Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:18th April 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Liquidity Boost to NBFCs:
- Ways and Means Advances (WMA)
- Special Drawing Rights (SDR)
- UV-C (ultraviolet light with wavelength 254 nanometres) device.
- Pseudocapacitors or supercapacitors :
- World Heritage Day
- Demo-2 mission
- Revised draft of Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2020 :
- Other important current affairs
1.Liquidity Boost to NBFCs:

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced a host of measures to provide liquidity support to Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), apart from giving them certain benefits for loans extended to the commercial real estate sector.
- The RBI would conduct Targeted Long-term Repo Operations (TLTRO 2.0) for an aggregate amount of Rs 50,000 crore, in installments of appropriate sizes.
- The banks have to invest the funds availed under TLTRO 2.0, in investment-grade bonds, commercial paper, and non-convertible debentures of NBFCs.
- RBI stipulated that small and mid-sized NBFCs and Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs) should receive at least 50% of these funds.
- The investments made by banks under this facility would be classified as ‘Held-to-Maturity’ (HTM), even more than 25% of the total investment permitted to be included in the HTM portfolio.
- Held to Maturity securities are securities that companies purchase and intend to hold until they mature.
- This will help in easing the liquidity problem faced by NBFCs and MFIs to some extent.
- NBFCs are facing liquidity pressure since banks have not extended any repayment moratorium to these entities even if NBFCs have to provide the same for their borrowers.
- The RBI has also decided to provide a special refinance facility of ₹50,000 crores to National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) and National Housing Bank (NHB) to enable them to meet sectoral credit needs.
- This would comprise:
- ₹25,000 crores to NABARD for refinancing Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), cooperative banks and Microfinance Institutions (MFIs).
- ₹15,000 crores to SIDBI for on-lending/refinancing.
- ₹10,000 crores to NHB for supporting Housing Finance Companies (HFCs).
- Extension of loans to the Real Estate Sector: The RBI has allowed the extension of the loans by NBFCs to delayed commercial real estate projects by a year without restructuring.
2.Ways and Means Advances (WMA) :
Recently, states like Kerala, Punjab, and Bihar have said that the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) decision to allow 60% higher borrowing under Ways and Means Advances (WMA) compared March 30, 2020 limit, is inadequate given the mounting expenses of states to counter the Covid-19 pandemic.
- The states welcomed the RBI move to allow 60% higher borrowing under Ways and Means Advances (WMA) but said it is a temporary relief and will have only a marginal impact upon the fiscal crisis the states are facing.
- They are saying that they can not go long for ways and means and have to slash their expenditure to a large extent because they do not have many avenues left for revenue augmentation.
- They said banks are not willing to lend for the long term large amounts of money because of their liquidity preference.
- They demanded from the Central government to raise the fiscal borrowing limits of states currently capped at 3% of the GSDP (Gross State Domestic Product) under the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act.
- The Centre can invoke Section 5(3) of Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003 which allows the RBI to “subscribe to the primary issues of Central Government securities” under very specific grounds.
- Those cover, among other things, “act of war” and “national calamity”.
- The RBI can also undertake increased secondary market purchases and sales of Central as well as state government securities.
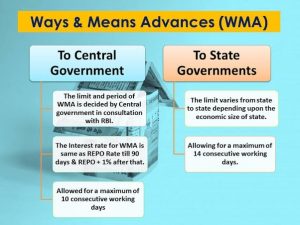
Ways and Means Advances (WMA)
- The WMA is short-term loan facilities which allow the Centre and states to borrow funds from the RBI to bridge their temporary mismatch between expenditure and receipts.
- The interest rate on WMA is the RBI’s repo rate.
- Repo rate is the rate at which RBI lends short-term money to banks.
- The WMA loans have a three-month tenure.
- States are allowed an overdraft facility (to borrow more than WMA limit) of 21 days.
3.Special Drawing Rights (SDR):
India is not supporting a general allocation of new Special Drawing Rights (SDR) by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) because it feels it might not be effective in easing COVID-19-driven financial pressures.
- The new SDR allocation was supposed to provide all 189 members with new foreign exchange reserves with no conditions.
- Such a major liquidity injection could produce potentially costly side-effects if countries used the funds for “extraneous” purposes.
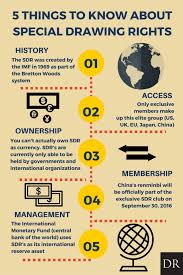
Special Drawing Right (SDR):
- The SDR is an international reserve asset, created by the IMF in 1969 to supplement its member countries’ official reserves.
- The value of the SDR is based on a basket of five currencies—the U.S. dollar, the euro, the Chinese renminbi, the Japanese yen, and the British pound sterling.
- So far SDR 204.2 billion (equivalent to about US$281 billion) has been allocated to members, including SDR 182.6 billion allocated in 2009 in the wake of the global financial crisis.
