Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:17th April 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- International Monetary and Finance Committee (IMFC):
- WATER CRISIS IN INDIA
- National Conference on Kharif Crops 2020
- Post-intensive care syndrome (PICS).:
- Software Technology Parks of India (STPI):
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based tool
- Trimeresurus Salazar
- Reserve Bank of India announced a slew of measures after GoI extended the lockdown till May 3, 2020
- World Hemophilia Day
- RBI launches OBICUS
1.International Monetary and Finance Committee (IMFC):

Union Minister of Finance & Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman recently attended through video-conference the Plenary Meeting of the International Monetary and Financial Committee.
- The discussions at the meeting were based on IMF Managing Director’s Global Policy Agenda titled, “Exceptional Times – Exceptional Action”.
- The members of the IMFC updated the committee on the actions and measures taken by member countries to combat COVID-19, and also remarked on IMF’s crisis-response package to address global liquidity and members’ financing needs.
IMFC:
- The IMFC has 24 members, drawn from the pool of 187 governors.
- Its structure mirrors that of the Executive Board and its 24 constituencies. As such, the IMFC represents all the member countries of the Fund.
- The IMFC meets twice a year, during the Spring and Annual Meetings. The Committee discusses matters of common concern affecting the global economy and also advises the IMF on the direction its work.
- At the end of the Meetings, the Committee issues a joint communiqué summarizing its views. These communiqués guide the IMF’s work program during the six months leading up to the next Spring or Annual Meetings. There is no formal voting at the IMFC, which operates by consensus.
2.Water Crisis in India:

Although hand hygiene is considered an effective means for warding off novel coronavirus infections, the lack of access to clean water itself is an ongoing challenge that the country has been facing for several years.
- In 2017, in a written reply in Lok Sabha, the Ministry of Water Resources said that average annual per capita water availability fell from 1820 cubic meters assessed in 2001 to to 1545 cubic meters in 2011, and could reduce further to 1341 and 1140 in the years 2025 and 2050 respectively.
- Annual per-capita water availability of less than 1700 cubic meters is considered a water-stressed condition.
- Annual per- capita water availability below 1000 cubic meters is considered a water scarcity condition.
- In a 2018 report, the water and sanitation advocacy group WaterAid ranked India at the top of 10 countries with the lowest access to clean water close to home, with 16.3 crore people not having such access.
3.National Conference on Kharif Crops 2020:

Recently, the Union Minister of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare addressed the National Conference on Kharif Crops in 2020 through a video conference.
Highlights of the Conference
- To discuss various issues and list out steps in consultation with the States about preparedness for Kharif cultivation given the lockdown situation.
- To take up the doubling of farmers’ income in mission mode.
- To urge states to explain the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana and Soil Health Card Scheme to each farmer.
- To implement the Home Ministry exemptions and relaxations for the Agricultural sector while ensuring social distancing and social responsibility norms.
- To start using the e-NAM (National Agriculture Market) extensively.
- The target of foodgrain production for the Financial Year 2020-21 has been fixed at 298.0 million tonnes.
- During the FY 2019-20, against the foodgrain production target of 291.10 million tonnes, higher production of about 292 million tonnes is anticipated due to the enhancement of area coverage and productivity of various crops.
4. Post-intensive care syndrome (PICS).:
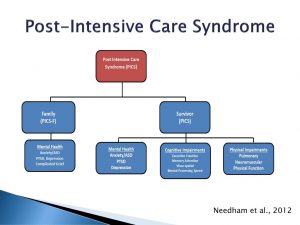
After leaving the ICU, some Covid-19 patients may suffer from what is known as post-intensive care syndrome (PICS).
- PICS is defined as a new or worsening impairment in physical (ICU-acquired neuromuscular weakness), cognitive (thinking and judgment), or mental health status arising after critical illness and persisting beyond discharge from the acute care setting.
- Further, such patients may experience neuromuscular weakness, which can manifest itself in the form of poor mobility and recurrent falls.
- A psychological disability may arise in a person in the form of depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- The most common PICS symptoms are generalized weakness, fatigue, decreased mobility, anxious or depressed mood, sexual dysfunction, sleep disturbances, and cognitive issues.
- PICS may be induced if a person was on prolonged mechanical ventilation, experienced sepsis, multiple organ failure and a prolonged duration of “bed-restore deep sedation”.
5.Software Technology Parks of India (STPI):

Because of the COVID19 outbreak and consequent lockdown, the Government provided relief from payment of four-month rental to the small IT units operating out of the Software Technology Parks of India (STPI).
Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) is an autonomous society under the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology and it has 60 centers across the country.
- Objective: Encouraging, promoting and boosting the export of software from India.
- Established in: 1991.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
Objectives of the Software Technology Parks of India are:
- To promote the development and export of software and software services including Information Technology (IT) enabled services/ Bio-IT.
- To provide statutory and other promotional services to the exporters by implementing Software Technology Parks (STP)/ Electronics and Hardware Technology Parks (EHTP) Schemes, SEZ scheme and other such schemes which may be formulated and entrusted by the Government from time to time.
- To provide data communication services including value-added services to IT / IT enabled Services (ITES) related industries.
- To promote micro, small and medium entrepreneurs by creating a conducive environment for entrepreneurship in the field of IT/ITES.
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based tool :

