Today Current Affairs: 11th January 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Quantum Technology
- Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE-2) regulations and BS-VI stage II norms :
- LiDAR
- MukundPura Meteorite
- H-1B visa
- K-shaped economic recovery
- Standard Operating Procedure for immunization
- Other important current affairs:
1.Quantum Technology:
The detailed project report for a National Mission on Quantum Technology and Applications (NMQTA) has been drawn out and finalized.
- Union Budget 2020-21 proposed to spend Rs 8,000 crore on the newly launched NMQTA.
- In 2018, the Department of Science & Technology unveiled a programme called Quantum-Enabled Science & Technology (QuEST) and committed to investing Rs. 80 crore over the next three years to accelerate research.
- The mission seeks to develop quantum computing linked technologies amidst the second quantum revolution and make India the world’s third-biggest nation in the sector after the US and China.
About Quantum Technology:
- Quantum Technology is based on the principles of Quantum mechanics that was developed in the early 20th century to describe nature at the scale of atoms and elementary particles.
- The first phase of this revolutionary technology has provided the foundations of our understanding of the physical world, including the interaction of light and matter, and led to ubiquitous inventions such as lasers and semiconductor transistors.
- A second revolution is currently underway with the goal of putting properties of quantum mechanics in the realms of computing.
Properties of Quantum Computing:
- The basic properties of quantum computing are superposition, entanglement, and interference.
2. Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE-2) regulations and BS-VI stage II norms :

The auto industry has requested the government to defer the implementation of Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE-2) regulations and BS-VI stage II norms to April 2024, given the impact of the lockdown measures.
- As of now, the CAFE-2 norms and BS-VI stage II norms are set to come into effect in 2022 and April 2023 respectively.
- Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE-2) Regulations:
- CAFE or Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency/Economy regulations are in force in many advanced as well as developing nations, including India.
- They aim at lowering fuel consumption (or improving fuel efficiency) of vehicles by lowering Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, thus serving the twin purposes of reducing dependence on oil for fuel and controlling pollution.
- Corporate Average refers to sales-volume weighted average for every auto manufacturer.
- The idea of CAFÉ is to push manufacturers to achieve fuel efficiency targets by producing and selling more fuel-efficient models, including electric vehicles
Launch in India:
- The CAFÉ standards were first notified in 2017 by the Union Ministry of Power (MoP) under Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- The regulation is in accordance with the fuel consumption standards of 2015 that aim to increase fuel efficiency of vehicles road by 35% by 2030.
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) is the nodal agency responsible for monitoring and reporting a summary of annual fuel consumption by automobile manufacturers at the end of each fiscal year.
- The regulation was introduced in two target phases: Carbon dioxide emission target of 130 gram/kilometre by 2022-23 and 113 g/km 2022-23 onwards.
The norms are applicable for petrol, diesel, Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) passenger vehicles.
BS-VI Stage II Norms:
- Bharat Stage (BS) emission standards are laid down by the government to regulate the output of air pollutants from internal combustion engine and spark-ignition engine equipment, including motor vehicles.
- These standards are targeted at making improvements in three areas – emission control, fuel efficiency and engine design.
- The central government has mandated that vehicle makers must manufacture, sell and register only BS-VI (BS6) vehicles from 1st April, 2020.
- BS-VI is equivalent to Euro-VI norms currently in place across countries in Europe.
- As per BS-VI emission norms, petrol vehicles will have to effect a 25% reduction in their NOx, or nitrogen oxide emissions.
- Diesel engines will have to reduce their HC+NOx (hydro carbon + nitrogen oxides) by 43%, their NOx levels by 68% and particulate matter levels by 82%.
- Sulphur content in fuel is a major cause for concern.
- BS-VI fuel’s sulphur content is much lower than BS-IV fuel.
- It is reduced to 10 mg/kg max in BS-VI from 50 mg/kg under BS-IV.
- Some of the measures to be introduced from 2023 onwards include deciding the confirmatory factor for in-service compliance, market surveillance and independent verification testing of in-use vehicles by regulatory authorities, adoption of more stringent driving cycle for emissions testing, public disclosure of emissions data by the manufacturers on publicly accessible websites, and on-board fuel consumption meters among others.
3. LiDAR:
With the start of LiDAR (Aerial Ground) Survey, High Speed Rail work gathered momentum for Delhi – Varanasi High Speed Rail Corridor.
- The LiDAR survey for Delhi-Varanasi High Speed Rail Corridor started from Greater NOIDA where a Helicopter fitted with state of art Aerial LiDAR and Imagery sensors took the first flight and captured the data related to ground survey.
- National High Speed Rail Corporation Limited is adopting Light Detection and Ranging Survey (LiDAR) technology which provides all the ground details and data in 3-4 months wherein this process normally takes 10-12 months.
- The ground survey is a crucial activity for any linear infrastructure project as the survey provides accurate details of areas around the alignment.
