Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 10th November 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- .National Agricultural Education Policy
- Chabahar Project:
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI)
- Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT):
- Pfizer vaccine:
- Other important current affairs:
1.National Agricultural Education Policy:

The first National Agricultural Education Policy is set to bring academic credit banks and degree programs with multiple entries and exit options to the 74 universities focussed on crop sciences, fisheries, veterinary and dairy training and research.
- The process for formulating the National Agricultural Education Policy was started about two months ago, after the release of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Earlier, the Prime Minister had pitched for taking farm education to the middle school level, saying necessary reforms have been made in this regard in the NEP 2020.
Agricultural Education Policy to be Aligned with NEP 2020:
Academic Credit Banks:
- These may be a service provider available to a desirable student community. It may facilitate the integration of the campuses and distributed learning systems, by creating student mobility within the inter and intra university system.
- It may help in seamlessly integrating skills and experiences into a credit-based formal system by providing a credit recognition mechanism.
- It will digitally store academic credits earned from recognised Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) and allow for credit redemption in order to be awarded a certificate, diploma or degree.
Experiential Education:
- In India, agricultural education is already ahead of its time and already aligned with the NEP.
- The NEP wants a shift to four-year undergraduate degrees, and agricultural degrees are already four-year programmes.
- The NEP mentions experiential education, which has been already mandated in agricultural education since 2016.
- Experiential education is a teaching philosophy that informs many methodologies in which educators purposefully engage with learners in direct experience and focused reflection in order to increase knowledge, develop skills, clarify values, and develop people’s capacity to contribute to their communities.
The Student READY (Rural Entrepreneurship Awareness Development Yojana) programme requires all students to undertake a six-month internship, usually in their fourth year, to gain hands-on training, rural awareness, industry experience, research expertise and entrepreneurship skills.
- One major challenge is to ensure that experiential learning is made available to all students if the multiple entry-exit system gets implemented.
- The option of multiple entry and exit provides students with the opportunity to earn a diploma or an advanced diploma, while they are given the choice to re-enter as and when they are able to resume their studies and earn a full college degree.
2.Chabahar Project:
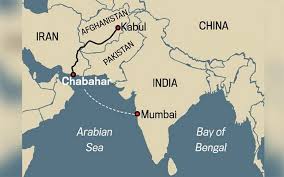
Iran’s Port and Maritime Organisation (PMO) has conveyed to India a request for locomotives and signaling equipment for the Chabahar-Zahedan railway line.
- Iran has been facing difficulty in procuring them directly due to the sanctions imposed by the USA.
- Iran has also asked India to activate the USD 150 million credit line which was offered to it by India during the Iranian President’s visit in 2018.
Chabahar Port
- It is located on the Gulf of Oman and is only 72 km away from the Gwadar port in Pakistan which has been developed by China.
- The port serves as the only oceanic port of Iran and consists of two separate ports named Shahid Beheshti and Shahid Kalantari.
Background:
- In May 2016, India, Iran, and Afghanistan signed the trilateral agreement which entailed the establishment of Transit and Transport Corridor among them using Chabahar port in Iran as one of the regional hubs for sea transportation.
- Construction of a rail line from Chabahar port to Zahedan, along the border with Afghanistan as an alternate trade route to Afghanistan and Central Asia, was also a part of it.
- The state-owned Indian Railways Construction Ltd. (IRCON) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Iranian Rail Ministry to provide all services, superstructure work and financing (around USD 1.6 billion).
Reasons for Excluding India:
- Iran’s Stand: In July 2020, Iran decided to proceed with the rail line construction on its own, citing delays from the Indian side in beginning and funding the project.
- India’s Stand: IRCON completed the site inspection and feasibility report, and had been waiting for the Iranian side to appoint a nodal authority.
- Although the project has secured a special waiver from the USA, India is hesitant to deal with the construction company which has links with the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) and is under sanctions.
- The IRGC is a hard-line force that operates its own military infrastructure in parallel to Iran’s regular armed forces. In April 2020, it launched Iran’s first military satellite, Noor.
- Fear of sanctions by the USA has also impacted Indian interest in the Farzad-B gas field project of Iran.
3.The Competition Commission of India (CCI):

The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has initiated a probe into alleged abuse of dominant position by the company to promote its payments app, Google Pay.