A University in Rome (Italy) is conducting a pilot run for a patented Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based tool developed by students and a professor from Mumbai, which they claim can test Covid-19 through voice-based diagnosis using a smartphone.
- The tool has already been tested on 300 individuals and has detected Covid-19 patients with 98% accuracy.
- The tool is based on a voice-based diagnosis through an app. It can find coronavirus from the tone of the voice.
- As someone speaks to the microphone on the app, the tool breaks down the voice in multiple parameters such as frequency and noise distortion.
- These values are then compared to a normal person’s values and the patented technique then determines if the patient is positive or not.
- Each human voice has 6,300 parameters, and only a few units, less than a dozen, specifically characterize individuals. The human ear, apart from colds, is not able to distinguish them, but artificial intelligence does.
- Each one of an individual’s internal organs is sort of a resonator, so if anyone has a problem with lungs or heart, this will be reflected in his/her voice.
- The current novel coronavirus cases could be detected this way.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- It describes the action of machines accomplishing tasks that have historically required human intelligence.
- It includes technologies like machine learning, pattern recognition, big data, neural networks, self algorithms, etc.
- AI involves complex things such as feeding a particular data into the machine and making it react as per the different situations. It is basically about creating self-learning patterns where the machine can give answers to the never answered questions like a human would ever do.
- AI technology helps in analyzing data and thus can improve the efficiency of systems like power management in cars, mobile devices, weather predictions, video and image analysis.
7. Trimeresurus Salazar :

A new species of green pit viper found in Arunachal Pradesh has a Harry Potter link.
- The scientific name Trimeresurus Salazar has been inspired by Salazar Slytherin, co-founder of J.K. Rowling’s fictional Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry.
- The new species is the fifth variety of reptiles to have been discovered in the State in a little more than a year.
- Salazar’s pit viper belongs to the genus Trimeresurus Lacépède and has been collected from the Pakke Tiger Reserve in Pakke-Kessang district.
8.World Hemophilia Day:

Every year April 17 is celebrated as World Hemophilia Day. Hemophilia is an inherited bleeding disorder in which blood does not clot properly
- The day is observed by the World Federation of Hemophilia.
- Apart from the organization, several other international organizations mark World Hemophilia Day.
- Theme: Get + Involved virtually and stay safe
- World Hemophilia Day is observed to increase awareness about hereditary bleeding disorders.
- On this day, people from different parts of the world come together to share the advances in the treatment for hemophilia.
9. The Reserve Bank of India announced a slew of measures after GoI extended the lockdown till May 3, 2020.:

The Apex bank cut the reverse repo rate to 3.75%. It cut the repo rate to 4.4% from 5.15%. Also, the central bank has announced Rs 50,000 crore for Long Term Repo Operation (LTRO).
- RBI has eased the Liquidity Coverage Ratio from 100% to 80%.
- The LCR is the assets held by the banks to make sure its ongoing ability to meet short-term obligations are fulfilled.
- The RBI will also provide Rs 50,000 crore special financial assistance to institutions such as SIDBI, NABARD, NHB.
- This is being done as these institutions are not able to raise fresh resources from the market due to the lockdown.
- This time the LTRO has been named LTRO 2.0 because this time the LTRO is to focus on the liquidity needs of microfinance and NBFC.
- Earlier the LTRO went largely to the public sector undertakings and larger corporations.
10.RBI launches OBICUS:

