Candida Auris : Deadly Fungus
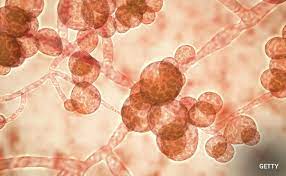
A drug-resistant and potentially deadly fungus ‘Candida Auris’ is spreading rapidly across the United States.
- Candida Auris (C. auris) is a multi-drug resistant fungus that is capable of causing invasive infections in the human body.
- It was first identified in Japan in 2009.
- Most cases of the fungus have been reported in healthcare settings, such as hospitals and nursing homes.
- It is generally thought to be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or by person-to-person transmission.
- People who are already suffering from other medical conditions, recent hospital stays, and invasive devices are most at risk of contracting the fungus.
- There are two ways C. auris can affect the body.
- The fungus can either live on a specific region, such as the skin, rectum, or mouth, in a process called “asymptomatic colonization,” where a patient has no symptoms but can spread it to other people.
- Symptoms:
- Its symptoms are often similar to those of other common diseases and hence diagnosis is difficult.
- The most common symptoms of C.auris include fever and chills that don’t go away after treatment with antibiotics.
- Mortality Rate: It is estimated to be between 30-60%.
- Treatment: Most C. auris infections are treatable with antifungal medications called echinocandins.




