Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 1st August 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Muslim Women Rights Day”
- Long Term Repo Operations (LTRO):
- Sample Registration System (SRS) 2018 report:
- The output of eight core industries contracted for the fourth consecutive month – shrinking by 15% in June 2020
- 1947 Tripartite Agreement on Gurkha soldiers:
- Other important current affairs:
1.Muslim Women Rights Day:

Recently, 1st August has been recorded as “Muslim Women Rights Day” in the country’s history to mark first anniversary of the passage of Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Marriage) Act, 2019.
Provisions of the Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Marriage) Act, 2019
- The Act makes all declaration of talaq, including in written or electronic form, to be void (i.e. not enforceable in law) and illegal.
- It also makes a declaration of talaq a cognizable offense ( only if information relating to the offense is given by a married woman against whom talaq has been declared), attracting up to three years imprisonment with a fine.
- A cognizable offense is one for which a police officer may arrest an accused person without warrant.
- The Magistrate may grant bail to the accused.
- The bail may be granted only after hearing the woman (against whom talaq has been pronounced), and if the Magistrate is satisfied that there are reasonable grounds for granting bail.
- The offense may be compounded (i.e. the parties may arrive at a compromise) by the Magistrate upon the request of the woman (against whom talaq has been declared).
- A Muslim woman against whom talaq has been declared is entitled to seek subsistence allowance from her husband for herself and for her dependent children.
Constitutional Provisions:
- The Triple Talaq was held to be violative of Article 14 (the right to equality), which is held by the Supreme Court from Shah Bano case (1986) to Shayara Bano case in 2017.
- Article 25 of the Constitution guarantees religious freedom like Freedom of Practice and Propagation of Religion.
- Like all other Fundamental Rights, it is subject to restrictions and does not protect religious practices that can negatively affect the welfare of citizens.
- Hence, Article 25 is overridden by Article 14, which guarantees the Right to Equality as triple talaq denies a Muslim woman’s equality before the law.
- Article 25 is also subject to Article 15 (1) which states that the State “shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex…” Since triple talaq does not work in the favour of women, it violates Article 15 (1) of the Constitution.
2.Long Term Repo Operations (LTRO):

According to RBI, LTRO operations initiated in February 2020 has created surplus liquidity in the system which has helped to reduce financing cost in the corporate bond market.
- Under LTRO, RBI will conduct term repos of one-year and three-year tenors of appropriate sizes for up to a total amount of Rs 1 lakh crore at the policy repo rate.
- RBI introduced LTRO to assure banks about the availability of durable liquidity at a reasonable cost relative to prevailing market conditions and to further encourage banks to undertake maturity transformation smoothly so as to augment credit flows to productive sectors.
- It is a measure that market participants expect will bring down short-term rates and also boost investment in corporate bonds. These new measures coupled with RBI’s earlier introduced ‘Operation Twist’ are an attempt by the central bank to manage bond yields and push transmission of earlier rate cuts.
3.Sample Registration System (SRS) 2018 report:

India released data on Young Population as part of the Sample Registration System (SRS) 2018 report.:
- The Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India released data on the Young Population as part of the Sample Registration System (SRS) 2018 report.
- For the first time, more than half of India’s population, irrespective of gender or whether it’s in urban or rural areas, is now 25 years or older.
- Overall, the under-25s in 2018 constituted 46.9% of the population. Nationally, 46.3% of the female population was below 25 years of age compared to 47.4% of males.
- Even among rural men, the proportion of those below 25 years of age had fallen to 49.9% from 50.2% in 2017. In all other categories urban women, urban men, and rural women those under 25 already constituted less than half the population.
- As India’s fertility rate goes down steadily along with a rise in life expectancy, the proportion of its young population is shrinking and the median age has been increasing.
- However, Bihar, with the highest fertility rate of 3.2, had the highest proportion of its population below 25 years, 57.2%, followed by UP with the second-highest fertility rate of 2.9, where the under-25 year population was 52.7%.
The Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India released data on Deaths in the 0-4 year age group as part of the Sample Registration System (SRS) 2018 report.:
Key findings:
- Madhya Pradesh has the highest under-five mortality rate of 56 and Kerala has the lowest of 10. Under-five mortality rate is the probability of dying before 5 years of age for every 1,000 newborns.
- Deaths in the 0-4 year age group account for 20% of total deaths in Madhya Pradesh. In contrast, deaths in this age group account for just 2% of total deaths in Kerala.
- Other than Madhya Pradesh, the proportion of deaths in the 0-4 age group is also high in Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Bihar in that order i.e. states with poor development indices.
- Other than Kerala, the proportion of deaths in the 0-4 age group is low in Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, and Maharashtra in that order.
