemic to the Indonesian island of Java, where it inhabits undisturbed rainforests up to an altitude of 2,450 m.
- It helps in regenerating forest vegetation by dispersing seeds.
- There are around 4,000 Javan gibbons left.
- It was declared Critically Endangered in 2004 but since has recovered to status of Endangered as per IUCN criterion. However, the latest IUCN estimate shows that their population is decreasing.
- Habitat:
- The Javan Gibbon wild population is only found in Java, Indonesia.
- It is not found in India (The hoolock gibbon is the only gibbon found in India).
- Protection Status:
- IUCN: Endangered (EN)
- CITES: Appendix I
Application Ecosystem For Integration Of Procurement Portals:

The Department of Food and Public Distribution has developed an application ecosystem for integration of procurement portals of all state governments.
- The Application Ecosystem will allow the integration of procurement portals of all state governments having Minimum Threshold Parameters (MTPs) for monitoring and strategic decision making.
- The introduction of MTPs in procurement operations are necessitated to avoid middlemen in procurement and ensure that farmers get the best value for their produce.
- MTPs will ensure uniformity and interoperability among the states.
- The MTPs are five key details which states are required to capture in their procurement portals, which are related to online registration, farmer data, digitized mandi and procurement, and billing.
- The integration of state portals with the central portal will go a long way in expediting the reconciliation of procurement figures with States and release of funds by the Centre Government to the States.
- Due to variations in the procurement systems, there emerge both systemic and implementation challenges for implementing the schemes of the central government.
- Reconciliation of the procurement operations with various states is sometimes a long-drawn exercise, leading to delays in the release of funds to states.
- Moreover, the non-standard procurement operations also lead to avoidable inefficiencies, which manifest in the form of middlemen in the procurement operations.
- There is no pan-India standard procurement ecosystem for monitoring and strategic decision making.
- Standardization of the operations are essential in helping the country achieve greater levels of transparency and efficiency in procurement operations, which ultimately lead to ensuring food security for the people of the country.
State Of Climate Services Report 2021: WMO:

The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) released the State of Climate Services report 2021. It focuses on Terrestrial Water Storage.
- Earlier, on water day (22nd March), in a report released by the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), one in five children worldwide reside in areas of high or extremely high water vulnerability.
Terrestrial Water Storage (TWS):
- TWS is the sum of all water on the land surface and in the subsurface, i.e. surface water, soil moisture, snow and ice and groundwater.
- Water is a key prerequisite for human development. But only 0.5% of water on Earth is usable and available as freshwater.
- Water resources across the world are under tremendous pressure due to human and naturally-induced stressors.
- These include population growth, urbanisation and decreasing availability of freshwater.
- Extreme weather events too have been responsible for the pressure on water resources realised across sectors and regions.
Global Scenario:
- TWS dropped at a rate of 1 cm per year in 20 years (2002-2021).
- The biggest losses have occurred in Antarctica and Greenland.
- But many highly populated, lower latitude locations have also experienced TWS losses.
Industrial Park Ratings System (IPRS) Report:

The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) has released the Industrial Park Ratings System Report.
- The IPRS pilot exercise was launched in 2018 with an objective of enhancing industrial infrastructure competitiveness and supporting policy development for enabling industrialization across the country.
- The IPRS report is an extension of the India Industrial Land Bank which features more than 4,400 industrial parks in a GIS-enabled database.
- It seeks to help investors identify their preferred location for investment.
- These ratings are assigned on the basis of key existing parameters and infrastructure facilities etc.
Highlights of the report:
- 41 Industrial Parks have been assessed as “Leaders” in the Industrial Park Ratings System Report released by DPIIT.
- 90 Industrial Parks have been rated as under the Challenger category while 185 have been rated as under “Aspirers”.