The Reserve Bank of India launched OBICUS. This is the 49th round of survey by the apex bank for the period January to March. The Capacity Utilisation declined to 68.6% from 69.1%.
- OBICUS is Order Books, Inventories and Capacity Utilization Survey (OBICUS).
- The survey provides an insight into the demands of the Indian manufacturing sector.
- The survey is conducted quarterly (4 times a year). It is being conducted since 2008.
- The survey covers 2,500 companies both in the public and private sectors.
- The survey also provides a ratio of total inventories to sales.
- Also, the survey provides a ratio of raw materials to finished goods.
- It helps to measure economic activity in the country
Other important current affairs:
1. The Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS) has developed a compact solid-state sensor to detect the heavy metal ions in water.
- It is a portable device that can help onsite detection in remote areas.
- The compact solid-state sensor can detect the heavy metal ions like lead ions (Pb2+) down to 0.4 parts per billion (ppb).
2. The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has issued an advisory that the ZOOM video conference is not a safe platform.
- USA based ZOOM video communication has seen an exponential rise in usage in India as office-goers remain at home owing to the present lockdown.
- The software used in the online platform is said to be made in China and some calls were being routed through servers in China.
- The Cyber Coordination Centre (CyCord), under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), issued a set of guidelines for its safe usage. It was not for use by government offices and officials
3. According to a WHO Information Note — ‘Tuberculosis and COVID-19’, there is a need to maintain TB services during the effective response to COVID-19.
- TB patients who have lung damage or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease may suffer from more severe illness if they are infected with COVID-19.
- India accounts for 27 percent of the world’s total TB patients and is among the top 8 countries with the highest number of TB cases.
- In 2018, as many as 4.4 lakh people died of TB in India which is 29 percent of the total 1.5 million deaths due to TB in the world.
- Out of a total of 7 million cases reported in 2018 across the world, India had 2.69 million cases, while, according to data available, it missed out on tracking down 5.40 lakh cases.
- Doctors claim that people suffering from TB and COVID-19 may have poorer treatment outcomes, especially if TB treatment is interrupted. The immunity of TB patients is very low.
4. Recently, researchers from the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) have started developing an inactivated virus vaccine for the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2).
- Inactivated vaccines are known for their safety and easy production.
- Active pathogens are grown in large numbers and then killed either by a chemical or heat.
- Although the pathogen is killed or made to lose its reproduction capacity, various parts of the pathogen are intact. E.g The antigen (the chemical structure) that is recognized by the immune system is left unimpaired.
- When this dead microbe is introduced in the body, the immune system is tricked to respond by producing antibodies against specific antigens still left intact, without knowing that the pathogen is defective.
- As the pathogen is dead, it cannot reproduce nor cause even a mild disease.
- Thus, it is safe to administer to even people with lesser immunity, like the old and those who have comorbidity.
Inactivated polio vaccine and the rabies vaccine are made this way.
5.Chitra GeneLAMP-N
- It is a diagnostic test kit that can confirm COVID19 in 2 hours at a low cost.
- It has been developed by the Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Trivandrum, an Institute of National Importance, of the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The confirmatory diagnostic test detects the N Gene of SARS- COV2 using reverse transcriptase loop-mediated amplification of viral nucleic acid (RT-LAMP).
- The test kit is highly specific for SARS-CoV-2 N-gene and can detect two regions of the gene, which will ensure that the test does not fail even if one region of the viral gene undergoes mutation during its current spread.
7. Surgeons at Chandigarh’s PGIMER have re-implanted the severed hand of an assistant sub-inspector in Punjab whose hand was chopped off by a group of Nihang sect members in Patiala over a curfew pass.
- The surgery, which took 7.5 hours, was a very complex procedure. It involves conjoining various parts of the arm and the hand bones, muscles, tendons, arteries, veins as well as nerves.
- The process is called anastomosis.
- An anastomosis is a surgical connection between two structures. It usually means a connection that is created between tubular structures, such as blood vessels or loops of intestine.
8. The scientists at Gujarat Biotechnology Research Centre (GBRC) have found three new mutations of the COVID-19 virus. With this, GBRC becomes the first government laboratory in the country to sequence the whole genome of COVID-19.
- There are six mutations of the virus that have been found so far. The scientists at GBRC have found three more new mutations.
- Therefore, so far 9 mutations of the virus have been found.
- Also, it has been mentioned that the virus can mutate manifold. The scientists believe that the virus can mutate twice a month.
- To obtain complete genome sequences of the virus, more samples of COVID-19 samples are required.
9. The Union Health Minister Shri Harsh Vardhan chaired the 12th Group of Minister meeting on COVID-19.
- The meeting was attended by External Affairs minister, home minister for state, shipping and chemical and fertilizer minister for state, member of NITI Aayog, etc.
- The Group of Ministers discussed actions taken so far to contain the spread of COVID-19.
- It was announced at the meeting that the death rate in the country due to COVID-19 is at 3% and the recovery rate is at 12%.
- The situation and recovery in India are better than most of the other countries.
- This is mainly due to the successful implementation of the lockdown.
- The Health Minister also announced that the growth of the virus has been declined by 40%
10. The Government of India launched the “Krishi Rath” application to help farmers to transport their agriculture produce to the mandis.
- The farmer has to post the quantity of agricultural produce he wishes to transport.
- After posting, he will get the availability of truck and price quote for the load.
- The prices quoted are from the transport aggregators.
- Once the farmer confirms, he will get details of the transporter. He can then directly connect with him and negotiate for prices.
- The load availability posted by the farmer will be visible to both traders and transporter
- The traders can learn farm produce from the application and can consolidate loads posted by different farmers.
- With this, he can easily arrange trucks to collect from multiple farmers.
- Currently, 5.7 lakh trucks have been listed and more are expected to join.
11. India is to attend BRICS foreign ministers meet by the end of April 2020. The members will discuss economic fallout due to the spread of COVID-19.
- The foreign ministers meeting of the BRICS grouping is to be conducted through video link.
- It is essential to conduct more of such meetings as the global economic growth is declining at its highest.
- The International Monetary Fund has projected the global growth rate to be -3% in the year 2020-21.




