Melioidosis:
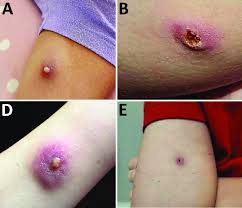
A recent study highlights how climate conditions, particularly monsoon-related factors, influence the spread of melioidosis.
- It is a bacterial infectious disease, linked to rainfall, temperature, and humidity.
- It is caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei and primarily acquired by inoculation, inhalation and/or ingestion of soil- and water-dwelling environmental saprophytes.
- South Asia (endemic to Bangladesh and Sri Lanka), including India, accounts for 44% of global melioidosis cases, with Odisha as a hotspot due to its agriculture and extreme weather.
- It is primarily found in Northern Australia and Southeast Asia.
- Symptoms range from mild skin infections to severe pneumonia and sepsis, with a fatality rate of up to 50% in septic cases.
- It is not transmitted from animals to humans, and human-to-human transmission is rare.
- Melioidosis can be treated with antibiotics




