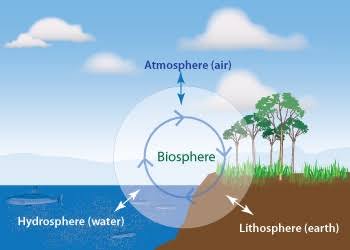
Biosphere Reserves can be defined as widespread areas of bio-diversity wherein fauna and flora are protected. Biosphere’ refers to water, land, and atmosphere that supply life on our planet. The word ‘reserve’ symbolizes that it is a special area designated for creating a balance between conservation and sustainable use.
Table of Contents
Introduction:
- Biosphere Reserve (BR) is an international designation by UNESCO for representative parts of natural and cultural landscapes extending over large areas of terrestrial or coastal/marine ecosystems or a combination thereof.
- BRs are thus special environments for both people and nature and are living examples of how human beings and nature can co-exist while respecting each others’ needs.
- These areas are internationally recognized within the framework of UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere (MAB) program, after receiving consent from the participating country.
Characteristics of Biosphere Reserve:
- It aims at Achieving the three international functions of conservation, development and logistic support.
- It Focuses on a multi-stakeholder approach with a high emphasis on the involvement of local communities for management
- It promotes proper dialogue for conflict resolution of any natural resource utilization.
- It Integrates cultural and biological diversity. the role of traditional knowledge in ecosystem management is highlighted.
Designation of biosphere reserve:
Designation procedure
Biosphere reserves are designated for inclusion in the Network by the International Coordinating Council (ICC) of the MAB Programme in accordance with the following procedure.
- States, through National MAB Committees where appropriate, forward nominations with supporting documentation to the secretariat after having reviewed potential sites, taking into account the criteria as defined in Article 4.
- The secretariat verifies the content and supporting documentation: in the case of an incomplete nomination, the secretariat requests the missing information from the nominating State.
- Nominations will be considered by the Advisory Committee for Biosphere Reserves for recommendation to ICC.
- ICC of the MAB Programme takes a decision on nominations for designation.
- The Director-General of UNESCO notifies the State concerned of the decision of ICC.
- States are encouraged to examine and improve the adequacy of any existing biosphere reserve, and to propose extension as appropriate, to enable it to function fully within the Network. Proposals for extension follow the same procedure as described above for new designations.
- Biosphere reserves which have been designated before the adoption of the present Statutory Framework are considered to be already part of the Network.
- The provisions of the Statutory Framework, therefore, apply to them.
Functions of biosphere reserve:
Conservation
- To ensure the conservation of landscapes, ecosystems, species and genetic variations.
- To encourage traditional resource use systems
- To understand the patterns and processes of functioning of ecosystems
- To monitor the natural and human-caused changes on spatial and temporal scales
Development:
- To promote, at the local level, economic development which is culturally, socially and ecologically sustainable.
- To develop the strategies leading to improvement and management of natural resources
Logistics Support:
- To provide support for research, monitoring, education and information exchange related to local, national and global issues of conservation and development
- Sharing of knowledge generated by research through site-specific training and education; and
- Development of community spirit in the management of natural resources.
Structure of Biosphere Reserve:
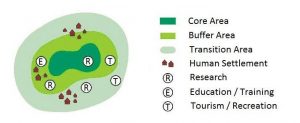
Structure and Design of Biosphere Reserves:
In order to undertake complementary activities of biodiversity conservation and development of sustainable management aspects, Biosphere Reserves are demarcated into three inter-related zones. These are:-
- The core area: It involves an entirely secured and protected ecosystem that contributes to the preservation of landscapes, ecosystems, species and genetic variation.
- The buffer zone: It encompasses or adjoins the core areas. It is utilized for activities compatible with sound ecological practices that can fortify scientific research, monitoring, training, and education.
- The transition area: It is the part of the reserve where the greatest activity is permitted to promote economic and human development that is sustainable.
List of the Biosphere in India – UPSC Notes:
As per the updated records of the government of India, there is a total of 18 biosphere reserves in our country.
1.Nilgiri:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1986,
- Nilgiri falls within the state boundaries of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, along the western ghats
2.Nanda Devi:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1988,
- Nanda Devi falls within the state boundaries of Uttarakhand, along the western Himalayas.