- The SDR was created as a supplementary international reserve asset in the context of the Bretton Woods fixed exchange rate system.
- The SDR serves as the unit of account of the IMF and some other international organizations.
- The SDR is neither a currency nor a claim on the IMF. Rather, it is a potential claim on the freely usable currencies of IMF members.
- SDRs can be exchanged for these currencies.
4.UV-C (ultraviolet light with wavelength 254 nanometres) device.:
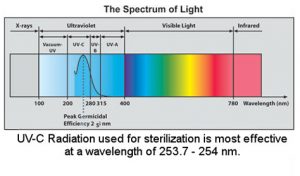
Defense Institute of Physiology & Allied Sciences (DIPAS) and Institute of Nuclear Medicine & Allied Sciences (INMAS), DRDO laboratories in Delhi have designed & developed Ultraviolet C Light-based sanitization box and handheld UV-C (ultraviolet light with wavelength 254 nanometres) device.
- The UV-C consists of a shorter, more energetic wavelength of light.
- It is particularly good at destroying genetic material in COVID-19. The radiation warps the structure RNA which prevents the viral particles from making more copies of themselves.
- The UV-C kills microbes quickly. Sanitization of the items by employing UV-C light avoids the harmful effects of the chemicals used for disinfection. This is environment friendly and is a contact-free effective sanitization method.
- The UV-C box is designed for disinfecting personal belongings like mobile phones, tablets, purse, currency, a cover of office files, etc. COVID-19 virus will be deactivated by using UVC lamps in one minute placed equidistantly in a box with a UV dose of 100 mJ/cm2.
5.Pseudocapacitors or supercapacitors :
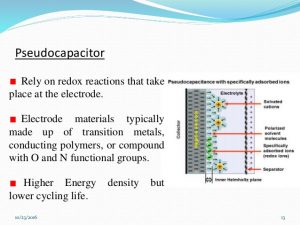
Scientists at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute under the DST, Government of India, have developed a stable material for pseudocapacitors or supercapacitors which store electrical energy by electron charge transfer.
- The material can offer a low-cost scalable energy storage solution as an alternative to batteries.
- Pseudocapacitors are a type of supercapacitors which store electrical energy by electron charge transfer.
- The team has developed the pseudocapacitive material, a hybrid xerogel structure (a solid formed from a gel by drying with unhindered shrinkage), for the very first time.
- The hybrid material was fabricated by the integration of a well-known organic molecule, dopamine onto a conductive matrix, like graphene.
- This class of xerogel architectures, although reported in the literature as alternatives to conventional pseudocapacitors, lack sufficient cycling stability to replace batteries in the consumer market.
6.World Heritage Day:

Every year 18th April is celebrated as the International Day for Monuments and Sites or World Heritage Day.
- The International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) established the day in 1982 and the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) approved it in 1983.
- Since then, it has been a day to celebrate and promote cultural heritage, and an opportunity to raise awareness about its diversity, its relevance, how vulnerable it can be and what the needs and benefits of its conservation are.
- The theme for 2020: Shared Cultures, Shared Heritage, Shared Responsibility.
- It is an important expression of global unity in the face of the ongoing worldwide health crisis (Covid-19 pandemic).
- International Council on Monuments and Sites
- It is a global non-governmental organization associated with UNESCO.
- Its mission is to promote the conservation, protection, use, and enhancement of monuments, building complexes and sites.
- It is an Advisory Body of the World Heritage Committee for the implementation of the World Heritage Convention of UNESCO.
- India has 38 world heritage sites that include 30 Cultural properties, 7 Natural properties, and 1 mixed site.
- Its creation in 1965 is the logical outcome of initial conversations between architects, historians and international experts that began in the early twentieth century and that materialized in the adoption of the Venice Charter in 1964.
7. Demo-2 mission:

NASA announced that it will launch its flight of astronauts on May 27, 2020.
- The mission is to use the Falcon-9 rocket.
- The astronauts are to be sent for an extended stay at the international space station.
- The mission is to be launched by SpaceX. It is the first crewed launch of the Elon Musk space company.
- The mission of NASA sending astronauts to International Space Station has been named “Commercial Crew Programme”.
- The Demo-1 Mission of NASA was launched by SpaceX. Demo-1 was the first uncrewed test flight to be launched to the International Space Station. Currently, SpaceX and Boeing are the space taxi providers of NASA.
Commercial Crew Programme
- The Commercial Crew Programme was funded by the US Government.
- It was administered by NASA. Under the program, the private vendors will operate crew vehicles to carry astronauts to the International Space Station.
- The unmanned mission Demo-1 is also a part of the Commercial Crew Programme.
8.Revised draft of Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2020 :
The Ministry of Power has made changes to the Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2020. This is being done to promote electricity generation from renewable sources.