- In India as a whole and in most states, the deaths in the 0-4 age group constitute a higher proportion of total deaths in rural than in urban areas, except in a few states such as Uttarakhand and Punjab, where the proportion is higher in urban areas.
Data from the recently released Sample Registration System’s 2018 report shows that India’s “demographic dividend” continues to swell, with the share of the working-age population in the country’s total population increasing.
Key findings:
- The SRS 2018 report estimates that in 2018, nearly 66% of the Indian population was between 15 and 59. This proportion has inched up each year from 2013 onwards.
- Those of working age constituted over two-thirds of the population in 12 of the 22 major states in 2018 while five years earlier, this was true in only four of the current states.
- Two states — Andhra Pradesh and Telangana — had over 70% of their populations in the working-age bracket and Bihar was the lone state in which they were less than 60% of the total.
- In general, states widely considered less developed had a lower proportion of their population in the working-age groups.
- Among the states with high development indicators, Kerala stands out as an exception with low working-age population. This is due to a relatively larger proportion of the elderly due to decades of low fertility and high life expectancy.
4. The output of eight core industries contracted for the fourth consecutive month – shrinking by 15% in June 2020.:
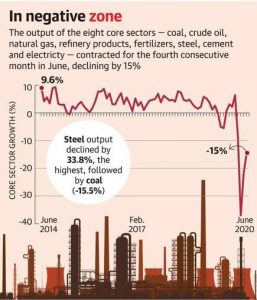
- The eight-core sector industries are coal, crude oil, natural gas, refinery products, fertilizers, steel, cement, and electricity.
- These eight industries account for 40.27% in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
Key Points
- A contraction in Total Output:
- During April-June 2020, the sector’s output dipped by 24.6% as compared to positive growth of 3.4% in the same period the previous year.
- However, 15% contraction in June 2020 implies some economic recovery as in May 2020, the industries’ output contracted by 22%.
- Economists expect the negative trend to continue for at least two more months.
- Industry-wise Performance:
- The fertilizer industry is the only one that saw actual growth in June, with output rising 4.2% in comparison to June 2019.
- This, however, is lower than the May 2020 growth of 7.5% but reflects the positive outlook in the agriculture sector where a normal monsoon is leading to expectations of a good Kharif crop.
- Rest seven sectors – coal (-15.5%), crude oil (-6.0), natural gas (-12%), refinery products (-9%), steel (-33.8%), cement (-6.9%), and electricity (-11%) – recorded negative growth in June.
- The steel sector continues to remain the worst performer, with a 33% drop in production in comparison to the previous year.
- Index of Industrial Production
- The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is an index that shows the growth rates in different industry groups of the economy in a fixed period of time.
- It is compiled and published monthly by the National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
6.1947 Tripartite Agreement on Gurkha soldiers:

Recently, Nepal’s Foreign Minister has said that the 1947 Tripartite Agreement between India, Nepal and the United Kingdom (that deals with the military service of Gurkha soldiers from Nepal) has become redundant.
- He also said that Nepal would prefer to handle the matter bilaterally with India and the United Kingdom.
The Tripartite Agreement:
- In 1947, when India became independent, it was decided to split Gurkha regiments between the British and Indian armies.
- From the first quarter of the 19th century, Gurkhas had served under the British, first in the armies of the East India Company, and then the British Indian Army.
- East India Company first recruited Gurkhas after suffering heavy casualties during the Anglo-Nepalese War also known as the Gurkha War.
- The war ended with the signing of the Treaty of Sugauli in 1816.
- It ensured that Gurkhas in British and Indian service would enjoy broadly the same conditions of service as that of British and Indian citizens.
- The services include all perks, remuneration, facilities and pension schemes, etc.
- Gorkha recruitment was the first window that was opened to Nepali youth to go abroad.
- The objection from Nepal regarding the Gurkhas serving in the Indian military has become prominent in the backdrop of Nepal-India territorial dispute over the Kalapani region of Pithoragarh district that Nepal claims as its own.
- Nepal has responded by publishing a new map that included the disputed territories of the Kalapani region.
- The issue became a talking point after Indian Army Chief remarked that Nepal’s strong protest against Indian road construction in the Limpiadora-Kalapani-Lipulekh area was at the behest of a third party (China).
- The Nepalese people believe that the Indian Army Chief, who is granted the honorary post of a General in the Nepal Army has hurt the sentiments of the Nepali Gurkha Army personnel who lay down their lives to protect India.
- Also, the Gurkha veterans have been alleging that the United Kingdom has been discriminating against them in terms of pay, pension, and other facilities.
- The British government started providing equal pay and pension to Gurkhas in 2007.