3.Nokrek:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1988,
- Nokrek falls within the state boundaries of Meghalaya, along the eastern Himalayas.
4.The Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1989,
- Great Nicobar falls within the boundaries of the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
5.Gulf Of Mannar:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1989,
- the Gulf of Mannar falls within the state boundaries of Tamil Nadu.
6.Sunderbans:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1989,
- Sunderbans falls within the state boundaries of West Bengal, along the Gangetic delta.
7.Manas:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1989,
- Manas falls within the state boundaries of Assam, along the eastern Himalayas.
8.Simlipal:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1994,
- Simlipal falls within the state boundaries of Odisha, along the Deccan peninsula.
9.Dibru-saikhowa:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1997,
- Dibru-saikhowa falls within the state boundaries of Assam, along the eastern Himalayas.
10.Dehang-dibang:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1998,
- Dehang-dibang falls within the state boundaries of Arunachal Pradesh, along the eastern Himalayas.
11.Panchmarhi:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 1999,
- Panchmarhi falls within the state boundaries of Madhya Pradesh. .
12.Khangchendzonga:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 2000,
- Khangchendzonga falls within the state boundaries of Sikkim, along the eastern Himalayas.
13.Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 2001,
- the Agasthyamalai biosphere reserve falls within the state boundaries of Kerala and Tamil Nadu, along the western ghats.
14.Achanakamar -Amarkantak:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 2005,
- Achanakamar –Amarkantak falls within the state boundaries of Madhya Pradesh and Chattisgarh, along the Maikala hills.
15.Great Rann of Kutch:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 2008,
- Great Rann of Kutch falls within the state boundaries of Gujarat.
16.Cold Desert:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 2009,
- Cold Desert falls within the state boundaries of Himachal Pradesh along the western Himalayas.
17.Seshachalam Hills:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 2010,
- Seshachalam hills fall within the state boundaries of Andhra Pradesh, along the eastern ghats.
18.Panna:
- Designated as a biosphere reserve in the year 2011,
- Panna falls within the state boundaries of Madhya Pradesh, along the ken river.
UNESCO MAB and biosphere program:
11 of the eighteen biosphere reserves are a part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves, based on the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme list.
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve -Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka- 2000
- Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve -Tamil Nadu- 2001
- Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve- West Bengal- 2001
- Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve- Uttarakhand -2004
- Nokrek Biosphere Reserve- Meghalaya -2009
- Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve- Madhya Pradesh- 2009
- Simlipal Biosphere Reserve -Odisha- 2009
- Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve- Great Nicobar -2013
- Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve- Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh -2012
- Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve -Kerala and Tamil Nadu- 2016
- Khangchendzonga National Park -Sikkim- 2018
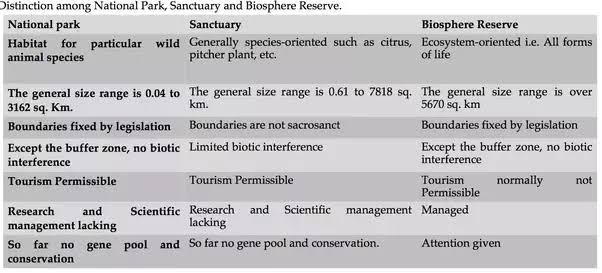
Difference between biosphere reserve and national parks and wildlife sanctuary:
National Biosphere Reserve Programme:
- The National Biosphere Reserve Programme was initiated in 1986.
- India has created a network of protected areas in the form of 96 National Parks, 510 Wildlife Sanctuaries, 28 Tiger Reserves, and 25 Elephant Reserves.
- The area covered under protected area network accounts for around 5% of the total geographical area of the country.
- The rich biodiversity in India has given shape to a variety of cultural and ethnic diversity which includes over 550 tribal communities of 227 ethnic groups spread over 5,000 forest villages.
Biosphere Conservation

- UNESCO is promoting the peaceful integration of man and nature for sustainable development through participatory dialogue, awareness on poverty reduction and human well-being improvement, respect for cultural values and society’s ability to cope with change.
- UNESCO has developed 631 biosphere reserves in 119 countries, out of which there are 14 transboundary sites, to foster economic and sustainable development.