Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS):
Physicians at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) have successfully treated a patient with severe depression by recognising and tapping into the brain circuits linked with depressive brain patterns.
- The physicians have tried to reset these patterns, which they have said is the equivalent of using a pacemaker for the heart. The work, which represents a landmark in the use of neuroscience to treat psychiatric disorders, has been published in the journal Nature Medicine.
- The doctors used an existing technique called deep brain stimulation (DBS), customising it for this patient’s case.
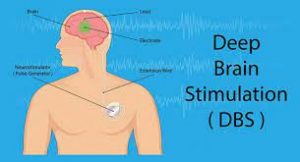
- DBS is a surgical procedure in which electrodes are implanted into certain brain areas. These electrodes, or leads, generate electrical impulses that control abnormal brain activity.
- The electrical impulses can also adjust for the chemical imbalances within the brain that cause various conditions.
A DBS system has three components
- The electrode, or lead. This is a thin, insulated wire inserted through a small opening in the skull and implanted into a specific brain area.
- The extension wire. This too is insulated, and is passed under the skin of the head, neck and shoulder, connecting the electrode to the third component of the system.
- The internal pulse generator (IPG) is the third component. It is usually implanted under the skin in the upper chest.




