Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia:
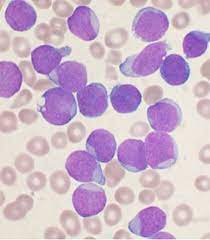
The researchers found a statistically significant correlation between a rise in soy production and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) deaths in children between 2008 and 2019 in Brazil’s Amazon and Cerrado biomes.
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL) is a type of cancer of the blood and bone marrow—the spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are made.
- The word “acute” in acute lymphocytic leukaemia comes from the fact that the disease progresses rapidly and creates immature blood cells rather than mature ones.
- It is the most common type of cancer in children.
- Symptoms: Bleeding from the gums, Bone pain, Fever, Frequent infections, frequent or severe nosebleeds, etc.
- It occurs when a bone marrow cell develops changes (mutations) in its genetic material, or DNA.
- A cell’s DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. Normally, the DNA tells the cell to grow at a set rate and to die at a set time.
- In ALL, the mutations tell the bone marrow cell to continue growing and dividing.
- When this happens, blood cell production becomes out of control.
- The bone marrow produces immature cells that develop into leukemic white blood cells called lymphoblasts.
- These abnormal cells are unable to function properly, and they can build up and crowd out healthy cells.
- Treatment may include chemotherapy or targeted drugs that specifically kill cancer cells.




