Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 29th December 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Adopt a Heritage’ project
- Rohingyas:
- Pneumosil:
- New Rule in GST
- China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)
- National Common Mobility Card :
- Other important current affairs:
1.Adopt a Heritage’ project:

So far, under the project, 27 Memorandum of Understandings (MoUs) have been awarded to 12 Monument Mitras for twenty-five (25) sites and two (2) Technological interventions across India.
Adopt a Heritage Project:
- The Scheme was launched on World Tourism Day i.e. 27th September 2017.
- This project is a key initiative of the Ministry of Tourism in close collaboration with the Ministry of Culture and Archeological Survey of India (ASI), to develop the heritage sites/monuments and making them tourist-friendly to enhance the tourism potential and their cultural importance in a planned and phased manner.
- The project plans to entrust heritage sites/monuments and other tourist sites to private sector companies, public sector companies and individuals for the development of tourist amenities. The project aims to develop synergy among all partners.
Monument Mitras:
- Successful bidders selected for adopting heritage sites/monuments by the Oversight and Vision Committee shall be called as Monument Mitras. The basic and advanced amenities of the tourist destinations would be provided by them.
- They would also look after the operations and the maintenance of the amenities. The ‘Monument Mitras’ would associate pride with their CSR activities.
Significance of this project:
- Adopt a Heritage project is meant to address the challenges that the Archaeological Survey of India and other government bodies are facing in operating tourism infrastructure at heritage sites.
- By allowing private players to build, operate and maintain “tourist-friendly” and “world class amenities at these sites, the expectation is that the project will boost domestic and international tourism.
2.Rohingyas:

Bangladesh has started moving Rohingya refugees to a controversial flood-prone Bhashan Char island in the Bay of Bengal despite opposition from rights activists.
- The island was formed from a build-up of silt in the Bay of Bengal only 20 years ago, and concerns have been consistently raised about Bhasan Char’s exposure to extreme weather and distance from the mainland in emergencies since Bangladesh first raised the idea in 2015.
Rohingyas:
- They are an Ethnic group, mostly Muslims.
- They were not granted full citizenship by Myanmar.
- They were classified as “resident foreigners or associate citizens”.
- Ethnically they are much closer to the Indo-Aryan people of India and Bangladesh than to the Sino-Tibetans of the Country.
- Described by UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres as “one of, if not the, most discriminated people in the world”.
- About 860,000 Rohingya live in the world’s largest and most densely populated refugee camp in southern Bangladesh.
- The Myanmar and Bangladesh governments continue to negotiate terms for the repatriation of Rohingya refugees to Myanmar.
- According to the Ministry of Home Affairs, there are approximately 40,000 Rohingyas living in India.
3.Pneumosil:
India’s first fully indigenously developed pneumococcal conjugate vaccine “Pneumosil” has been launched.
- Developed by: Serum Institute of India (SII), through a collaboration with PATH and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Serum Institute of India is a Pune based world’s largest vaccine manufacturer by number of doses produced and sold globally.
- PATH is an international, nonprofit global health organization based in Seattle (USA).
- The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) is an American private foundation, founded by Bill and Melinda Gates.
- Based in Seattle, Washington, the primary goals of the foundation are to enhance healthcare and reduce extreme poverty across the globe, and to expand educational opportunities and access to information technology in the USA.
- The vaccine targets the pneumococcal bacterium, which causes pneumonia and other serious life-threatening diseases such as meningitis and sepsis, and is estimated to cause nearly four lakh deaths in children under five years of age each year worldwide.
- It will be available in the market at an affordable price in single-dose and multidose presentations.
- While pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) have helped reduce pneumococcal deaths, they are difficult for many countries to afford.
- The unique feature of the vaccine is its composition, which is specially tailored to the prevailing serotype prevalence of S Pneumoniae in India and other regions of the world.
- A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals.
- It was licensed by the Drugs Controller General (India) in July 2020.
4.New Rule in GST:

The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) has made it mandatory for businesses with a monthly turnover of more than Rs. 50 lakh to pay at least 1% of their Goods and Services Tax (GST) liability in cash.
- It will be effective from 1st January 2021.