Other important current affairs:
1. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has relaxed the norms for preferential allotment for companies that have stressed assets, thereby making it easier for such entities to raise funds.
- Listed entities with stressed assets can make preferential allotment at a price that is “not less than the average of the weekly high and low of the volume-weighted average prices of the related equity shares during the two weeks preceding the relevant date.”
- A company would be eligible to be called stressed if it has defaulted on its payment obligations for more than 90 days or if the credit rating agencies have downgraded its securities to ‘D’.
- An entity, which has an inter-creditor agreement in terms of Reserve Bank of India (Prudential Framework for Resolution of Stressed Assets) Directions 2019, will also be identified as stressed.
2. The Labour and Employment Ministry has notified the draft Code on Wages (Central) Rules under the Code on Wages, 2019 for public comments.
- The normal working day shall comprise of “eight hours of work and one or more intervals of rest which in total shall not exceed one hour”. Provisions of the Factories Act will not be affected by this rule.
- It would fix a National Floor Minimum Wage based on factors like Net intake of 2,700 calories per day, 66 meters cloth per year per standard working-class family, housing rent expenditure as 10 percent of food and clothing expenditure, three adult consumption unit, etc.
- The Centre shall constitute a technical committee which would advise on the skill categories, while an advisory board may recommend the minimum wage.
3. The High-Level Group (HLEG) on Agricultural Exports set up by the Fifteenth Finance Commission has submitted its report to the Commission.
- The HLEG was set up to recommend measurable performance incentives for states to encourage agricultural exports and to promote crops to enable high import substitution.
- Recommendations:
- Crop Value Chains:
- It emphasizes focusing on 22 crop value chains with a demand-driven approach.
- The demand-driven approach refers to a development strategy where the people themselves are expected to take the initiative and the responsibility for improving the supply situation rather than being passive recipients of the Government services.
- It also suggests solving Value Chain Clusters (VCC) holistically with a focus on value addition.
- State-led Export Plan:
- It is a business plan for a crop value chain cluster, that will lay out the opportunity, initiatives and investment required to meet the desired value chain export aspiration.
- These plans will be action-oriented, time-bound, and outcome-focused.
- Such plans should be collaboratively prepared with private sector players and Commodity Boards presenting the participation of all stakeholders.
- Participation of Private Sector:
- The private sector players need to play a pivotal role in ensuring demand orientation and focus on value addition.
- It also needs to ensure project plans are feasible, robust, implementable and appropriately funded; providing funds for technology based on business cases and for creating urgency and discipline for project implementation.
- Crop Value Chains:
4. China has formally launched the full global services of its BeiDou-3 Navigation Satellite System (BDS).
- The name BeiDou comes from Chinese word for the Big Dipper or Plough constellation.
- China’s BeiDou navigation project was launched in the early 1990s. The system then became operational within China in 2000 and in the Asia-Pacific region in 2012.
- The navigation satellite system was completed in three steps: BDS-1 which provided services to China, BDS- 2 to provide services to the Asia-Pacific region, and BDS-3 which provides services worldwide.
5. Recently, an Israeli team arrived in India with a multi-pronged mission, codenamed Operation Breathing Space to work with Indian authorities on the Covid-19 response.
- India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Israel’s defence ministry research and development team are working together to develop four different kinds of rapid testing kit for Covid-19 which can give the result within 30 seconds.
- Types of Tests:
- The tests include an audio test, a breath test, thermal testing, and a polyamine test which.
- In the audio test, a patient’s voice would be recorded and evaluated through artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- In the breath test, the patient will blow into a tube that will detect the virus using terra-hertz (high frequency) waves.
- Thermal testing will enable the identification of the virus in a saliva sample.
- Poly amino acids test seeks to isolate proteins related to Covid-19.
6. The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the Eurozone reduced by 12.1% in the April-June 2020 quarter, compared to the previous quarter.
- The Eurozone consists of 19 members of the European Union (EU), which uses the Euro as their official currency.
- 8 EU members (Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Sweden) do not use the euro.
- The 27-country European Union saw a decline of 11.9% in its economy for the same period.
7. The Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises has approved a programme for the benefit of artisans involved in manufacturing of Agarbatti under the Gramodyog Vikas Yojana.
- The programme will initially include four pilot projects, including one in the northeastern part of the country.
- Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) will provide training and assistance as well as work and raw material to artisans working in this area, in tie-up with Agarbatti manufacturing machines.
- KVIC is a statutory body established by Khadi And Village Industries Commission Act, 1956.
- It is an apex organization under the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises charged with the planning, promotion, organization, and implementation of programs for the development of Khadi and other village industries in the rural areas