Lidar,:
- Lidar which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth.
- These light pulses combined with other data recorded by the airborne system generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
- A lidar instrument principally consists of a laser, a scanner, and a specialized GPS receiver.
4.MukundPura Meteorite:

A recent study has shed light on the mineralogy of the meteorite named Mukundpura CM2 which fell in Mukundpura village near Jaipur in 2017.
- A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon.
- The meteorite named Mukundpura CM2 was classified to be a carbonaceous chondrite.
- The composition of carbonaceous chondrites are also similar to the Sun.
- Chondrites are silicate droplet bearing meteorites, and this Mukundpura chondrite is the 5th carbonaceous meteorite known to fall in India.
Classification Of Meteorite:
- Meteorites are classified into three groups: Stony (silicaterich), Iron (Fe–Ni alloy), and Stony Iron (mixed silicate iron alloy).
- Mukundpura CM2 is a type of stony meteorite, considered the most primitive meteorite and a remnant of the first solid bodies to accrete in the solar system.
- Components of Meteorite:
- Detailed spectroscopic studies revealed that the meteorite had very high (about 90%) phyllosilicate minerals comprising both magnesium and iron.
- Forsterite and FeO olivine, calcium aluminium rich inclusion (CAI) minerals.
- Few magnetites, sulphides, aluminium complexes and calcites were also found.
5.H-1B visa:

The US administration has once again amended the H-1B visa norms.
Changes:
- Rules to give priority to higher wages and skills for selection of deserving candidates.
- The old lottery system of work visa selection will not be followed now.
H-1B work visas:
- In 1952, after the US started expanding its presence in the science, technology, engineering and mathematics disciplines, it felt the need to hire quality workers who could help the country achieve innovation in these areas at reasonable costs.
- The need to hire workers paved way for the introduction of the H-1 work visa system in US.
- This work visa system was further subdivided into H-1B, H-2B, L1, O1, and E1 visas, depending on the qualification required and the area for which workers were sought.
- Of these, the H-1B visa remains the most popular due to the relatively better wage chance it offers.
- Priority in selection of visas to applications of those employers where the “proffered wage equals or exceeds” the prevailing level in that area of employment
- This regime will also take into account the skill set that the respective worker brings to the country and cross check it whether such skill set is available at the same cost among the US workers.
6.K-shaped economic recovery:
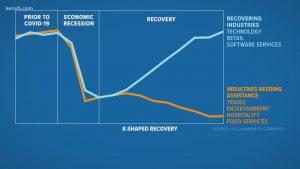
The prospects of a K-shaped recovery from COVID are increasing both in India and across the world.
- A K-shaped recovery happens when different sections of an economy recover at starkly different rates.
- Households at the top of the pyramid are likely to have seen their in- comes largely protected, and savings rates forced up during the lockdown, increasing ‘fuel in the tank’ to drive future consumption.
- Meanwhile, households at the bottom are likely to have witnessed permanent hits to jobs and incomes.
Implications of a K-shaped recovery:
- Upper-income households have benefitted from higher savings for two quarters.
- Households at the bottom have experienced a permanent loss of income in the forms of jobs and wage cuts; this will be a recurring drag on demand, if the labour market does not heal faster.
- To the extent that COVID has triggered an effective income transfer from the poor to the rich, this will be demand-impeding because the poor have a higher marginal propensity to consume (i.e. they tend to spend (instead of saving) a much higher proportion of their income.
- If COVID-19 reduces competition or increases the inequality of incomes and opportunities, it could impinge on trend growth in developing economies by hurting productivity and tightening political economy constraints.
7.Standard Operating Procedure for immunization:
The Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Immunisation Division) has issued a Standard Operating Procedure for the Ministry of Home Affairs in case of Adverse Events Following Immunisation (AEFI).
- Emergencyy Use Authorisation or Accelerated Approval has been granted by the National Regulator for two vaccines (Covishield and Covaxin) which have established safety & immunogenicity against covid 19.
Standard Operating Procedure:
- The SOP is meant to help the investigator ensure appropriate handling of the vaccine, victim assistance as well as timely and effective law enforcement.
- In case of an AEFI, the officer must ensure proper handling of the vaccine and diluent as evidence, and make sure the samples are preserved maintaining proper cold chain.
- The police officer must also ensure that the AEFI victims, and any witnesses, are provided assistance and appropriate protection, care and attention.
- The SOP also provides for investigation/interrogation of the vaccinator, if needed.
- This will help in monitoring immunisation safety, correcting unsafe immunisation practices, reducing negative impact of the event on health and contributing to the quality of immunisation.
- Documentation and completed requisition form for transportation of AEFI samples to a laboratory must have same official stamp.
- The seal will ensure the samples and details sent to the lab are not tampered with during transportation.