- The new rule restricts use of Input Tax Credit (ITC) for discharging GST liability to 99%.
- The CBIC has booked about 12,000 cases of ITC fraud and arrested 365 persons in such cases so far.
- The move will curb tax evasion by way of fake invoicing.
- ITC is provided to set off tax paid on the purchase of raw materials, consumables, goods or services that were used in the manufacturing of goods or services. This helps in avoiding double taxation and the cascading effect of taxes.
However, this restriction will not apply in cases:
- Where the managing director or any partner has paid more than Rs. 1 lakh as income tax, or
The registered person has received a refund amount of more than Rs. 1 lakh in the preceding financial year on account of unutilized input tax credit. - This comes to only 0.37% of the total businesses registered in the GST system.
- Of the total GST taxpayer base of 1.2 crore, only about 4 lakh have monthly supply value greater than Rs. 50 lakh.
- Of these, only about 1.5 lakh pay less than 1% of their GST liability in cash and when exclusions in the rule are applied, around 1.05 lakh taxpayers get further excluded.
- Thus, the rule would apply only to 40,000 to 45,000 taxpayers.
5.China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC):
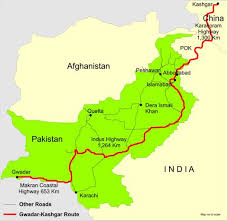
China defends the progress of Pak. corridor and rejects reports of seeking additional guarantees from Islamabad before sanctioning a loan for CPEC.
About CPEC:
- The CPEC is the flagship project of the multi-billion-dollar Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a pet project of Chinese President Xi Jinping, aimed at enhancing Beijing’s influence around the world through China-funded infrastructure projects.
- The 3,000 km-long China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) consists of highways, railways, and pipelines.
- CPEC eventually aims at linking the city of Gwadar in South Western Pakistan to China’s North Western region Xinjiang through a vast network of highways and railways.
- The proposed project will be financed by heavily-subsidized loans, that will be disbursed to the Government of Pakistan by Chinese banks.
- It passes through PoK.
- CPEC rests on a Chinese plan to secure and shorten its supply lines through Gwadar with an enhanced presence in the Indian Ocean. Hence, it is widely believed that upon CPEC’s fruition, an extensive Chinese presence will undermine India’s influence in the Indian Ocean.
- It is also being contended that if CPEC were to successfully transform the Pakistan economy that could be a “red rag” for India which will remain at the receiving end of a wealthier and stronger Pakistan.
- Besides, India shares a great deal of trust deficit with China and Pakistan and has a history of conflict with both.
- As a result, even though suggestions to re-approach the project pragmatically have been made, no advocate has overruled the principal strands of contention that continue to mar India’s equations with China and Pakistan.
6.National Common Mobility Card :

Expanded to the Airport Express Line of Delhi Metro, which was started in Ahmedabad last year.
Key features:
- Dubbed as ‘One Nation One Card’, the inter-operable transport card would allow the holders to pay for their bus travel, toll taxes, parking charges, retail shopping and even withdraw money.
- The idea was floated by the Nandan Nilekani committee set up by the Reserve Bank of India.
- NCMC is an automatic fare collection system. It will turn smartphones into an inter-operable transport card that commuters can use eventually to pay for Metro, bus and suburban railways services.
- This card runs on RuPay card.
- The stored value on card supports offline transaction across all travel needs with minimal financial risk to involved stakeholders.
- Ministry of housing & urban affairs brought to the fore the National Common Mobility Card (NCMC) to enable seamless travel by different metros and other transport systems across the country besides retail shopping and purchases.
Need for and significance of NCMC:
- Public transport is extensively used across India as the economical and convenient mode of commuting for all classes of society.
- Cash continues to be the most preferred mode of fare payments across public transport.
- However, there are multiple challenges associated with cash payment such as cash handling, revenue leakages, cash reconciliation, etc.
- Various initiatives have been taken by transit operators to automate and digitize the fare collection using the Automatic Fare Collection System (AFC).
- The introduction of closed-loop cards issued by these operators helped to digitize the fare collection to a significant extent. However, the restricted usability of these payment instruments limits the digital adoption by customers.