Features of the bill
- Electricity Contract enforcement Authority is to be created
- Launch of National Renewable Energy Policy
- Payment security has been made necessary to schedule the distribution of electricity and also to facilitate cross border trade.
- Privatization of discoms using franchises and sub-licenses
- Power Tariff is to be determined without subsidy
- The appellate tribunal of electricity is to have similar powers as that of civil courts
Other important current affairs:
1. The scientist who visualized the first human coronavirus was virologist June Almeida.
- She pioneered the technique of electron microscopy, used for viral diagnosis, and became the first individual to see the human coronavirus in 1965.
- June Dalziel Almeida (1930 – 2007) was a Scottish virologist who, with little formal education, became a Doctor of Science and a pioneer in virus imaging, identification, and diagnosis.
- She discovered a new type of coronavirus. She published Manual for rapid laboratory viral diagnosis in 1979.
- Almeida produced the first images of the rubella virus using immune-electron microscopy. David Tyrrell and Almeida worked on characterizing a new type of coronavirus.
- This family includes the SARS virus and the SARS-CoV2 virus that causes COVID-19.
2. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued guidelines for people who are at increased risk of getting severely ill from Covid-19.
- These include those who are 65 years or older, people with chronic lung disease or moderate to severe asthma, those with heart disease and immunocompromised people.
- In some people, the immune system is weakened, which means that their immune systems cannot function efficiently and therefore, make it difficult to recover or in some cases, may lead to more severe outcomes.
- Such people are said to be immunocompromised and there can be various reasons for this, such as cancer treatment, existing comorbidities, age and genetics among others.
3. Recently, a petition has been filed in the Supreme Court for directing the Andhra Pradesh government to conduct Covid-19 tests among the tribal population living along the Godavari river valley area.
- The petition said the Godavari river valley area, where the tribal people live is close to the Polavaram irrigation project area.
- The Godavari river valley area spreads across Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh.
- The Covid-19 lockdown has been blatantly violated for the construction of the Polavaram irrigation project on the Godavari river in Andhra Pradesh.
- A large number of migrant workers are still working on the project site without sanitizers and masks. These workers lived close to the tribal population.
- Lack of awareness among the tribal people, who live in dense forest and other scheduled areas of the river valley, made them more prone to Covid-19 infections.
- Konda, Koyas, and Kolam are the popular tribes living in Godavari valley.
- Konda reddis and Kolam are part of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG).
5. The Centre has permitted the export of formulations (medicinal products) made from Paracetamol. However, the restriction on the export of Paracetamol Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) will continue.
- The API is the part of any drug that produces the intended effects.
- Paracetamol and its formulations were among the 13 APIs and their formulations that figured in the March 3, 2020 notification by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
- The formulations made from Paracetamol, including FDC (Fixed-Dose Combinations), under any ITCHS code have been made free for export with immediate effect.
6. Over 10 crore people have been excluded from the Public Distribution System (PDS) because outdated 2011 census data is being used to calculate State-wise National Food Security Act (NFSA) coverage, according to economists Jean Dreze and Reetika Khera.
- Under the NFSA, the PDS is supposed to cover 75% of the population in rural areas and 50% of the population in urban areas, which works out to 67% of the total population, using the rural-urban population ratio in 2011.
- India’s population was about 121 crore in 2011 and so PDS covered approximately 80 crore people.
- However, applying the 67% ratio to a projected population of 137 crores for 2020, PDS coverage today should be around 92 crores.
- Even taking into account growing urbanization, the shortfall would be around 10 crore people.
- With the 2021 census process being delayed due to the COVID-19 crisis, any proposed revision of PDS coverage using that data could now take several years.
7. The Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with King George Medical University to sequence the strains of COVID-19 virus samples obtained from different patients.
- According to the MoU, a Lucknow based lab is to sequence the virus strains.
- This is to be done under a “Digital and Molecular Surveillance”.
- A molecular surveillance system is a collection, reporting, and analysis of genetic sequences.
- Molecular surveillance is currently being used in HIV drug testing, foodborne infections, and TB.
8. The Union Minister of culture Shri Prahlad Singh Patel launched the National List of Intangible Cultural Heritage.
- The list is to include 13 elements that are already included in the UNESCO Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- The initiative is a part of Vision 2024 of the Ministry of Culture.
- It aims to increase awareness about intangible cultural heritages. The list will recognize the diversity in Indian Culture.
- The list already has 100 elements. However, the Ministry updates the list regularly.
9. India attended the Development Committee meeting of the World Bank-International Monetary Fund. India was represented by the Finance Minister Smt Nirmala Sitaraman.
- India participated in the 101st meeting of the development committee that was held through video conference.
- The experts that attended the meet discussed the response to COVID-19 emergency and COVID-19 debt initiatives.
- The major debt initiative is the International Call for Action in Support of IDA countries.




