Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 30th December 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Data on Police Organisations
- Dedicated Freight Corridor
- 7th National Summit on Good, Replicable Practices & Innovations
- Ruthenium 106:
- Digital Ocean:
- Mission Sagar-III.
- MP anti-conversion Bill:
- Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunisation (GAVI):
- Zero coupon bonds:
- Other important current affairs
1.Data on Police Organisations:

The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD) has released data on police organisations.
- It shows different aspects of policing in the country like woman police, police expenditure, constabulary ratio, transport facilities, communication facilities, representation of various castes and police training centres.
General Data:
- The government has spent Rs. 1,566.85 crore in 2019-20 for expenditure and police training.
- It highlights that Backward Classes, Dalits and Tribals constitute almost 67% of India’s population, but their representation in police forces in the country is only at 51%.
- The goal of proportionate representation has remained unfulfilled despite all state governments providing reservations to these categories.
- Vacant Posts:
- Over 5.31 lakh posts in police forces of different states and 1.27 lakh posts in Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) are lying vacant.
- Scheduled Tribes:
- They form 8.6% of the population and have 12% representation in the police forces, placing them at a comparatively better position.
- Only STs have better representation in police forces in comparison to their share in population while all other backward classes fare poorly.
- Dalits:
- 14% of all positions in police forces across the country were represented by Dalits at the end of 2019.
- According to Census 2011, Dalits make up 16.6% of India’s population.
- Other Backward Classes:
- OBCs fare the worst on the representation front as, despite their 41% share in the population, they constitute only 25% of the police forces.
- Women:
- Women are highly under-represented with 10% share in the actual strength of the police in the country, even though their share in population is 48%.
- However, their situation has improved considerably over the past years as the actual strength of women in police forces has almost doubled since 2014.
- Women population per woman police ratio stands at 3,026 nationally which is very low.
- Poor representation of women in the police is posing serious challenges in dealing with crimes against women and women criminals.
2.Dedicated Freight Corridor:
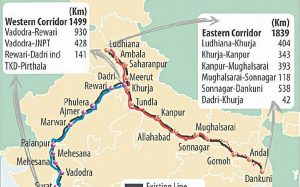
The Prime Minister of India has inaugurated a 351-km section of the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC) and an Operation Control Centre (OCC) between Khurja and Bhaupur in Uttar Pradesh.
- EDFC is a 1,839-km project billed as the largest rail infrastructure being built in independent India and has been in the making since 2006.
Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC):
- It is a high speed and high capacity railway corridor that is exclusively meant for the transportation of freight, or in other words, goods and commodities.
- DFC involves the seamless integration of better infrastructure and state of the art technology.
- DFC consists of two arms:
- Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC):
- It starts at Sahnewal (Ludhiana) in Punjab and ends at Dankuni in West Bengal.
- The EDFC route has coal mines, thermal power plants and industrial cities. Feeder routes are also being made for these.
- The EDFC route covers Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal
- The World Bank is funding a majority of the EDFC.
- The 351-km-long ‘New Bhaupur-New Khurja section’ will decongest the existing Kanpur-Delhi main line and double the speed of freight trains from 25 kmph to 75 kmph.
- Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC):
- The other arm is the around 1,500-km WDFC from Dadri in Uttar Pradesh to Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust in Mumbai, touching all major ports along the way.
- The WDFC covers Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh.
- It is being funded by the Japan International Cooperation Agency.
- Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC):
Connecting Link for Eastern and Western Arm: It is under construction between Dadri and Khurja.
The industrial corridor of Delhi-Mumbai and Amritsar-Kolkata are also being developed around both these DFCs.
3.7th National Summit on Good, Replicable Practices & Innovations:

The Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare digitally inaugurated the 7th National Summit on Good, Replicable Practices & Innovations through a video conference.
- The New Health Management Information System (HMIS) along with the Operational Guidelines for Tuberculosis services at Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centres and the Operational Guidelines 2020 on Active Case Detection and Regular Surveillance for Leprosy was launched at the Summit.
About the Summit:
- The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare holds the National Summit on Good, Replicable Practices and Innovations in Public Healthcare Systems in India.
- The first such summit was held in 2013 at Srinagar to recognize, showcase and document various best practices and innovations in the public healthcare system.
- The practices and innovation presented in these summits span across programmatic areas ranging from RMNCH+A (Reproductive, Maternal, Neonatal, Child Health and Adolescent Health) to communicable diseases (including Tuberculosis, Malaria and other vector borne diseases and Leprosy) to new areas of Non-Communicable Disease control programmes.
- They also include innovations that apply systems thinking to health problems such as the use of information technology to strengthen continuum of care, and to address human resource shortages and challenges in capacity building.
Highlights of the 7th National Summit:
- In the year 2020, 210 new initiatives were uploaded by the States and UTs in the National Healthcare Innovation Portal.
- National Health Innovation Portal was launched to serve as a platform in the public domain to facilitate collection and dissemination of good practices and innovations that are found to be replicable.
- The Covid-19 pandemic has made the country self-reliant in the area of manufacturing of PPE kit, Ventilator, mask, vaccine etc.
- More than 1 million tele-consultations have been done on the e-Sanjeevani digital platform of the Health Ministry.
- e-Sanjeevani is a doctor to doctor telemedicine system, being implemented under the Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centre (AB-HWCs) program.
- Department of Health and Family Welfare has won the Digital India award 2020 under the Open Data Champion category for thee-Sanjeevani digital platform.
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC), under the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), has been conducting the biennial Digital India Awards to promote innovation in eGovernance and digital transformation of government service delivery mechanism.
- Digital transformation has enabled the country to develop a national digital health ecosystem that supports Universal Health Coverage in an efficient, accessible, inclusive, affordable, timely and safe manner.
- There is a need to involve and integrate the grassroots healthcare workers for brainstorming on the innovations in the healthcare ecosystem and benefit from the collective wisdom which emanates from years of experience and expertise of working with people’s health delivery systems.
4.Ruthenium 106:

Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), Mumbai has developed Eye Cancer therapy in the form of the first indigenous Ruthenium 106 Plaque for treatment of Ocular Tumours.
- The handling of plaque is very convenient for the Surgeon and it has been acknowledged to be at par with the international standards.
- So far the BARC plaques made in India through the Department of Atomic Energy have been used for seven cases for Ocular Cancer.
- Ocular tumours are tumours inside the eye. They are collections of cells that grow and multiply abnormally and form masses.
Ruthenium-106:
- Ruthenium-106 is a radioactive form of the rare heavy metal ruthenium, which is a “platinum group” metal similar to platinum.
- Ruthenium-106 is produced from the fission or splitting of uranium-235, the type of uranium used in nuclear fission reactors, so it’s found in spent nuclear fuel.
- It’s used in medicine for cancer radiation therapy, especially for eye and skin tumours. It’s also used in radioisotope thermoelectric generators that power satellites.
5.Digital Ocean:

The Ministry of Earth Sciences inaugurated the web-based application DigitalOcean developed by Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) in a Virtual Meeting held in New Delhi.
- Digital Ocean is a new state of the art data platform for Ocean Data Management.
- It is the first such platform to provide ocean data related services at one place.
- It includes a set of applications developed to organize and present heterogeneous oceanographic data by adopting rapid advancements in geospatial technology.
- It facilitates an online interactive web-based environment for data integration, 3D and 4D (3D inspace with time animation) data visualization, data analysis to assess the evolution of oceanographic features, etc.
Significance:
- Digital Ocean is a big step towards Prime Minister’s vision of Digital India that is to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
- It will serve as a one stop-solution for all the data related needs of a wide range of users including research institutions, operational agencies, strategic users, academic community, maritime industry, policy makers and the public.
- It will also contribute to the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- It will play a central role in sustainable management of the oceans and expanding the government’s Blue Economy initiatives.
- It will be promoted as a platform for capacity building on Ocean Data Management for all Indian Ocean Rim countries.
6.Mission Sagar-III:

The Indian Naval Ship (INS) Kiltan has arrived at Sihanoukville Port, Cambodia as part of ongoing Mission Sagar-III.
- The ship will deliver 15 tons of Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) stores for the flood-affected people of Cambodia, which will be handed over to Cambodia’s National Disaster Management Committee (NDMC).
- Earlier, the ship delivered 15 Tons of HADR Stores for the flood-affected people of Central Vietnam.
Mission Sagar-III is part of India’s HADR assistance to friendly foreign countries during the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic. - In November 2020, as part of Mission Sagar-II, INS Airavat delivered food aid to Sudan, South Sudan, Djibouti and Eritrea.
- Launched in May 2020, ‘Mission Sagar’ was India’s initiative to deliver Covid-19 related assistance to the countries in the Indian Ocean Littoral states. The countries included were Maldives, Mauritius, Madagascar, Comoros and Seychelles.
- This Mission is being undertaken in accordance with the Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) vision and reiterates India’s position as a dependable partner, and the Indian Navy as the Preferred Security Partner and First Responder.
- The Mission also highlights the importance accorded to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries and further strengthens the existing bonds.
- Cambodia and Vietnam are member nations of the ASEAN.
7.MP anti-conversion Bill:

The proposed law is called the Madhya Pradesh Dharmik Swatantrata (Freedom of Religion) Bill 2020.
- Madhya Pradesh Cabinet has given its nod to an ordinance on the Bill.
Key Provisions:
- Seeks to regulate inter-faith marriages in the state.
- Exempts reconversion to parental religion from its purview.
- Jail term of up to 10 years and a fine of ₹1 lakh for “conversion through marriage or other forcible means”.
- The bill seeks to prohibit religious conversions or an attempt of conversion by means of misrepresentation, allurement, threat, undue influence, coercion, marriage, and any other fraudulent means.
- The conspiracy and (the act of) abetting a person for conversion has also been prohibited.
- Forceful conversions and marriages will be a cognizable offence and be non-bailable.
Issues and concerns:
- States are opting for laws on freedom of religion for marriage (‘love jihad’).
- The Prohibition of Unlawful Conversion of Religion Ordinance, 2020, was notified by Uttar Pradesh last month.
- Haryana and Karnataka announced intentions to enact such laws.
8.Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunisation (GAVI):

Union Health Minister Harsh Vardhan has been nominated by the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunisation (GAVI) as a member on the GAVI Board.
- Dr. Harsh Vardhan will be representing the South East Area Regional Office (SEARO)/ Western Pacific Regional Office (WPRO) constituency on the GAVI Board.
GAVI Board:
- The GAVI Board is responsible for strategic direction and policymaking, oversees the operations of the Vaccine Alliance and monitors programme implementation.
- With membership drawn from a range of partner organisations, as well as experts from the private sector, the Board provides a forum for balanced strategic decision making, innovation and partner collaboration.
- Created in 2000, Gavi is an international organisation – a global Vaccine Alliance, bringing together public and private sectors with the shared goal of creating equal access to new and underused vaccines for children living in the world’s poorest countries.
- Members: Gavi brings together developing country and donor governments, the World Health Organization, UNICEF, the World Bank, the vaccine industry in both industrialised and developing countries, research and technical agencies, civil society, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and other private philanthropists.
- Main activities:
- GAVI’s strategy supports its mission to save children’s lives and protect people’s health by increasing access to immunisation in poor countries.
- It contributes to achieving the United Nations’ Millennium Development Goals by focusing on performance, outcomes and results.
- Its partners provide funding for vaccines and intellectual resources for care advancement.
- They contribute, also, to strengthening the capacity of the health system to deliver immunisation and other health services in a sustainable manner.
9.Zero coupon bonds:

The government has used financial innovation to recapitalise Punjab & Sind Bank by issuing the lender Rs 5,500-crore worth of non-interest bearing bonds valued at par.
- These are special types of zero coupon bonds issued by the government after proper due diligence and these are issued at par.
- These are “non-interest bearing, non-transferable special GOI securities”.
- They have a maturity of 10-15 years and issued specifically to Punjab & Sind Bank.
- These recapitalisation bonds are special types of bonds issued by the Central government specifically to a particular institution.
- It is not tradable, it is not transferable.
- It is held at the held-to-maturity (HTM) category of the bank as per the RBI guidelines. Since it is held to maturity, it is accounted at the face value (and) no mark-to-market will be there.
- Though zero coupon, these bonds are different from traditional zero coupon bonds on one account — as they are being issued at par, there is no interest; in previous cases, since they were issued at discount, they technically were interest bearing.
Other important current affairs:
1.Madhya Pradesh Government is organizing ‘Raag-Bhopali’ exhibition to promote Zari-Zardozi crafts of Bhopal.
- Embroidery done with metallic threads is called kalabattu and forms the zari.
- The main zari production centres are Bhopal in Madhya Pradesh.
- Here the metal ingots are melted into metal bars called pasa from which lengths are got by beating it after treatment.
- This is then pulled through perforated steel plates to make it into wires, followed by the tarkashi process to make it thin with rubber and diamond dies.
- The last stage is called badla where the wire is flattened and twisted with silk or cotton thread to become kasab or kalabattu.
- Zardozi: This is a heavy and more elaborate embroidery work which uses varieties of gold threads, spangles, beads and gota. It is used to embellish wedding outfits, heavy coats, cushions, curtains etc.
- Kamdani : This is a lighter needlework which is done on lighter material like scarves, veils, and caps.
- Mina Work : This is thus called owing to its resemblance with enamel work. The embroidery is done in gold.
2.After it came to light that the grave of Naushera ka Sher Brigadier Mohammad Usman, the senior-most officer killed in the first India-Pakistan war of 1947-48, was damaged, an Army source said it was looking into the issue and the grave will be restored soon.
- Brigadier Mohammad Usman MVC (1912 – 1948) was one of only 18 Brigadiers in the Army at the time of Independence and was posthumously awarded the Maha Vir Chakra for his gallant action during the 1947-48 war.
- In January–February 1948 Usman repulsed fierce attacks on Nowshera and Jhangar, both highly strategic locations in Jammu and Kashmir.
- During the defence of Naushera against overwhelming odds and numbers, Indian forces inflicted around 2000 casualties on the Pakistanis while Indian forces suffered only 150 casualties. His defence earned him the nickname Lion of Naushera.
- The grave is located on the Jamia Millia Islamia (JMI) campus in New Delhi. Brig. Usman’s funeral was done with full state honours and the prayer was led by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad.
- Naushera is a town and tehsil in the Rajouri district in the Indian Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
3.Prime Minister Narendra Modi flagged off the 100th Kisan Rail train, which is also plying between Devlali and Danapur — a popular offering which has now been extended to run between Sangola to Muzaffarpur and has carried over 15,450 tonnes of produce.
- The Kisan Rail train carries vegetables such as cauliflower, capsicum, cabbage, drumsticks, chillies, onion, etc, as well as fruits like grapes, oranges, pomegranate, banana, custard apple.
- The loading and unloading of perishable commodities will be permitted at all en route stoppages and no minimum or maximum size of consignment. The government has extended a subsidy of 50 per cent on transportation of fruits and vegetables.
- The multi-commodity train service has been popular as it also carries relatively small quantities of produce brought in by small, individual farmers.
- So far, the Kisan Rail has run regularly on 10 routes. One route — between Yeshvantpur and Delhi — exhausted its seasonal demand a while ago.
- Kisan Rail trains have ferried around 27,000 tonnes of produce so far, and half of the trips made so far were by trains running between Devlali in Maharashtra and Danapur in Bihar.
4.‘TiHAN-IIT Hyderabad’ Inaugurated recently:
- It is India’s first Test bed for Autonomous Navigation Systems (Terrestrial and Aerial).
- Special Features of this Facility include Test Tracks, Emulation of Real-World Scenarios, State of the Art Simulation Technologies, Road Infrastructure, V2X Communication, Drone Runways and Landing Area and many more.
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, has sanctioned Rs. 135 crores to IIT Hyderabad under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS) to set up a Technology Innovation Hub on Autonomous Navigation and Data Acquisition Systems (UAVs, RoVs, etc.).
- Cyber Physical Systems (CPS) are a new class of engineered systems that integrate computation and physical processes in a dynamic environment. CPS encompasses technology areas of Cybernetics, Mechatronics, Design and Embedded systems, Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data, Artificial Intelligence (AI) among others.