- While probing serious AEFI, which has resulted in death, the police must “always keep the perspective that the event might be coincidental and/or reaction to the vaccine and it may not be criminal negligence of the vaccinator and/or other workers, for which causality assessment report by an expert is needed”.
Other important current affairs:
1.Thousand Islands:
- On 9 January 2021, a Boeing 737-500 (PK-CLC) operating Sriwijaya Air Flight 182 went missing after taking off from Jakarta Soekarno–Hatta Airport on route to Pontianak Supadio Airport.
- The aircraft crashed near the Thousand Islands.
- The Thousand Islands (officially Kepulauan Seribu) are a chain of islands to the north of Jakarta’s coast.
- It forms the only regency of Jakarta, the capital of Indonesia.
- It consists of a string of 342 islands stretching 45 km (28 mi) north into the Java Sea at West Jakarta Bay and in fact north of Banten Province.
2.Arunachal Pradesh is likely to become India’s prime producer of vanadium.
- Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23.
- It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal.
- The elemental metal is rarely found in nature.
- It is recovered as a by-product from the slag collected from the processing of vanadiferous magnetite ores (iron ore).
- Vanadium is a high-value metal used in strengthening steel and titanium.
- The largest deposits of vanadium of the world are in China, followed by Russia and South Africa.
- China, which produces 57% of the world’s vanadium, consumed 44% of the metal in 2017.
- India is a significant consumer of vanadium, but is not a primary producer of the strategic metal.
- According to data provided by the GSI, India consumed 4% of about 84,000 tonnes of vanadium produced across the globe in 2017.
3.U.S. removes restrictions on diplomatic contact with Taiwan.
- The move is expected to upset China.
- Recent developments:
- The Trump administration has sought to strengthen bilateral relations with Taiwan.
- It announced UN Ambassador Kelly Craft would go to Taiwan, a move that sparked sharp criticism from Beijing and a warning that the U.S. would pay a heavy price.
- In August, Health and Human Services Secretary became the first Cabinet member to visit Taiwan since 2014.
- China and Taiwan:
- The Chinese government maintains that mainland China and Taiwan are parts of “one China.”
- China has been stepping up its threats to bring the self-governing island under its control by military force with frequent war games and aerial patrols.
- It has been using its diplomatic clout to stop Taiwan from joining any organisations that require statehood for membership.
4.Jharkhand exited from a Tripartite Agreement (TPA) between the state, Government of India (GOI) and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).:
- An agreement was signed between GOI, Jharkhand state and RBI in 2017 stating that the state government shall ensure that the state power utilities make the supply payment due to the Central Public Sector Units in this case, Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC) within the period specified in the supply agreement.
- In the event of State Power Utilities committing a breach in the terms, the state government shall independently and as a principal debtor become liable for the payment.
- As per the TPA, it authorises the GOI to instruct RBI to act promptly on its instructions i.e. to debit the amount.
- As per the tripartite agreement, the Centre has the power to auto-debit the dues of a state to central power discoms from the state’s RBI account.
- Jharkhand cabinet decided to pull out of the agreement as it is not in the best interest of the state.
- It says, the Centre’s decisions like these affect the federal structure of the country.
5.Recent surveys by the Atomic Minerals Directorate for Exploration and Research (AMD) have shown the presence of lithium resources in Mandya district, Karnataka.
- AMD is the oldest unit of the Department of Atomic Energy.
- About Lithium:
- It is a chemical element with the symbol Li.
- It is a soft, silvery-white metal.
- Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element.
- It is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in mineral oil.
- It is an alkali metal and a rare metal.
- The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, caesium, and francium. Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table.
- Rare Metals (RM) include Niobium (Nb), Tantalum (Ta), Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Cesium (Cs) etc. and Rare Earths (RE) include Lanthanum (La) to Lutetium (Lu) besides Scandium (Sc) and Yttrium (Y).
- These metals are strategic in nature with wide application in the nuclear and other high tech industries such as electronics, telecommunication, information technology, space, defense etc.
- Uses:
- Lithium metal is used to make useful alloys.
- For example, with lead to make ‘white metal’ bearings for motor engines, with aluminium to make aircraft parts, and with magnesium to make armour plates.
- In Thermonuclear reactions.: To make electrochemical cells. Lithium is an important component in Electric Vehicles, Laptops etc.
6.The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has issued a notification to facilitate the issuance of International Driving Permit (IDP) for Indian citizens whose IDP has expired while they are abroad.
- There was no mechanism for its renewal while citizens were abroad and their IDP had expired.
- Now, with this amendment, it is proposed that Indian citizens can apply for renewal through the Indian Embassies/Missions abroad, from where these applications would move to the VAHAN portal in India, to be considered by the respective RTOs.
- IDP would be couriered to the citizen at his/her address abroad by the respective RTOs.
- This notification also removes the conditions of a Medical Certificate and a valid visa at the time of making the request for the IDP in India.