Other important current affairs:
1.India’s External Affairs Minister met the top leaders of Qatar and discussed strengthening the economic and security cooperation between the two countries.
- The visit is part of India’s ongoing outreach to West Asia, which the country sees as part of its extended neighborhood.
- Qatar is a member of the Gulf Cooperation Council.
- India and Qatar agreed to maintain regular consultations and coordination on all issues of mutual interest at multilateral fora.
- Issues of mutual interest include energy, power, petrochemicals, investments, infrastructure, development, project exports and education.
- Discussed ways to strengthen the multifaceted bilateral relationship in areas such as energy, trade, investment, food processing, healthcare, education, culture, defense, and security.
- Bilateral trade was worth USD 10.95 billion in 2019-20.
2.The Prime Minister has inaugurated the country’s first fully automated Metro, (Driverless Metro) on Delhi Metro’s Magenta Line.
- He also extended the fully operational National Common Mobility Card (NCMC) to the Airport Express Line of the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC).
- Driverless Metro:
- With this achievement, DMRC has entered the elite league of 7% of the world’s Metro networks where such a facility is available.
- In 2014, only five cities had Metro rail and currently, it is present in 18 cities and the number of Metro users has also increased manifold.
- The driverless trains will be fully automated, eliminating the possibility of human error.
- The technology has different levels or Grades of Automation (GoA):
- In GoA 1, trains are run by one driver.
- In GoA 2 and GoA 3, the role of the driver is reduced to operating doors and for taking over in case of emergencies and the starting and halting of trains is automated.
- In GoA 4, trains are set on a completely unattended operations mode.
3.The government has used financial innovation to recapitalize Punjab & Sind Bank by issuing the bank Rs. 5,500 crore worth Special Zero-Coupon Recapitalisation Bonds.
- Punjab & Sind Bank is a Government of India undertaking.
- Bank Recapitalisation:
- It means infusing more capital in state-run banks so that they meet the capital adequacy norms.
- Indian public sector banks are emphasized to maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) of 12%.
- CAR is the ratio of a bank’s capital in relation to its risk-weighted assets and current liabilities.
- The government, using different instruments, infuses capital into banks facing shortage of capital. As the government is the biggest shareholder in public sector banks, the responsibility of bolstering banks’ capital reserves lies with the government.
- The government infuses capital in banks by either buying new shares or by issuing bonds.
4.A recent report published by the Centre for Economics and Business Research (CBER) has predicted that India will again overtake the UK to become the fifth largest economy in 2025 and race to the third spot by 2030.
- CBER is a UK based company that gives independent economic forecasts for public and private firms.
- The Indian economy will expand by 9% in 2021 and by 7% in 2022.
- This growth trajectory will see India become the world’s third largest economy by 2030, overtaking the UK in 2025, Germany in 2027 and Japan in 2030.
- China in 2028 will overtake the USA to become the world’s biggest economy, five years earlier than previously estimated due to the contrasting recoveries of the two countries from the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Japan would remain the world’s third-biggest economy, until the early 2030s when it would be overtaken by India, pushing Germany down from fourth to fifth.
5.Astronomers at the $100 million Breakthrough Listen project, started by the legendary physicist Stephen Hawking, have recently picked up an “intriguing” radio wave emission from the direction of Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our Sun.
- The news has sparked renewed interest in Proxima Centauri, one of whose planets is believed to revolve in the star’s habitable zone, giving rise to the possibility that it could have, or does, sustain life.
- Proxima Centauri is 4.2 light-years away from the Sun – considered a close distance in cosmic terms.
- Its mass is about an eighth of the Sun’s, and it is too dim to be seen with the naked eye from Earth.
- Proxima b, one of the two planets that revolve around the star, is the subject of significant curiosity.
- Sized 1.2 times larger than Earth, and orbiting its star every 11 days, Proxima b lies in Proxima Centauri’s “Goldilocks zone” i.e. the area around a star where it is not too hot and not too cold for liquid water to exist on the surface of surrounding planets (e.g. Earth is in the Sun’s Goldilocks zone).
- However, this does not mean for sure that water is present on Proxima b. It could also be hostile to life, if its atmosphere has been stripped away by solar flares from Proxima Centauri.