- CCI highlighted two main anti-market practices by google to unfairly push Google Pay its payment app:
- Mandatory Use: Google’s policy of mandatory use of Google Play’s payment system for purchasing the apps and IAPs (in-app purchases) in the Play Store.
- Exclusionary Practices: It excluded other mobile wallets/UPI (Unified Payments Interface) apps as one of the effective payment options in Google Play’s payment system.
- The CCI also criticized Google’s policy to charge 30% commission for all app and in-app purchases.
- Since Google’s Play store cornered about 90% of all downloads, a significant volume of payments being processed in the market would thus be controlled by it.
- If the application developers raise their subscription fees to offset the costs of google’s commission or remove/reduce premium/paid subscription offers for users, it may affect user experience, cost, and choice.
- Such conditions imposed by the app stores limit the ability of the app developers to offer payment processing solutions of their choice to the users.
- CCI also highlighted reports of Google abusing its dominant position in the Android-television market by creating barriers for companies that wanted to use or modify its Android operating systems for their smart televisions.
- The probe against Google Pay comes days after the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) allowed rival Facebook-owned WhatsApp to go live on the UPI in the multi-bank model.
Competition Commission of India:
- It is a statutory body of the Government of India, responsible for enforcing the Competition Act, 2002 throughout India and to prevent activities that have an adverse effect on competition.
- Functions of the commission:
- It is the duty of the Commission to eliminate practices having an adverse effect on competition, promote and sustain competition, protect the interests of consumers and ensure freedom of trade in the markets of India.
- The Commission is also required to give an opinion on competition issues on a reference received from a statutory authority established under any law and to undertake competition advocacy, create public awareness and impart training on competition issues.
4.Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT):

Prime Minister Narendra Modi will inaugurate the state-of-the-art office-cum-residential complex of Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) at Cuttack on 11th November 2020.
- Income Tax Appellate Tribunal, also known as ITAT, is an important statutory body in the field of direct taxes and its orders are accepted as final, on findings of fact.
- It is presently headed by Mr. Justice (Retd) P.P. Bhatt, formerly Judge of the High Court of Jharkhand and High Court of Gujarat.
- ITAT was the first Tribunal to be created on 25th January 1941 and is also known as ‘Mother Tribunal’.
- Starting with three benches in the year 1941, at Delhi, Bombay and Calcutta it has now grown to 63 Benches and two circuit benches spread across thirty cities of India.
- The Cuttack Bench of the ITAT was created and started functioning on 23rd May, 1970.
- The jurisdiction of Cuttack Bench extends to the whole of Odisha.
5. Pfizer vaccine:

American pharma company Pfizer has claimed that its vaccine candidate BNT162b2 is more than 90% effective in preventing Covid-19 in participants without evidence of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection.
BNT162b2:
- It is a single nucleoside-modified messenger RNA (modRNA) vaccine, which is made of a short segment of genetic material (the messenger RNA/mRNA) which provides instructions for a human cell to make a harmless version of a target protein, in this case the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, in order to activate an immune response.
- The mRNA vaccine is a new approach to protecting against viral infection.
- Unlike traditional vaccines, which work by training the body to recognize and kill proteins produced by pathogens, mRNA tricks the patient’s immune system to produce viral proteins itself.
- The proteins are harmless, but sufficient to provoke a robust immune response.
- It’s phase 3 clinical trial began in July with 43,538 participants, 38,955 of whom had received a second dose by November.
- The case split between vaccinated individuals and those who received the placebo indicates a vaccine efficacy rate above 90%, 7 days after the second dose.
- It means that protection is achieved 28 days after the initiation of the vaccination, which consists of a 2-dose schedule.
- Pfizer has become the first firm to release promising late-stage trial data of a potential vaccine for Covid-19, even though the announcement does not have scientifically conclusive evidence on the safety and efficacy of the vaccine candidate.
- However, the analysis of the vaccine candidate by an external independent Data Monitoring Committee (DMC) has not reported any serious safety concerns.
- The announcement comes days before the company plans to submit safety and efficacy data from the trial to the American regulator, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) seeking emergency use authorization.
Other important current affairs:
1.Andhra Pradesh government recently said that it is planning to complete the Polavaram project by 2022 Kharif season, and six other projects Vamsadhara-Phase 2, Vamsadhara-Nagavali link, Owk tunnel-2, Velugonda-Phase 1, and Nellore and Sangam barrages in 2020-21.
