2D Protein Monolayer Unravels Amyloidosis:
Researchers have achieved a significant breakthrough in disease study through the creation of a two-dimensional (2D) protein monolayer using lysozyme molecules
Highlights of the Research:
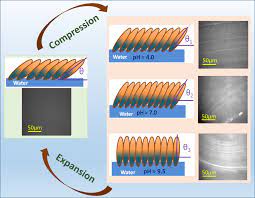
- Scientists assembled lysozyme molecules into a 2D monolayer at the interface of a pure water subphase.
- These meticulously arranged layers of lysozyme, positioned at different interfaces, provide an exceptional model for delving into the complexities of Amyloidosis.
- Employing the sophisticated Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) technique was crucial in forming this specialized two-dimensional protein layer.
- The Langmuir-Blodgett technique is a process used to create monolayers of molecules, including proteins, at air-water and air-solid interfaces.
- The changes observed in the structure and shape of lysozyme molecules under different pH conditions remarkably mirror the abnormalities seen in Amyloidosis.
- This groundbreaking research not only paves the way for a more profound comprehension of Amyloidosis but also establishes a versatile platform for probing disease mechanisms.
- Furthermore, it presents exciting possibilities for exploring nanotechnology applications within the realm of protein science.