- About the Polavaram project:
- The dam is being built across the Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh.
- It will facilitate an inter-basin transfer to the Krishna river basin through its Right canal.
- Its reservoir spreads in parts of Chhattisgarh and Orissa States also.
- The project is a multipurpose major terminal reservoir project for the development of Irrigation, Hydropower, and drinking water facilities.
- The project was accorded national status in 2014 in the Andhra Pradesh Bifurcation Act and its design was changed.
2.A pilot project of saffron cultivation has yielded successful results in the Yangyang village of Sikkim, which produced its first crop of saffron recently.
- Saffron is a plant whose dried stigmas (thread-like parts of the flower) are used to make saffron spice.
- Saffron cultivation is believed to have been introduced in Kashmir by Central Asian immigrants around the 1st Century BCE.
- It has been associated with traditional Kashmiri cuisine and represents the rich cultural heritage of the region.
- It is a very precious and costly product.
- In ancient Sanskrit literature, saffron is referred to as ‘bahukam’.
- It is cultivated and harvested in the Karewa (highlands) of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Importance:
- It rejuvenates health and is used in cosmetics and for medicinal purposes.
- It has been associated with traditional Kashmiri cuisine and represents the rich cultural heritage of the region.
- Season:
- In India, saffron Corms (seeds) are cultivated during the months of June and July and at some places in August and September.
- It starts flowering in October.
- Conditions:
- Saffron grows well at an altitude of 2000 meters above sea level. It needs a photoperiod (sunlight) of 12 hours.
- Soil:
- It grows in many different soil types but thrives best in calcareous (soil that has calcium carbonate in abundance), humus-rich, and well-drained soil with a pH between 6 and 8.
- Climate:
- For saffron cultivation, we need an explicit climatological summer and winter with temperatures ranging from no more than 35 or 40 degrees Celsius in summer to about –15 or –20 degrees Celsius in winter.
- Rainfall:
- It also requires adequate rainfall that is 1000-1500 mm per annum.
4.Denmark has recorded over 200 human cases infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants that are associated with farmed minks.
- Mink are dark-colored carnivorous mammals from the Mustelidae family, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets.
- More than 50 million mink a year are bred for their fur, mainly in China, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Poland.
- Mink oil is used in some medical products and cosmetics, as well as to treat, preserve, and waterproof leather.
- There are two extant species referred to as “mink”: the American mink and the European mink.
- The European mink is listed by the IUCN as Critically Endangered due to an ongoing reduction in numbers.
- Mink, like their close relatives, ferrets, are known to be susceptible to coronavirus.
- Like humans, they can show a range of Covid-19 symptoms, from no signs of illness at all to severe problems, such as pneumonia.
5.National e-Governance Division (NeGD) in partnership with National Law Institute University, Bhopal, launched an Online PG Diploma program on ‘Cyber Law, Crime Investigation & Digital Forensics’ on 9th November 2020.
- This initiative will offer a nine-month Online PG Diploma Course in Cyber Law, Crime Investigation & Digital Forensics to about 1000 officials through NeGD’s Digital Learning Management System (LMS) in collaboration with NLIU Bhopal under the “Digital India Programme”.
- The goal of this Programme is to enable Police Officers, State Cyber Cells, Law Enforcement Agencies, Prosecutors, and Judicial Officers to acquire the requisite skills to deal with Cyber Forensics cases efficiently & effectively as per the Indian Cyber Law.
- A Cyber Forensics Lab is being established in the premises of National Law University (NLU) Delhi for facilitating this course.
6.The Ministry of Power, Government of India issued a notification to cover all the Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs) under the preview of the Energy Conservation (EC) Act, 2001.
- The notification was formulated in consultation with the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- According to it, all entities having issued distribution license by State/Joint Electricity Regulatory Commission under the Electricity Act, 2003 (36 of 2003)” are notified as Designated Consumers (DCs).
- After this notification, all the DISCOMs will be governed under the various provisions of the EC Act, such as Appointment of Energy Manager, Energy Accounting & Auditing, etc. for each DISCOMs.
- Earlier, the DISCOMs whose annual energy losses were equal to or above 1000 MU were only covered as DCs. Now with this notification, the number of DISCOMs covered under the EC Act will increase from 44 to 102.




